
Milk somatic cells include macrophages, polymorphonuclear neutrophils, lymphocytes, epithelial cells, and milk-producing cells. The number of these cells per mL of milk is the somatic cell count. Milk somatic cells are an important indicator of the health of dairy animal and milk quality. Enumeration of somatic cells can help to identify dairy animals with mastitis so that treatment can be administered promptly. Better hygiene and proper nutrition help to reduce milk somatic cells, which means higher quality milk and longer shelf life of milk. Lifeasible offers services to help with the enumeration of somatic cells in milk.
We help determine somatic cell counts mainly based on two methods, namely the microscopic method and the fluoro-opto-electronic counter method. We also offer mechanized and automated cell-counting-based equipment for the determination of somatic cell counts, which are calibrated by international standard methods prior to use.
Microscopic method
The method is suitable for determining somatic cells in raw and chemically preserved milk. In addition, mechanized /automated somatic cell counting equipment can be calibrated based on this method.
The method involves smearing the test portion, then staining cells with Newman-Lampert stain solution, and finally counting the stained cells under a microscope.
Operation flow:
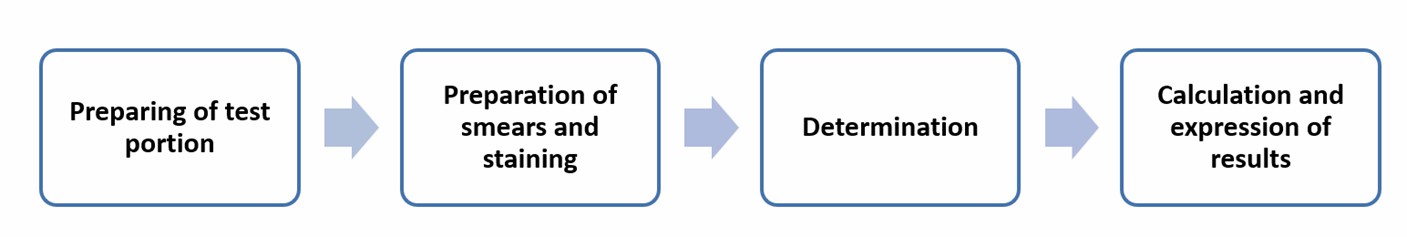
Main reference standard:
ISO 13366-1:2008
Fluoro-opto-electronic counter method
This method is suitable for the determination of raw milk from species of cow, goat, sheep, and buffalo. The advantage of this method is that no smear is required, and it is easier to perform the test.
In this method, the staining solution is first mixed with the sample, and a portion of the homogeneously mixed piece is subsequently transferred to the counting section. Then, each stained particle observed by the fluorescence microscope produces an electrical pulse filtered, amplified, and recorded.
The stains that can be used in the method include Patent Blue V (less than 0.15 mg/100 ml of the test sample), Yellow Orange S (E110)( less than 1 mg/100 ml of the test sample), and a mixture of Patent Blue V and Eosin B (less than 0.03 mg/100 ml and 0.45mg/100mL of the test sample, respectively).
In this method, if the methylene blue concentration exceeds 0.06 mg/100 mL in the sample, it will affect the determination.
Operation flow:
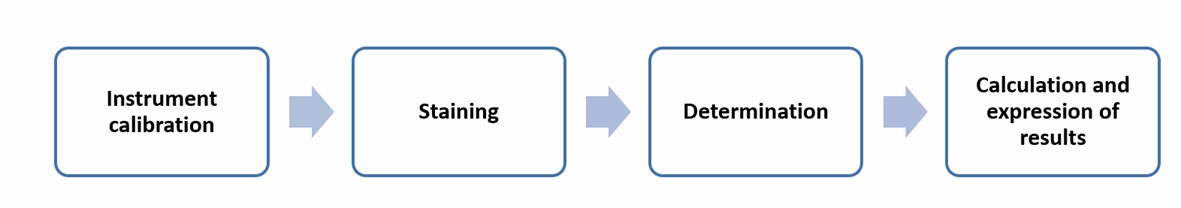
Main reference standard:
ISO 13366-2:2006
Other mechanized/automated cell-counting-based equipment
We can also help with somatic cell counts based on instruments such as flow cytometers and disc cytometry. We always calibrate our instruments prior to counting to ensure the accuracy of the determination.
Sample preservation and delivery
Samples are best stored at 2-4°C. For longer storage or transport, chemical preservatives can be added, such as boric acid (less than 0.6 g/100 ml of the test sample), bronopol (less than 0.05 g/100 ml of the test sample), and potassium dichromate (less than 0.1 g/100 ml of the test sample).
Addition of chemical preservatives or stains
Adding chemical preservatives or stains must not exceed the limits as this will affect the determination.
Lifeasible specializes in milk-related testing and offers services to help with the enumeration of somatic cells. Feel free to contact us for services.
References