Pelteobagrus fulvidraco belongs to the class Osteichthyes, Siluriformes, Bagridae, Pelteobagrus. The flesh is delicious, nutritious, and free of intermuscular spines, and is an important freshwater breeding species in China.
Pelteobagrus fulvidraco spermatozoa mature later than the ovaries, and the male growth rate is faster than the female, so the male is larger. Under the same breeding conditions, the first-year male Pelteobagrus fulvidraco grows about 30% faster than females of the same age, and the difference between male and female growth in the second year can even approach three times.
 Figure 1. Yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) is a species of freshwater fish.
Figure 1. Yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco) is a species of freshwater fish.
The supply of YY supermales used to produce all-male fry is tight and expensive, and in addition, the serious inbreeding phenomenon has led to degradation of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco germplasm, reduced growth rate, and reduced disease resistance and stress tolerance. This has seriously restricted the sustainable development of the Pelteobagrus fulvidraco breeding industry, so there is an urgent need to purify and rejuvenate the existing germplasm of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and select and breed pure lines of super male and all-female fish with excellent genetic traits.
CRISPR/Cas9 technology services
Most scleractinian fishes lack the portal system, GnRH synthesized in the hypothalamus acts on the pituitary gland through axon terminals and binds to GnRHR in the pituitary gland to induce the synthesis and release of FSH and LH. FSH and LH act on the gonads through the circulatory system to regulate steroid hormone synthesis, gamete development, and maturation. In addition, GnRH may regulate the sexual behavior of animals by regulating the levels of local gonadotropins and steroidal sex hormones in the blood through paracrine or autocrine modes.
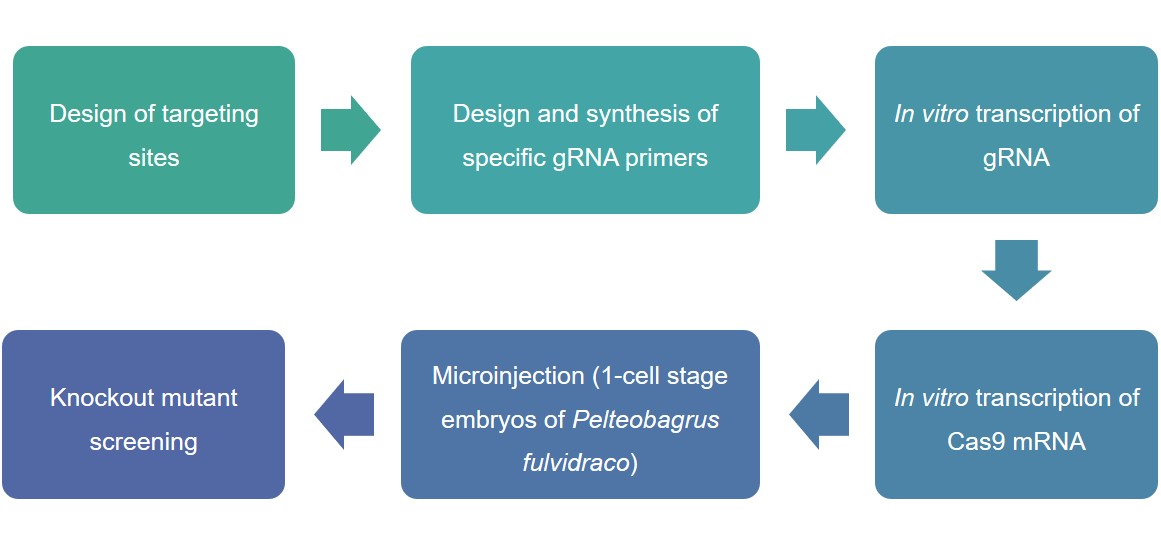 Figure 2. Lifeasible's process for editing target genes in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco using CRISPR/Cas9 technology.
Figure 2. Lifeasible's process for editing target genes in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco using CRISPR/Cas9 technology.
GnRHR may be involved in sex differentiation and gonadal development in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Lifeasible can construct and screen the GnRHR mutant in Pelteobagrus fulvidraco using CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology. This will help researchers to investigate the role of GnRHR mutants in reproductive development and provide technical support to further understand the reproductive regulation mechanism of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco and explore the artificial reproduction technology of Pelteobagrus fulvidraco.
For more information or any inquiry requirements, please contact Lifeasible.