Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP), also known as binding site analysis, specifically enriches DNA bound to target proteins in living cells and is a powerful tool for studying protein-DNA interactions in vivo, usually for the exploration of transcription factor binding sites or histone-specific modification sites. Chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-Seq) technology, which combines ChIP with second-generation sequencing technology, can efficiently detect DNA segments that interact with histones, transcription factors, etc., on a genome-wide scale.
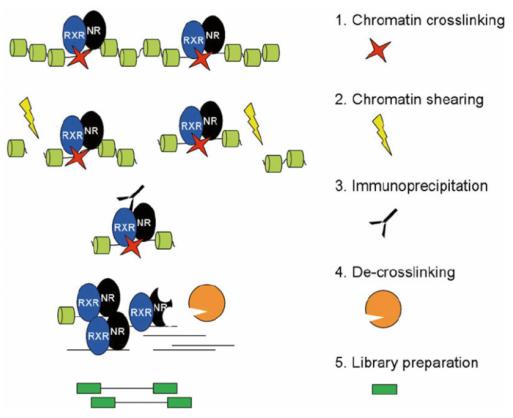 Figure 1. Diagram of the main steps of ChIP-Seq. (Dániel, Bence, et al. 2014)
Figure 1. Diagram of the main steps of ChIP-Seq. (Dániel, Bence, et al. 2014)
Lifeasible first specifically enriches the target protein-binding DNA fragments by ChIP and then purifies them and constructs libraries; the enriched DNA fragments are then sequenced in high throughput based on the Illumina system.
Our ChIP-seq projects involve a wide range of reference animal species, such as pigs, mice, rats, zebrafish, and primates. From material selection, and library sequencing, to data analysis, we ensure that each step is scientifically and meticulously designed to guarantee high-quality research results.
Lifeasible uses advanced sequencing platforms to quickly read high-quality sequencing data and ensure efficient data processing and secure data storage. "Scientific protocol design, strict quality control management, professional analysis team, rich project experience, and quality project service" are our ideal. We look forward to cooperating with you; please feel free to contact us.
Reference