Circular RNA (circRNA) is a class of single-stranded circular RNA molecules with covalent bond closures. In the early days, circRNAs were often considered splicing byproducts and had no biological function. However, with the rapid development of high-throughput sequencing technology and bioinformatics, circRNAs have been identified in large numbers in various eukaryotic organisms, and some circRNAs have been found to have biological functions. Basic and applied research on circRNAs will become a new hot area.
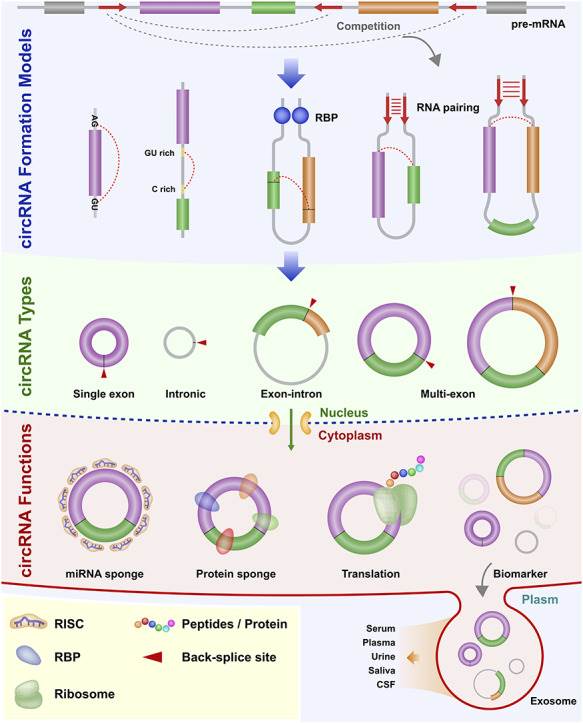 Figure 1. Diagram of the biogenesis pattern of circRNA. (Chen, L, et al. 2021)
Figure 1. Diagram of the biogenesis pattern of circRNA. (Chen, L, et al. 2021)
Lifeasible has been engaged in plant-related research for over a decade and has provided satisfactory plant biology services to many clients. We can combine advanced biotechnology and big data analysis methods to comprehensively analyze plant Ribo-minus RNA-seq to deeply mine plant circRNA and reveal the characteristics of plant circRNAs.
CircRNAs are not degraded by RNA enzymes and are more stable than linear RNAs, so their isolation, enrichment, identification, and detection are also easier and more reliable. Our bioinformatics analysis service for plant circRNAs enables clients to explore all information about circRNAs, including splicing signals, variable splicing profiles, potential coding properties, prediction of possible miRNA binding sites, inter-species conservation, etc. Our bioinformatics analysis services for plant circRNAs are detailed below.
Use ploy(T) oligonucleotides to isolate mRNA with a ploy(A) tail or use ploy(T) primers to bind random short reverse-transcribed oligomers. After ploy(A) purification, break the mRNA molecule into small segments, then ligated to sequencing system-specific oligomers. After sequencing, rRNA deletion or RNase R processing is chosen to build the library.
Since the mechanism of formation of most plant circRNAs is unknown, we make predictions about the mechanism of formation of plant circRNAs based on several circRNA formation mechanisms currently known to be confirmed in animals, i.e., based on RNA-binding protein (RBP), reverse complementary sequences, and lasso structure-mediated cyclization.
We used high-throughput sequencing reads to search for variable splice sites of fusion circRNAs on the hypothetical reference sequence based on the alignment of exon sequences of the fusion gene pairs (hypothetical reference sequence).
There are four main isoforms of circRNAs: exonic circRNAs (ecircRNAs), cyclic intronic circRNAs (cirRNAs), exon-intron circRNAs (EIciRNAs), and tRNA intronic circRNAs (tricRNAs). We can analyze circRNA types using a variety of biological software.
Transcripts that can produce circRNAs and transcripts that can produce differentially expressed circRNAs were analyzed separately for GO annotation.

Lifeasible provides bioinformatics analysis services for plant circRNA with a "scientific, accurate, and customizable" service philosophy. We sincerely look forward to working with you, and if you have any questions, please contact us directly.
Reference