Artificial Seed Preparation
Artificial seed is a capsule structure which consist of an embryoid produced by tissue culture techniques and protective substances that can provide enough nutriments and keep the embryoid from spoiling. The whole artificial seed is composed of the embryoid, the artificial endosperm and the artificial seed coat.
Artificial seed have relatively stable hereditary level and can be put into commercial production for their reproductive characters. They can also shorten the breeding cycle and accelerate the propagation of improved varieties. Besides that, artificial seeds are suitable for long-term storage and transportation.
Artificial seed preparation is an emerging bioengineering technology that can link the agricultural production and genetic breeding, it will have great application prospects in many industries, such as agriculture and forestry.
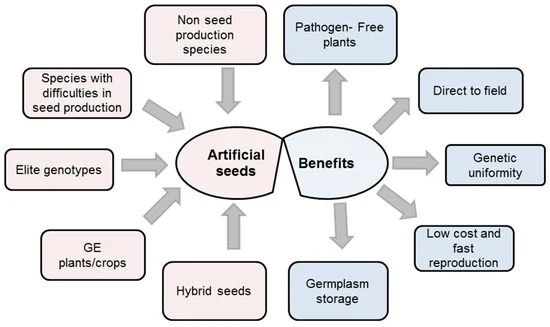 Figure 1. Artificial seed uses and benefits (Rihan, H.; et al. 2017)
Figure 1. Artificial seed uses and benefits (Rihan, H.; et al. 2017)
Principle
The embryoid have cell totipotency that can form plants through embryonic development under appropriate conditions. Artificial seed is an organism structure that have the core part: embryoid, from which it can germinate and grow like natural seeds.
Procedures
A. Induce the somatic embryoid of artificial seed
- Cut the tissue at the base of a petiole into 1-2 mm cultured in callus proliferation medium [ Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 1 mg/L 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) ] for 14 days to get EC (Embryoid callus), then the ECs are transferred to liquid medium [ Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 1 mg/L 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) ] which grow in the shaker incubator (180 rpm/min) for 12-14 days.
- Use a cell strainer (80um) to filter the culture solution in the clean bench, then the cell suspension solution is cultured in a shaker incubator (90 rpm/min) to get a large number of embryoids.
B. Preparation of artificial endosperm solution
- Compound artificial endosperm solution: 1/2Murashige and Skoog (MS) + 1mg/L 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyaceticacid (2,4-D) + 0.1 mg/L α-naphthalene acetic acid (NAA) + 1.5% potato starch hydrolysate + 0.4 g/L cephalotin sodium salt.
- Use the above solution to make up 1% sodium alginate as the embedding medium. The sodium alginate should be added by small quantities in high frequency and heating in water bath until it dissolves completely, then put aside for cooling.
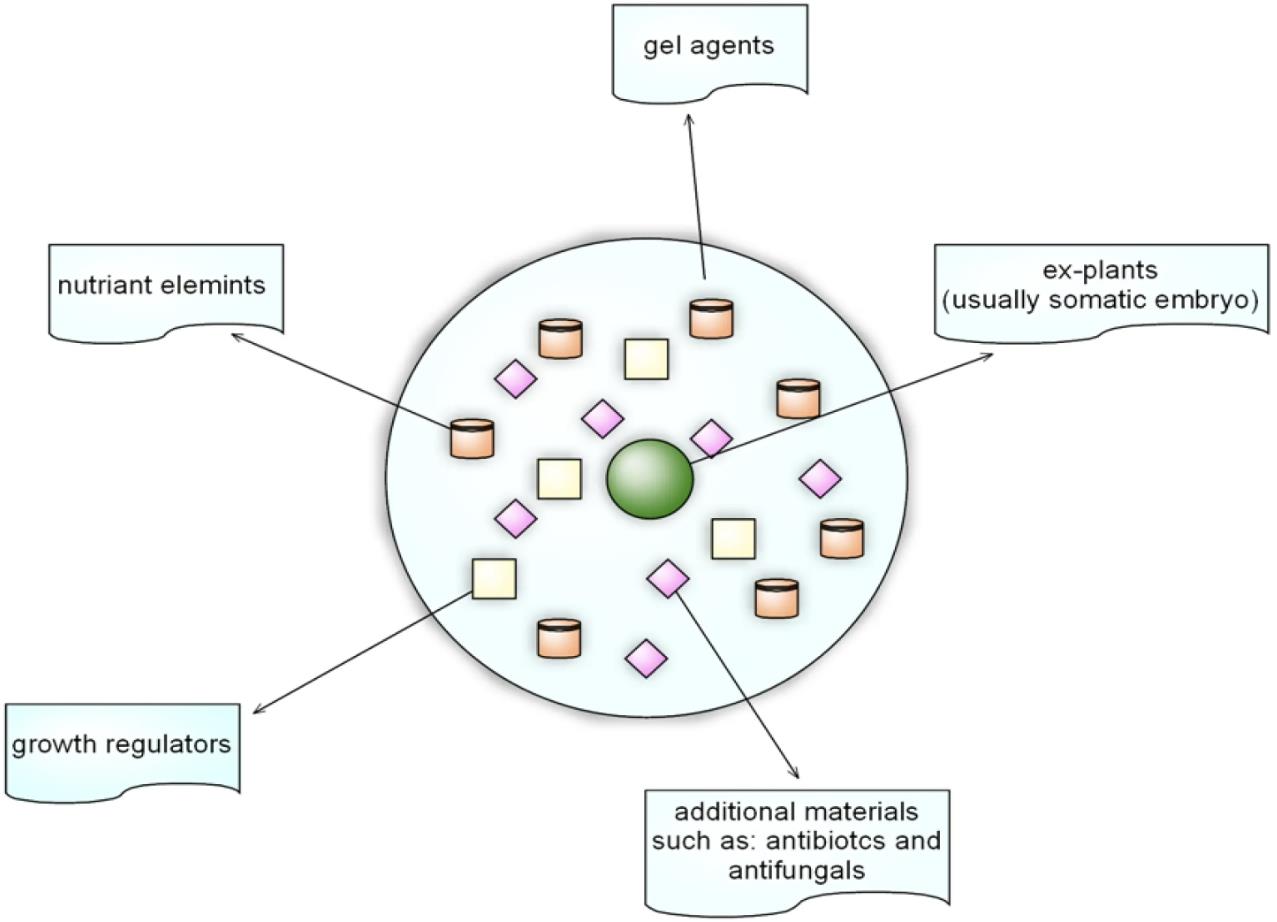 Figure 2. Artificial seed concept (Rihan, H.; et al. 2017)
Figure 2. Artificial seed concept (Rihan, H.; et al. 2017)
C. Make artificial seed coat
- Mix the embryoid with the embedding medium and stir it evenly with glass rod.
- Add the above mixture drop by drop into the 100 mM/L calcium chloride solution and allow it combine for 20 or 30min, which can form a complex compound.
- Soak the complex compound in sterile aqueous for 20min, which can avoid the formation of too thick seed coat.
- Add complex compound into chitosan solution and make it bind for 10min, from which can form a veil of resilient and protective layer.
Reference
- Rihan, H.; et al. Artificial seeds (principle, aspects and applications). Agronomy. 2017, 7(4): 71.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Figure 1. Artificial seed uses and benefits (Rihan, H.; et al. 2017)
Figure 1. Artificial seed uses and benefits (Rihan, H.; et al. 2017) Figure 2. Artificial seed concept (Rihan, H.; et al. 2017)
Figure 2. Artificial seed concept (Rihan, H.; et al. 2017)