
Spodoptera litura is a species of the genus spodoptera litura in the order Lepidoptera, and it is an important agricultural pest with a worldwide distribution. With the continuous enrichment and improvement of insect genome information, functional genome research plays an increasingly important role in spodoptera litura, and genetic manipulation is an indispensable means in functional genome research. Genome editing technologies such as zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs), transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALEN), and CRISPR-Cas9 have provided new means of insect genetic manipulation.
Gene editing technology is the most advanced genetic modification technology in biological sciences, and gene editing technology is widely used in insects. Lifeasible provides ZFNs, TALEN and CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing services for spodoptera litura to screen out them with good traits include BLOS2, PBP and other genes according to your needs to reduce the damage of spodoptera litura to plants.
| Editable genes | Relevant traits exhibited after editing |
| BLOS2 |
|
| PBP |
|
| TLRs |
|
| SlitOBPs |
|
| GSTs |
|
Lifeasible uses ZFNs to edit spodoptera litura by fusing a zinc finger DNA-binding domain to a DNA-cleavage domain. We engineered zinc finger domains to target specific desired DNA sequences and this enables zinc-finger nucleases to target unique sequences within complex genomes. By taking advantage of endogenous DNA repair machinery, these reagents can be used to precisely alter the genomes of spodoptera litura.
Lifeasible provides gene editing services in spodoptera litura through TALEN to cut specific sequences of DNA. We engineered transcription activator-like effectors to bind to practically any desired DNA sequence and cut DNA at specific locations when combined with a nuclease.
Lifeasible provides gene editing services in spodoptera litura through the system of CRISPR/Cas9 based on an acquired immune mechanism found in bacteria and archaea that silences the expression of target genes by genome editing of target genes through chimeric double-stranded RNA-mediated Cas9 proteins. We use this method to edit the spodoptera litura with gene knock out, tag insertion and gene fragment insertion.
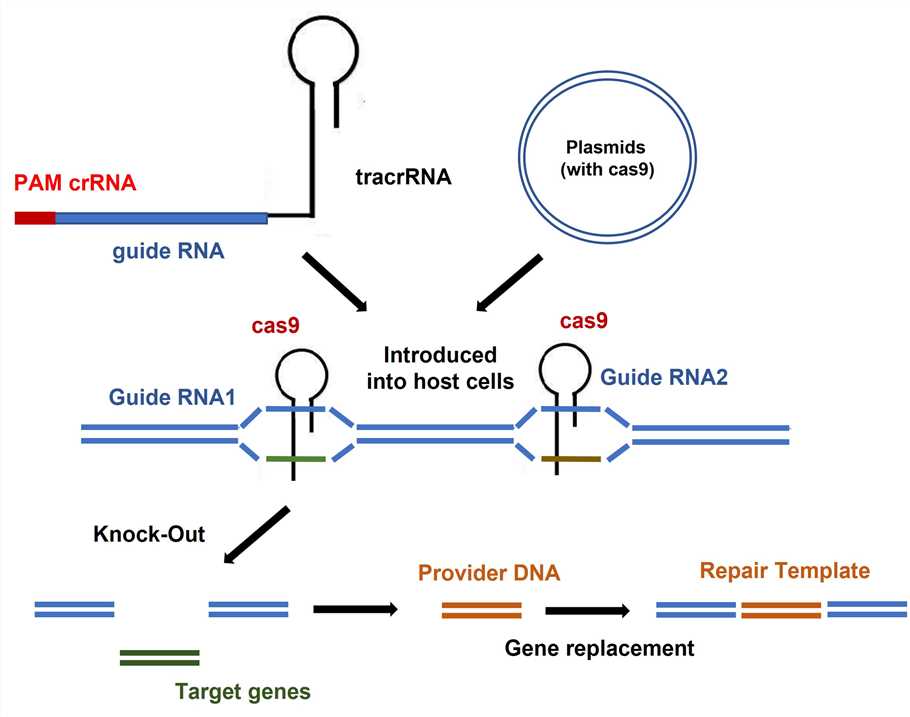 Fig 1. Principle of CRISPR/Cas9.
Fig 1. Principle of CRISPR/Cas9.
Lifeasible offers three means of gene editing include ZFNs, TALEN and CRISPR/Cas9 in spodoptera litura by experienced teams with several advantages like multiple genes can be mutated simultaneously, high editing efficiency, the insertion of tag and gene fragment and gene knockout in this specific species. If you are interested in our services, please click online inquiry for more detailed information.