Analysis of Potato Stem Rot Nematode Diseases
Rotten stem nematode, also known as sweet potato stem nematode, is the most common occurrence in potato planting. The disease has the characteristics of the epidemic, sudden, hidden, and so on, and is sensitive to environmental temperature. It will cause serious harm to potato’s normal growth, manifested in the loss of nutrients, the overall decline of disease resistance, and the induction of a variety of compound diseases. Therefore, the planting yield decreases significantly, and the economic value shrinks.
Lifeasible is committed to helping our customers achieve effective and successful research. We provide conveniently and guaranteed analysis of potato stem rot nematode diseases. In addition, we deliver reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
Pathogen Analysis of Potato Stem Rot Nematode Diseases
- Potato stem rot nematode (Ditylenchus destructor) has been reported in many countries and regions since 1945 when it was isolated from Ditylenchus dipsaci as a separate species. It is a migratory endo-parasitic nematode that infects the underground parts of plants and can survive by feeding on soil fungi without higher host plants.
- Lifeasible provides nematode identification services, including morphological and molecular identification. We also analyze nematode life habits, including living temperature, humidity, pH, salinity, soil texture, etc.
- In addition, we provide host analysis, with potatoes as the model host, root crops such as sweet potatoes, beets, and peanuts included; Scaly bulb crops such as onion and garlic; Angelica, ginseng, mint, and other medicinal plants.
Analysis of Pathogenesis Pathway and Regularity
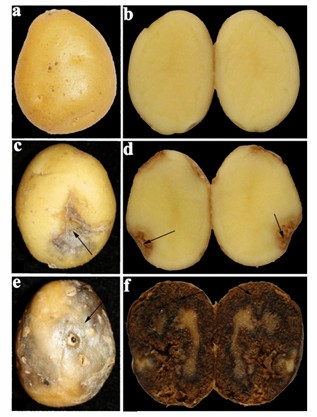 Fig.1 External and internal symptoms in potato tuber caused by Ditylenchus destructor. (Li Y et al., 2022)
Fig.1 External and internal symptoms in potato tuber caused by Ditylenchus destructor. (Li Y et al., 2022)
- It is a prerequisite for effective control of potato stem rot nematode disease to know the regularity of its occurrence. It has been reported that potato stem rot nematodes are infected in a variety of ways, mainly through infected potato tubers, or can be adsorbed to the soil on the tubers for transmission.
- We provide analysis of pathogenesis pathway and regularity, such as appropriate onset time, temperature and humidity, analysis of nematode population dynamics within the host, the correlation between nematode population base and incidence degree, and so on.
Analysis of Pathogenic Mechanism
We provide cloning and functional analysis of potato stem rot nematode related genes using RACE techniques, bioinformatics, fluorescent quantitative PCR, and dsRNA immersion in vitro to induce target gene silencing in plant nematodes to help our customers analyze pathogenic mechanisms.
Lifeasible has extensive experience and expertise in plant science. We are committed to providing you with timely and high-quality deliverables. At the same time, we guarantee the cost-effectiveness, completeness, and simplicity of the report. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Reference
- Li Y, et al. (2022). “Molecular characterization of internal transcribed spacer (ITS) of ribosomal RNA gene, haplotypes and pathogenicity of potato rot nematode Ditylenchus destructor in China.” Phytopathol Res. 4, 22.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 External and internal symptoms in potato tuber caused by Ditylenchus destructor. (Li Y et al., 2022)
Fig.1 External and internal symptoms in potato tuber caused by Ditylenchus destructor. (Li Y et al., 2022)