Biotic stress is caused by many factors, including infection by fungi, bacteria, viruses, nematodes and competition with weeds. Biotic stress can lead to severe losses in forage yield and quality, making control of biotic stresses very important. Using fungicides and insecticides in forage grasses is limited due to their cost and human and environmental safety considerations. One of the most effective strategies to control pests and diseases is to breed disease resistant forage varieties. A promising grass variety must contain genes for resistance to biotic stresses. Forage grasses have many strategies to protect themselves from biotic stresses, such as allergic reactions and the production of plant antitoxins. The isolation of genes for biotic stress resistance in forage grasses and the analysis of molecular mechanisms of biotic stress resistance have become a focus of interest.
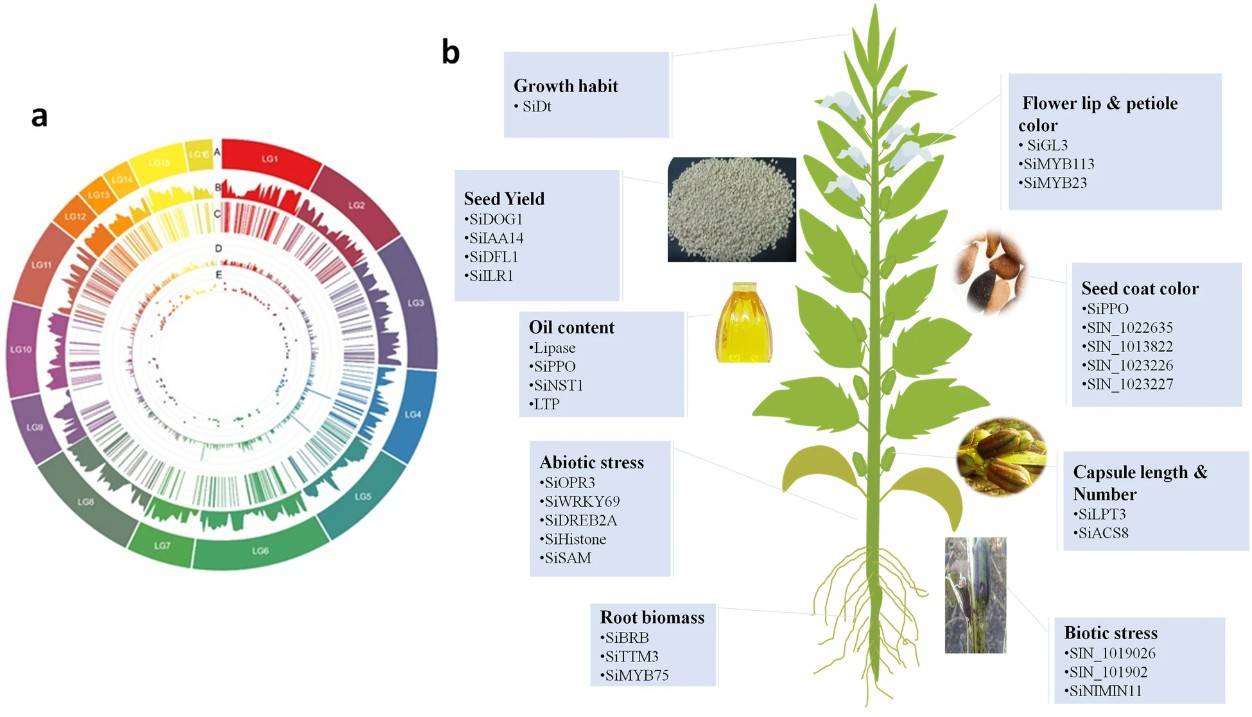 Fig.1. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) applications in sesame. (Berhe M et al., 2022)
Fig.1. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) applications in sesame. (Berhe M et al., 2022)
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) provide advanced tools to identify genetic loci associated with traits of interest using a high density of markers across the genome. We developed GWAS to analyze the genetic architecture of forage quality-associated shapes and are particularly well suited for analyzing single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers associated with quality traits. As an ideal partner for forage research, Lifeasible offers a customized process for genome-wide association analysis of forage quality-related traits.
Our advanced next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology platform is used to develop high-density SNPs on a genome-wide scale, and we offer near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) to assess a variety of forage quality traits, including crude protein, indigestible crude protein, soluble protein, fiber, fiber digestibility, non-fiber carbohydrates, and more. In addition, we used sequencing genotyping methods to genotype SNPs in the same germplasm set.
We provide statistical analysis of all quality traits to map the frequency distribution of quality traits related to fiber digestibility and protein content.
We provide a comprehensive GWAS analysis service to identify marker loci associated with forage quality traits at high resolution. It is important to note that gene identification for forage quality traits in GWAS is performed in natural populations. The same genotyping data and the exact populations can be used repeatedly for different traits.
We also provide extraction of the flanking regions of each important marker and search through the database for annotation of genes close to important SNP.
The forage quality-related parameters we measured cover almost all the basic quality-related traits. The correlation results between these traits help simplify evaluating alfalfa quality. We aim to help our customers identify the genetic factors that influence alfalfa forage quality and to use the genetic information obtained for the genetic improvement of higher-quality forages. For more information or to discuss in detail, please contact us.
Reference