Medaka is a small freshwater fish with a small body size in adults, generally 2-4 cm in length, and there is a clear difference in appearance between female and male medaka at sexual maturity. The embryos of medaka are not sticky, but often adhere to a sticky filament to form a string, and can be collected for microinjection during the breeding season. Medaka embryos are highly viable, tolerate a wide range of temperature and salinity changes, and are highly resistant to disease, making them easy to raise in laboratory conditions.
 Figure 1. Swimming medaka.
Figure 1. Swimming medaka.
The genomic and transcriptomic databases of medaka are well established, and the advantages of medaka, such as many strains, small size, easy breeding, high fertility, short reproductive cycle, and obvious sex differences, make it a unique advantage in microinjection and cell transplantation, and it is an ideal material for gene function research. Among fish, medaka is another important model organism after zebrafish and has become an important research object in the field of life science.
Key genes for gene editing
Gene editing technology services
CRISPR/Cas9 is a technology derived from a bacterial acquired immune system, which can modify target genes after artificial modification, and has the advantages of simple construction method, high efficiency, low cost, and wide range of use. Currently, it has been successfully applied to the precise modification of genomes in bacteria as well as many plants and animals and is the most promising gene-editing technology for clinical applications.
Lifeasible can accomplish mutation of prmt5 and knockout of two genes, prmt5 and mep50, in medaka using CRISPR/Cas9 and other technologies. In addition, we also performed gene editing of Tyr and Nanog genes in medaka by using zebrafish codon-optimized Cas9 coding sequences. We screened the mutant progeny, observed the growth and development of embryos as well as mutant pure progeny, and successfully studied the function of key genes by reverse genetics.
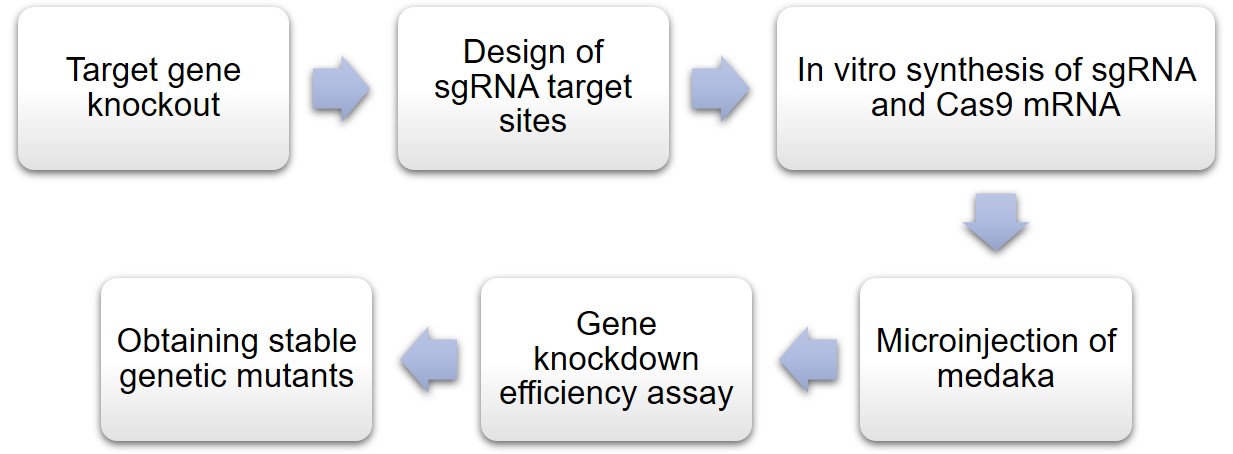
In addition, Lifeasible can also improve the original NgAgo-gDNA system to make it a new system adapted to medaka gene editing. We use the improved system to knock out the medaka mep50 gene, which can assist our customers to carry out studies on the functions of prmt5 and mep50 in medaka growth and development, etc. For more information or any inquiry requirements, please contact Lifeasible.
References