Analysis of Plant Telomere Stability
Telomeres, which are repetitive DNA sequences at the ends of chromosomes, play a critical role in preserving the stability and integrity of plant genomes. They protect chromosome ends from degradation, fusion, and recombination events. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in understanding the mechanisms underlying telomere stability in plants. It can offer valuable information about telomere stability during replication and potential mechanisms of plant telomere maintenance.
As a leading company in biological research, Lifeasible holds a distinct advantage in analyzing plant telomere stability. Our ability to combine advanced genomic techniques with a deep understanding of plant biology allows us to decipher the complexities of telomere stability.
DNA Damage Response (DDR) Pathways Affecting Plant Telomere Stability
- To counteract the detrimental effects of DNA damage, plants have evolved intricate DNA damage response pathways. These pathways are responsible for sensing DNA damage, activating repair mechanisms, and coordinating cell cycle progression.
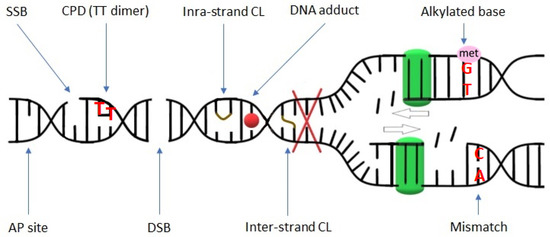 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of various DNA damages. (Szurman-Zubrzycka M, et al., 2023)
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of various DNA damages. (Szurman-Zubrzycka M, et al., 2023)
- We assess plant telomere stability by analyzing DNA damage response pathways, which are the factors that influence telomere fragility. Telomeres can be susceptible to DNA damage caused by internal factors, such as replication errors, or external stressors, like radiation and environmental toxins.
- We help our customers analyze the protein ATM (Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated) that acts as a central player in recognizing DNA damage at telomeres. Plants deficient in ATM or other key DDR components exhibit telomeric abnormalities. These abnormalities include telomere shortening, loss of telomeric repeats, and increased telomeric fusions.
Telomere Recombination Events Affecting Plant Telomere Stability
- We recognize telomere recombination events, specifically homologous recombination, can impact plant telomere stability. It is a DNA repair mechanism that can lead to telomere lengthening or shortening, depending on the specific events occurring at the telomeric regions.
- We focus on alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT), one of the key plant recombination processes. It is a telomerase-independent mechanism that allows cells to elongate telomeres by utilizing recombination events. Several proteins, such as RAD50 and MRE11, have been identified to be involved in ALT-mediated telomere recombination.
Telomere-Associated Genomic Rearrangements Affecting Plant Telomere Stability
- At Lifeasible, we have conducted extensive research on telomere-associated genomic rearrangements in plants, which refers to structural changes in the genome that involve telomeric regions. The presence of genomic rearrangements in telomeric regions can significantly impact plant telomere stability.
- By utilizing advanced genomic techniques, we can help study a variety of rearrangements, including telomere fusions, deletions, and inversions.
Through our expertise and advanced analytical capabilities, Lifeasible provides key insights and solutions for advancing plant science and agriculture. If you are interested in our services or have some questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Reference
- Szurman-Zubrzycka M, et al. (2023). "How Do Plants Cope with DNA Damage? A Concise Review on the DDR Pathway in Plants." Int J Mol Sci. 24 (3), 2404.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of various DNA damages. (Szurman-Zubrzycka M, et al., 2023)
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of various DNA damages. (Szurman-Zubrzycka M, et al., 2023)