Screening and Compounding of Herbal Medicinal Component Groups
Inquiry
The substance basis of herbal medicine refers to the chemical components of herbal medicine and its compound formulations, which are responsible for the safety, efficacy, and quality control of herbal materials and products. However, due to the complexity of herbal components and the limitations of research methods, the quality-quantity-effect relationships of most complex herbal systems have not been effectively elucidated. Lifeasible is working on the construction of pharmacodynamic component groups through the screening and identification of pharmacodynamic component groups, which can simplify the complexity of multi-component herbal medicines. It is characterized by a clear substance basis, a clear mechanism of action, and a high degree of controllability.

Identification of herbal medicinal component groups
- Activity tracing isolation method
We extract, isolate, identify, and screen the activity of the chemical components of herbs to identify the active ingredients. A large amount of material basis and potency information can be provided for most single herbs.
- In vivo pharmacodynamic component characterization correlation analysis
| Serum medicinal chemistry |
Based on the components that are absorbed into the blood to be effective. We use modern analytical methods to characterize migrating components in human/animal serum, including prototypes or metabolites, to resolve the material basis of herbal medicine. We mostly use mass shortage filtration techniques, background deduction, and statistical processing in liquid mass spectrometry to reduce endogenous components' interference in blood and identify and characterize migrating components in blood. |
| Pharmacokinetics |
Based on the fact that most drug-active ingredients may exert their pharmacodynamic effects in the organism through extensive metabolic transformation into active metabolites, including a prototype component group with appropriate kinetic characteristics and active metabolomics, are essential for revealing the complex pharmacodynamic component groups in herbal medicines in vivo. We use new concepts such as multi-component integrated pharmacokinetics, in vivo and ex vivo association network analysis, and metabolomics to help you unravel the material basis of the in vivo effects of herbal medicines, identify associated biomarkers, and clarify the in vivo mechanisms of action. |
- Identification method based on informative data mining
| Spectro-effective relationship analysis |
We construct a correlation between the chemical information of the fingerprint profile and the pharmacodynamic activity and use mathematical methods to model and find clusters of pharmacodynamic substances. |
| Computerized virtual screening |
We search for compounds with affinity to the target macromolecule from a database of small molecules against a three-dimensional structure or conformational relationship model of the disease-specific target biomolecule. Commonly used methods include virtual screening based on small ligand molecules and receptor macromolecules to predict the activity of ligand small molecules and evaluate small ligand ligand-receptor binding activity. This method has the advantages of powerful arithmetic, good prediction accuracy, and orientation. It is a good reference for evaluating the activity of target compounds, strongly avoiding blindness in research and saving research time and money to a large extent. |
| Integrating effect correlation analysis |
We applied the combined multi-indicator integrated index method and artificial neural network to the association analysis of herbal effects and active ingredient groups. This method allows for the synthesis and generalization of a large amount of data generated from basic research to obtain more intuitive effect evaluation results, while correlation analysis allows for the association of chemical components with specific effects, thus allowing for more accurate identification and evaluation of herbal effectors. |
| Identification by bio-chromatographic coupling |
We have developed a target (biofilm, target cell, target molecule) screening mechanism based on the fact that most drugs are required to bind to receptors, enzymes, target cells, etc., on cell membranes or enter the cell interior, thereby causing apoptosis, division, or cell cycle arrest. This method can efficiently and rapidly reveal the material basis of herbal medicine, exclude impurity components' interference, and facilitate the verification and tracking of drug efficacy and activity. |
| Knock-in/knock-out identification method |
We use modern isolation techniques to selectively "knock out" the target components, taking the "spectrum-potency" and "quantity-potency" relationships of herbal medicines as the entry point. By comparing the biological activities of the target components, the negative samples, and the herbal medicine as a whole in parallel, the critical efficacy components can be identified. The target components can be "knocked in," i.e., different doses of the target components are added to the negative samples and compared with the efficacy of the herbal medicine as a whole to establish the quantitative efficacy of the target components and to obtain a scientific and reasonable The target components were compared with the overall potency of the herb to establish a quantitative relationship between the target components and the potency of the herb. |
Construction/compounding of herbal medicinal component groups
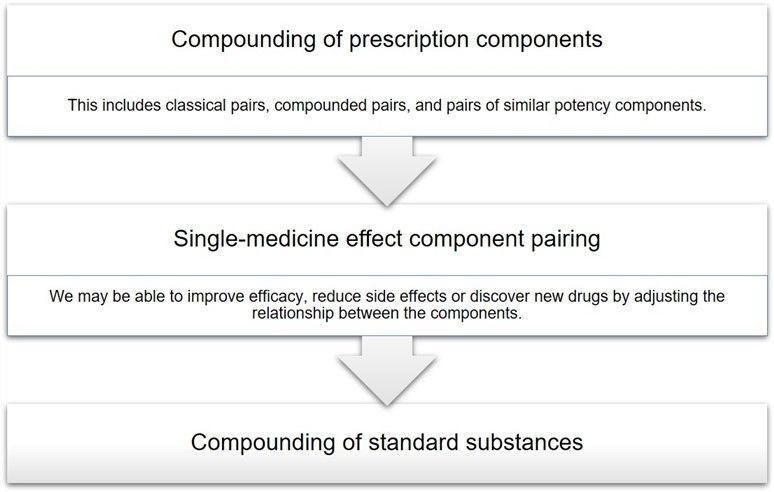
Lifeasible starts with the screening ideas, component pairings, and quality control models of the current pharmacodynamic component groups to find the pharmacodynamic component groups and build pairing relationships from the complex component groups. We aim to help you identify the key components of your herbal medicines quickly and accurately, to realize your vision of herbal quality standards, and support you in building your herbal medicine quality assessment system. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
Related Services


