Lifeasible offers multiple methods to help determine the lactose content. Particularly, we have extensive experience in determining the lactose content of milk and milk products with the "lactose-free" designation.
Determination of lactose content in milk is essential. The nutritional properties of milk are influenced by lactose content. Lactose is the main sugar and carbohydrate in mammals' milk, and the energy value of milk is closely related to lactose. Then, the lactose content can help identify any issues with the production process, such as changes in the feed of cows, which can affect lactose content. In addition, knowing lactose content is also useful for those who are lactose intolerant, as it allows them to make informed decisions about the dairy products they consume. Lifeasible offers multiple services to help determine lactose in milk and milk products to help determine that the milk and milk products meet regulatory standards.
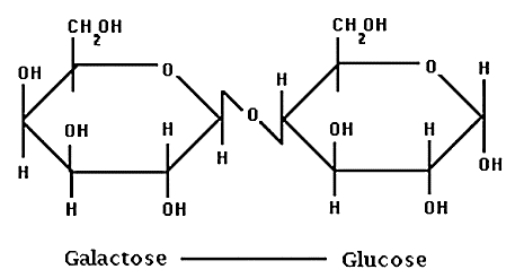 Fig. 1 Lactose is a disaccharide composed of 2 monosaccharides, glucose and galactose, linked via a β-1,4-glucosidic bond (Grenov et al., 2016).
Fig. 1 Lactose is a disaccharide composed of 2 monosaccharides, glucose and galactose, linked via a β-1,4-glucosidic bond (Grenov et al., 2016).
We help determine the lactose content mainly based on methods that comply with international standards, including the HPAEC-PAD method, the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method, the enzymatic method using the difference in pH, the glucose moiety of the lactose, or the galactose moiety of the lactose.
For the most accurate lactose content determination, we recommend using the HPAEC-PAD method. Based on this method, it is also possible to determine a variety of sugars in milk and milk products. Please click to see the details of this method.
This method can determine the lactose content of raw milk, heat-treated milk, dried milk, raw cream, and pasteurized cream. It is not applicable to fermented milk and milk with added oligosaccharides.
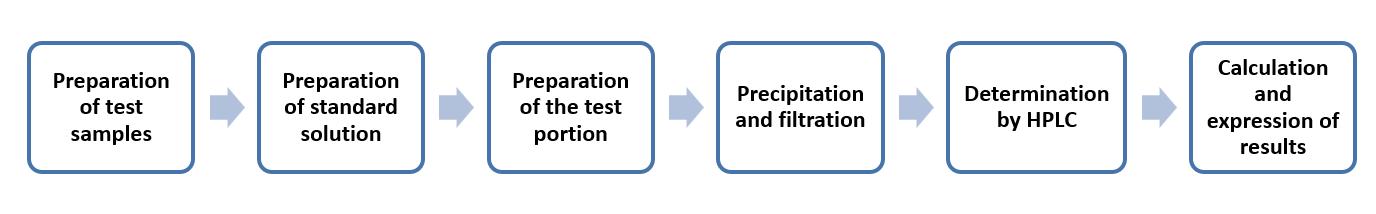
The method takes D (+)-melezitose as the internal standard. Firstly, Biggs-Szijarto solution is added to precipitate the fat and protein compounds of the sample. After two filtrations, the determination is performed using HPLC, with a cation exchange column and a differential refractometer detector or other suitable detectors.
Operation flow:
Main reference standard:
ISO 22662:2007
Enzymatic method using the difference in pH
The method applies to milk and reconstituted milk and requires only the differential pH analyzer.
It is based on the hydrolysis of lactose to obtain glucose, which can be phosphorylated to cause pH changes to be measured.
Operation flow:

Main reference standard:
ISO 26462:2010
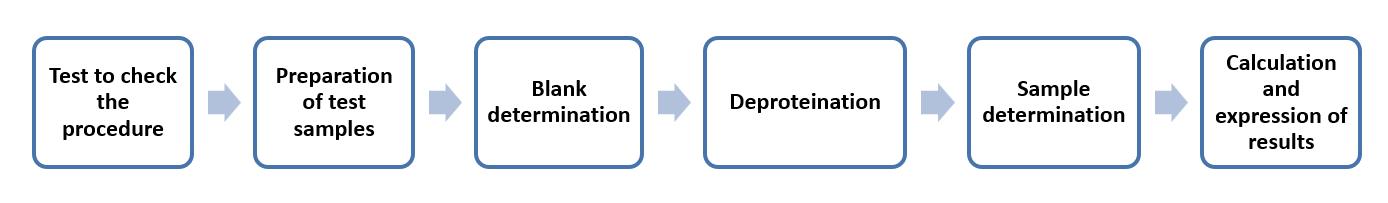
Enzymatic method using the glucose or galactose moiety of the lactose
The method applies to all types of dried milk, ice-mixes in dry form in the presence of other carbohydrates and reducing substances, and processed cheese. It is not possible to accurately determine lactose in heat-treatment milk and milk products.
It is based on the hydrolysis of lactose to obtain glucose and galactose with the enzyme β-galactosidase. The amount of glucose or galactose is then converted to NADPH or NADH content to be measured. When the original sample contains high glucose, the galactose-based determination is chosen. When the original sample contains high galactose, the glucose-based determination is chosen. It is not applicable to samples with high contents of both glucose and galactose.
Operation flow:
Main reference standards:
ISO 5765-1:2002
ISO 5765-2:2002
Lifeasible helps to determine the lactose content in milk and milk products based on multiple specialized methods. Please contact us to tell us the basic information about your sample and the purpose of the lactose test. We will recommend the right solution for your determination.
References