Understanding the specific plant protection mechanisms of metabolites is necessary for the practical use of plant protection. Lifeasible offers research services on the anti-microbial mechanisms of metabolites to explore the anti-microbial mechanisms of metabolites in depth.
The anti-microbial activity of metabolites can be divided into direct and indirect anti-microbial activity. Those metabolites that directly affect the survival of pathogenic microorganisms have direct anti-microbial effects, including those that disrupt the cell wall of bacteria, disrupt the cell wall of fungi, disrupt protein synthesis, and disrupt nucleic acid synthesis. Metabolites that protect plants from pathogenic microorganisms by regulating plant immunity or physically hindering pathogenic microbial attack have an indirect protective effect. For example, the metabolite surfactin stimulates induced systemic resistance (ISR) in beans, tomatoes, and tobacco and causes resistance to Botrytis cinerea.
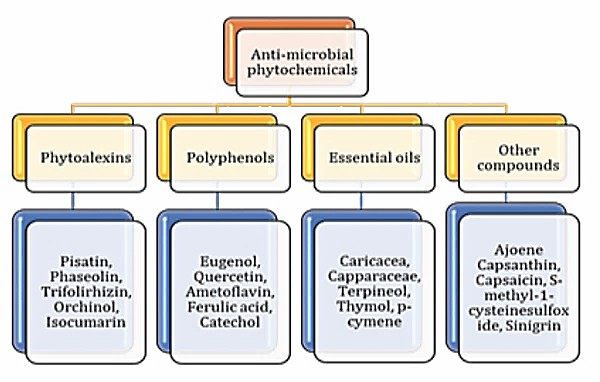 Fig. 1 Anti-microbial phytochemicals (Rex et al., 2018).
Fig. 1 Anti-microbial phytochemicals (Rex et al., 2018).
Lifeasible provides anti-microbial mechanism research services to help explore the anti-microbial mechanisms of plant primary metabolites, plant secondary metabolites, and microbial metabolites. We help explore the direct and indirect mechanisms of action of metabolites against microorganisms.
Exploration of the anti-bacterial mechanism of metabolites
We offer services to help explore the anti-bacterial mechanisms of metabolites. For metabolites that act directly on bacteria, we provide mechanistic exploration mainly under four directions, including inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, affecting cell membrane function, affecting the synthesis or function of important bacterial proteins, and interfering with bacterial nucleic acid metabolism. In exploring the mechanism of inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, we focus on the peptidoglycan synthesis. For metabolites that act indirectly on bacteria, we provide the exploration of plant immune induction mechanisms, the exploration of anti-bacterial components induced in plants, and the exploration of physical protection mechanisms related to metabolites.
Exploration of the anti-fungal mechanism of metabolites
We offer services to help explore the anti-fungal mechanisms of metabolites. For metabolites that act directly on fungi, we focus on five directions, including the effects of interfering with fungal cell wall synthesis, disrupting fungal cell membranes, inhibiting fungal cell membrane synthesis, interfering with fungal metabolism, and interfering with fungal protein synthesis and function. For metabolites that do not act directly on fungi, we offer the exploration of mechanisms related to the induction of plant immunity and immune substances and the exploration of physical protection mechanisms related to the protection of plants from fungal persecution.
Exploration of anti-microbial mechanisms aided by structural analysis of metabolites
The structure of a substance determines its function of the substance. Structural analysis of a metabolite and finding the function of structural analogs can help speculate on the metabolite's anti-microbial mechanism. We have established metabolite databases of metabolites with plant-protective effects that document the structure and plant-protective function of metabolites. This assists us in efficiently achieving anti-microbial mechanistic exploration of metabolites.
Combination of morphological and omics analysis
For metabolites that directly interfere with the survival of microorganisms. We perform microbial inhibition experiments and detect changes in the morphological structure, transcriptome, and metabolome of pathogenic microorganisms to help rapidly discover anti-microbial mechanisms. Then, we help explore the indirect plant protective effects caused by metabolites by examining the metabolome and transcriptome of plants.
Leverage the research results of plant protection mechanism
For metabolites that stimulate plant immune responses, we take full advantage of the known plant protection mechanisms to explore their specific plant protective effects. Based on the identified plant protection mechanisms, we can quickly find ways in which metabolites activate plant immunity and can speculate on the protective substances that plants subsequently produce.
Lifeasible helps to study the protection mechanisms of plant metabolites and microbial metabolites against plant pathogenic microorganisms. If we can be of any service to you, don't hesitate to ask!
References