Plants, especially economic species, are plagued by viruses that lead to low yields and poor quality, and plant stem tip detoxification is one of the common countermeasures to address this problem. Plant detoxification by heat treatment takes a long time, making the plant susceptible to death and the detoxification rate is not high. Stem tip culture requires cutting very short stem tips under a dissecting microscope, which is difficult to operate and culture, and has a low detoxification rate. By combining heat treatment with stem tip meristem culture, larger stem tips can be cut and cultured to obtain virus-free plants, thus not only overcoming the limitation of high technical requirements for shoot grafting after heat treatment alone, but also solving the problem of low survival rate of conventional stem tip culture by taking small material. Especially for those viruses that are difficult to be removed by one method alone, this combined detoxification method can significantly improve the detoxification effect.
Viruses are unevenly distributed in plants and are intolerant of high temperatures, so heat treatment can blunt the virus and expand the virus-free zone of the stem tip, which has the advantage of taking a small amount of apical meristem tissue to produce a complete plant.
The plants selected must be robust, stoloniferous and free from diseases and pests. The stolons with leaflets not yet fully expanded are cut 3~5 cm, washed with detergent solution, rinsed with flowing water for 30 min, and placed in a 40℃ water bath for 4h (Fig 1).
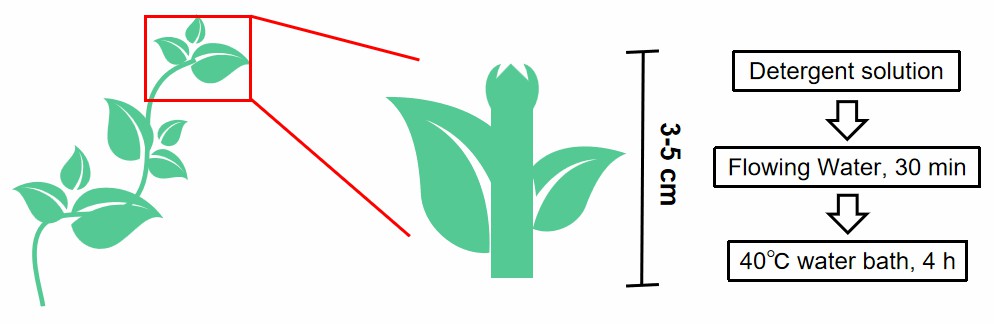 Fig 1. The procedures of material selection and sterilization
Fig 1. The procedures of material selection and sterilization
Then the explants are transferred to the ultra-clean bench, disinfected with 70% alcohol for 30s, rinsed with sterile water for 1-2 times, disinfected with 0.1% mercuric chloride for 5min and stirred continuously, and rinsed with sterile water for 4~6 times (Fig 2). Finally, the water on the plant was blotted dry with sterile filter paper.
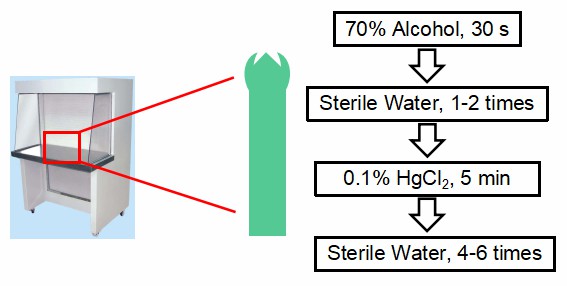 Fig 2. The procedures of material selection and sterilization (2)
Fig 2. The procedures of material selection and sterilization (2)
The stem tips below 0.5 mm were cut under dissecting microscope and inoculated into the induction medium for sterile culture (Fig 3).
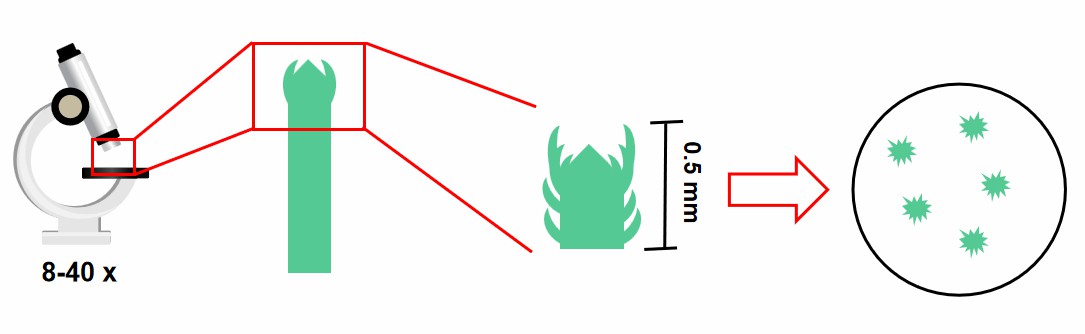 Fig 3. The procedures of stripping stem tips and inoculation
Fig 3. The procedures of stripping stem tips and inoculation
The 0.5 mm long stem tip can be cut and cultured into test tube seedlings, and then the test tube seedlings can be heat treated (Fig 4). The seedlings can adapt to high temperature in a sealed environment, the troublesome operation of root protection can be eliminated, and the plant survival rate and detoxification rate are higher.
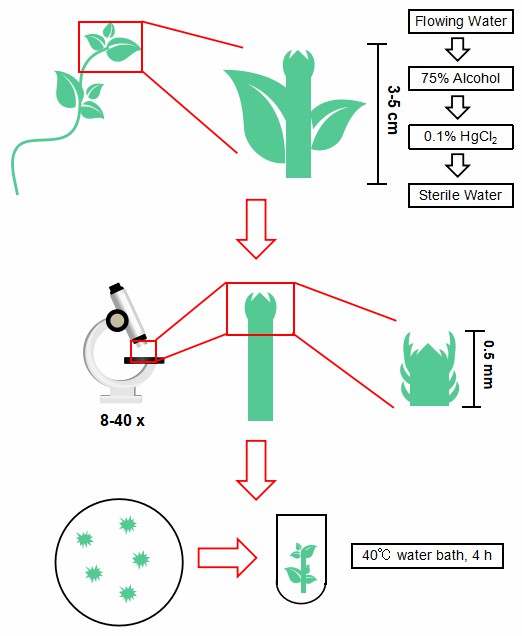 Fig 4. Alternative steps
Fig 4. Alternative steps