Isoprenoid Biosynthesis Service from Algae
Isoprenoids, also termed terpenoids or terpenoids, are essential components of all living organisms. Algae have considerable potential as cellular factories for the production of isoprenoids.
As a pioneer in biosynthesis from algae, Lifeasible has been working on the production of isoprenoids from algae for many years. Hence, we are capable of providing quality isoprenoid biosynthesis services from algae.
Isoprenoid in Eukaryotic Algae
The present research on algal isoprenoid metabolism is motivated by applied studies aimed at increasing productivity as well as changing the profile of algal acquisition. Except for the major primary isoprenoids in all eukaryotes, such as sterols, the C15 and C20-polyprenyls, medium-chain polyprenyls (9 to 11 C5-units), and the long-chain polyprenyl dolichol, the main metabolites of eukaryotic photosynthesis include four additional classes of isoprenoids.
- Phytol as part of chlorophylls, tocopherols, and phylloquinones;
- A wide variety of carotenoids, which are essential as functional and structural elements of the photosynthetic apparatus;
- A medium-chain polyolefin that is a component of the photosynthetic electron carrier plastoquinone;
- Isoprenoids are precursors or constituent parts of various phytohormones, mainly cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid, strychnine, and brassinosteroids.
Metabolic Pathway Baseline of Isoprenoid
The biosynthesis of isoprenoids can be divided into three major stages among eukaryotes:
- The formation of active isoprene (IPP or DMAPP) through the mevalonate (MVA) pathway and the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway.
- Linear condensation of isoprene units to polyolefin diphosphates of different chain lengths.
- Further modification of polyisoprene diphosphates to metabolize them to a large number of isoprene end products with various functions.
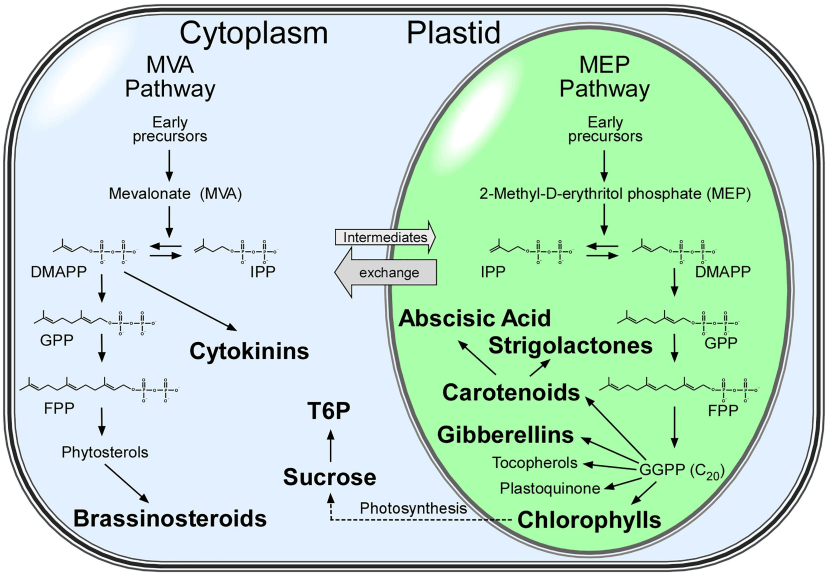 Fig.1 Isoprenoid biosynthetic pathways in plants. (Gawarecka, K., et al., 2021, Frontiers in Plant Science)
Fig.1 Isoprenoid biosynthetic pathways in plants. (Gawarecka, K., et al., 2021, Frontiers in Plant Science)
Metabolic Pathway Isoprenoid in Algae
While the MVA pathway functions in the cell membrane, the MEP pathway is also active in the plastid. However, the MVA pathway seems to be lost several times in various (sub)algal species, whereas it can be assumed that the MEP pathway, once acquired, is essential for the further survival of the organism.
Our Services
Obtaining sufficiently high levels of specific isoprenoid molecules while tolerating reduced growth will be a major challenge in the metabolic engineering of algae.
What We Provide
Manipulating metabolic fluxes by increasing fluxes, changing fluxes, or introducing new functions requires a thorough understanding of the underlying isoprenoid metabolism of the selected species. Lifeasible has many years of experience in isoprenoid biosynthesis and can provide you with quality services, as shown below.
- Design and modification of algal metabolic pathways;
- Engineered algae that can efficiently synthesize isoprene.
How to Conduct Engineering
We have a variety of key strategies for pathway engineering within the isoprenoid metabolism in algae to meet your needs.
- The first strategy for engineering is to redirect and strengthen the metabolic flux to an endogenous downstream product.
- The second possibility is to downregulate specific enzymes leading to the accumulation of precursor molecules in existing pathways.
- The third approach is to increase the supply of IPP/DMAPP by upregulating the MVA and/or MEP pathways.
- The fourth strategy is that new pathways can be introduced to harness algae as cell factories.
Why Choose Us
Lifeasible has the professional equipment and experienced teams to support our isoprenoid biosynthesis services from algae. Please contact us for more information.
Reference
- Gawarecka, K., & Ahn, J. H. (2021). Isoprenoid-derived metabolites and sugars in the regulation of flowering time: Does day length matter?. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2948.
Our services are for research use only and not for any clinical use.