Lifeasible has expertise in milk testing and offers services to help detect antibiotic residues in milk and milk products.
The detection of antibiotic residues in milk and milk products has been the focus of milk testing. Numerous antibiotics are widely used in feeding milk-producing animals, mainly β-lactams and tetracyclines, resulting in antibiotic residues in milk and milk products. The antibiotic residues seriously interfere with the production of fermented milk products. Long-term consumption of milk or milk products containing low doses of antibiotic residues can harm human health over time. In addition, some antibiotics can cause cancer, such as nitrofurazone (Fig. 1). Lifeasible helps detect a wide range of antibiotic residues that may be present in milk and milk products to ensure that they are safe for consumption.
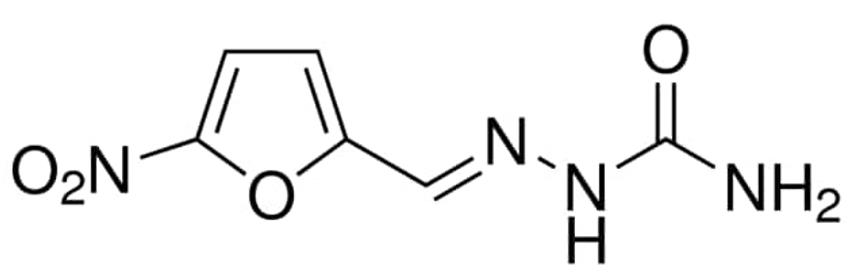 Fig. 1 Chemical structure of nitrofurazone.
Fig. 1 Chemical structure of nitrofurazone.
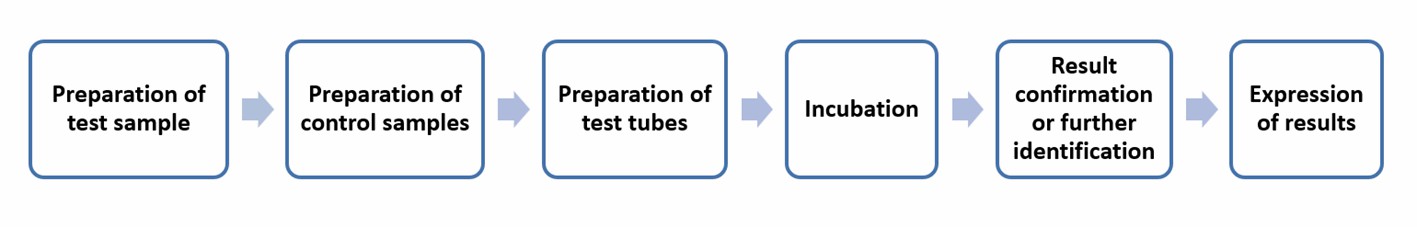
Tube diffusion tests for determining several antibiotics
Based on tube diffusion tests, we help detect various antimicrobial residues in milk and milk products, including β-lactams, tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, macrolides, sulfonamides, and methotrexate residues. The method can be used to determine antimicrobial residues in raw milk, heat-treated milk, and reconstituted dry milk. When specific antibiotic residues cannot be determined directly by tube diffusion tests, we can help with further determination using methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC), and immunoassays.
The method requires using Geobacillus stearothermophilus ATCC 10149, whose normal growth causes a change in pH, which causes the pH indicator in the test tube to change color from purple to yellow. The pH indicator stays purple when substances that inhibit microbial growth are present in the milk or milk products.
Operation flow:
Main reference standard:
ISO/TS 26844:2006
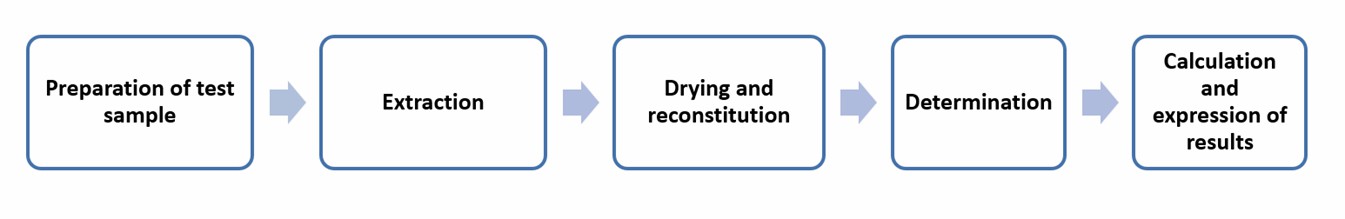
LC-MS/MS method for determining nitrofurazone
The method is primarily used for quantitatively determining nitrofurazone, a carcinogenic antibiotic, and is stable for heat treatment in excess of pasteurization conditions and for spray driving. This method has been validated to measure trace levels of intact nitrofurazone in liquid milk and milk powder. The method is highly accurate and can detect nitrofurazone below 1 ng/g on a whole-product (i.e., powder) basis.
The method uses 13C15N2 -nitrofurazone as an internal standard. After adding the internal standard to the sample, the nitrofurazone extraction is performed in steps using acetonitrile, a mixture of MgSO4 and NaCl, and a mixture of MgSO4/PSA/C18 sorbents. The extracted portion containing nitrofurazone is evaporated to dryness and reconstituted in methanol for LC-MS/MS analysis.
Operation flow:
Main reference standard:
ISO 22186:2020
Lifeasible helps detect a wide range of antibiotics in milk and milk products, including tetracyclines, β-lactams, macrolides, aminoglycosides, sulfonamides, trimethoprim, and nitrofurazone. We help detect antibiotic residues based on international standard methods and advanced analytical methods. We also offer services to detect antibiotics in other foods. We guarantee to provide you with excellent services, please contact us for services.
References