Plant hormones are highly dynamic chemical messengers that play essential roles in the regulation of plant physiological processes, including cell growth, organ differentiation, and response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Therefore, analysis and monitoring of plant hormones forms a valuable tool in plant performance improvement and new crop trait development.
As the plant hormones often present at fairly low concentrations, and their amounts and distributions and are actively changing, it is critical to analyze the hormone levels in real time with high sensitivity. Lifeasible, as a leading plant biotechnology with a long history of plant physiological studies, provides both biosensor-based and mass spectrometry-based approaches that ensure continuous and accurate detections of plant hormones.
Biosensor-based methods allow continuous monitoring of hormone levels, as well as visualization of local distributions of targeted hormones. Lifeasible provides a list of biosensors that can be applied to the detection of a wide range of hormones in various types of plant tissues.
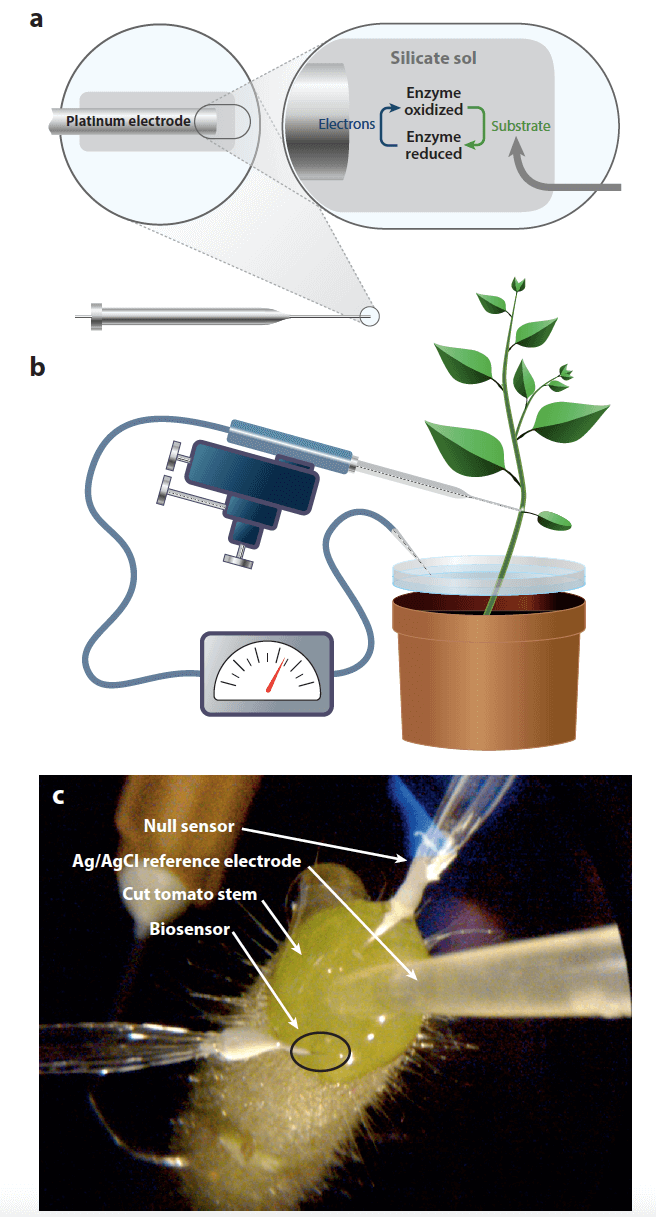 Figure 1. A schematic illustration of electrochemical biosensor setup for measurement in tomato root exudate (Novak, Napier et al. 2017).
Figure 1. A schematic illustration of electrochemical biosensor setup for measurement in tomato root exudate (Novak, Napier et al. 2017).
Mass spectrometry-based methods are highly sensitive approaches that allow accurate identification and quantification of plant hormones.
Sample requirements:
With state-of-the-art technologies, as well as our teams of excellent scientists and experts, Lifeasible is devoted to providing our worldwide customers with the best services at competitive rates. Our high-capacity lab facilities allow hormone analysis of a wide range of plant species, at cell, tissue and whole plant levels. Moreover, we proudly offer our customers with one-stop services, covering all steps from experimental designing to data reporting. Welcome to contact us for questions, inquiries or collaborations.
Reference
Table 1 List of detectable plant hormones and related compounds at Lifeasible
| NO. | Phytohormone | Abbreviation | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Indole-3-acetic acid | IAA | Auxin |
| 2 | Methyl indole-3-acetate | ME-IAA | Auxin |
| 3 | Indole-3-butyric acid | IBA | Auxin |
| 4 | Indole-3-carboxaldehyde | ICAld | Auxin |
| 5 | Indole-3-carboxylic acid | ICA | Auxin |
| 6 | 3-Indolepropionic acid | IPA | Auxin |
| 7 | 1-O-Indol-3-ylacetylglucose | IAA-Glc | Auxin |
| 8 | Indoleacetyl glutamic acid | IAA-Glu | Auxin |
| 9 | 3-Indoleacetonitrile | IAN | Auxin |
| 10 | Indole-3-acetyl-lglutamic acid dimethyl ester | IAA-Glu-diMe | Auxin |
| 11 | Indole-3-acetyl-L-leucine methyl ester | IAA-Leu-Me | Auxin |
| 12 | Indole-3-acetly-L-valine methyl ester | IAA-Val-Me | Auxin |
| 13 | Indole-3-acetyl glycine | IAA-Gly | Auxin |
| 14 | 2-Oxindole-3-acetic acid | OxIAA | Auxin |
| 15 | Indole-3-acetyl-L-aspartic acid | IAA-Asp | Auxin |
| 16 | N-(3-Indolylacetyl)-L-leucine | IAA-Leu | Auxin |
| 17 | N-(3-Indolylacetyl)-L-valine | IAA-Val | Auxin |
| 18 | Indole-3-acetyl-L-phenylalanne methyle ester | IAA-Phe -Me | Auxin |
| 19 | Indole-3-acetyl-L-tryptophan | IAA-Trp | Auxin |
| 20 | 3-Indoleacetamide | IAM | Auxin |
| 21 | Tryptamine | TRA | Auxin |
| 22 | Indole-3-lactic acid | ILA | Auxin |
| 23 | 3-Indoleacrylic acid | IA | Auxin |
| 24 | N-(3-Indolylacetyl)-L-alanine | IAA-Ala | Auxin |
| 25 | L-Tryptophan | TRP | Auxin |
| 26 | N-(3-Indolylacetyl)-L-phenylalanine | IAA-Phe | Auxin |
| 27 | N6-Isopentenyladenine | IP | CK |
| 28 | trans-Zeatin | tZ | CK |
| 29 | cis-Zeatin | cZ | CK |
| 30 | Dihydrozeatin | DZ | CK |
| 31 | Isopentenyladenosine | IPR | CK |
| 32 | trans-Zeatin riboside | tZR | CK |
| 33 | Dihydrozeatin-7-glucoside | DHZ7G | CK |
| 34 | Dihydrozeatin ribonucleoside | DHZR | CK |
| 35 | cis-Zeatin riboside | cZR | CK |
| 36 | 4-[[(9-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-9H-purin-6-yl)amino]methyl]phenol | pT9G | CK |
| 37 | 2-Chloro-trans-zeatin | 2CltZ | CK |
| 38 | para-Topolin | pT | CK |
| 39 | meta-Topolin | mT | CK |
| 40 | meta-Topolin riboside | mTR | CK |
| 41 | ortho-Topolin | oT | CK |
| 42 | 6-Benzyladenine | BAP | CK |
| 43 | 6-Benzyladenosine | BAPR | CK |
| 44 | Kinetin | K | CK |
| 45 | Kinetin riboside | KR | CK |
| 46 | para-Topolin riboside | pTR | CK |
| 47 | ortho-Topolin riboside | oTR | CK |
| 48 | cis-Zeatin-9-glucoside | cZ9G | CK |
| 49 | N6-Isopentenyl-adenine-9-glucoside | IP9G | CK |
| 50 | N6-Isopentenyl-adenine-7-glucoside | IP7G | CK |
| 51 | trans-Zeatin-O-glucoside | tZOG | CK |
| 52 | Dihydrozeatin-O-glucoside riboside | DHZROG | CK |
| 53 | cis-Zeatin-O-glucoside riboside | cZROG | CK |
| 54 | meta-Topolin-9-glucoside (mT9G) | mT9G | CK |
| 55 | ortho-Topolin-9-glucoside | oT9G | CK |
| 56 | N6-Benzyladenine -9-glucoside | BAP9G | CK |
| 57 | N6-Benzyladenine-7-glucoside | BAP7G | CK |
| 58 | Kinetin-9-glucoside | K9G | CK |
| 59 | 2-Methylthio-N6-isopentenyladenine | 2MeSiP | CK |
| 60 | 2-Methylthio-cis-zeatin | 2MeScZ | CK |
| 61 | 2-Methylthio-cis-zeatin riboside | 2MeScZR | CK |
| 62 | 2-Methylthio-N6-isopentenyladenosine | 2MeSiPR | CK |
| 63 | Methyl jasmonate | MEJA | JA |
| 64 | Jasmonic acid | JA | JA |
| 65 | Dihydrojasmonic acid | H2JA | JA |
| 66 | Jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine | JA-ILE | JA |
| 67 | 12-Oxophytodienoic acid | OPDA | JA |
| 68 | N-[(-)-Jasmonoyl]-(L)-phenalanine | JA-Phe | JA |
| 69 | N-[(-)-Jasmonoyl]-(L)-valine | JA-Val | JA |
| 70 | (±)-OPC-4 | OPC-4 | JA |
| 71 | (±)-OPC-6 | OPC-6 | JA |
| 72 | Salicylic acid | SA | SA |
| 73 | Salicylic acid 2-O-β-glucoside | SAG | SA |
| 74 | Abscisic acid | ABA | ABA |
| 75 | ABA-glucosyl ester | ABA-GE | ABA |
| 76 | Gibberellin A1 | GA1 | GA |
| 77 | Gibberellin A3 | GA3 | GA |
| 78 | Gibberellin A4 | GA4 | GA |
| 79 | Gibberellin A5 | GA5 | GA |
| 80 | Gibberellin A6 | GA6 | GA |
| 81 | Gibberellin A7 | GA7 | GA |
| 82 | Gibberellin A8 | GA8 | GA |
| 83 | Gibberellin A9 | GA9 | GA |
| 84 | Gibberellin A12 | GA12 | GA |
| 85 | Gibberellin A15 | GA15 | GA |
| 86 | Gibberellin A19 | GA19 | GA |
| 87 | Gibberellin A20 | GA20 | GA |
| 88 | Gibberellin A24 | GA24 | GA |
| 89 | Gibberellin A29 | GA29 | GA |
| 90 | Gibberellin A34 | GA34 | GA |
| 91 | Gibberellin A44 | GA44 | GA |
| 92 | Gibberellin A51 | GA51 | GA |
| 93 | Gibberellin A53 | GA53 | GA |
| 94 | 1-Aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid | ACC | Ethylene |
| 95 | Brassinolide | BL | BRs |
| 96 | 24-epi-Brassinolide | 24-epiBL | BRs |
| 97 | 28-Norbrassinolide | 28-norBL | BRs |
| 98 | 28-Homobrassinolide | 28-homoBL | BRs |
| 99 | Castasterone | CS | BRs |
| 100 | 6-Deoxocastasterone | 6-deoxoCS | BRs |
| 101 | 28-Norcastasterone | 28-NorCS | BRs |
| 102 | 28-Homocastasterone | 28-HomoCS | BRs |
| 103 | 6-Deoxo-24-epi-castasterone | 6-Deoxo-24-epiCS | BRs |
| 104 | Typhasterol | TY | BRs |
| 105 | 28-Norteasterone | 28-norTE | BRs |
| 106 | Strigol | ST | SL |
| 107 | 5-Deoxystrigol | 5DS | SL |
| 108 | Melatonine | MLT | MLT |