Isolation and Identification of Plant Pathogenic Fungi
Fungal species are huge and diverse, among which there are more than 8,000 species of phytopathogenic fungi that can cause more than 30,000 kinds of plant diseases. The common smut, powdery mildew, rust, downy mildew, etc., on plants are caused by fungi. In recent years, the study of the pathogenic mechanism of plant pathogenic fungi has also become one of the hot issues in the field of plant pathology, and understanding the mechanism of interactions between plants and pathogenic fungi is of great significance for the effective control of pathogenic fungal damage and selection of disease-resistant varieties.
Lifeasible has extensive experience in the isolation and identification of plant pathogenic fungi and can help customers achieve the identification of pathogenic fungi using DNA molecular marker technology.
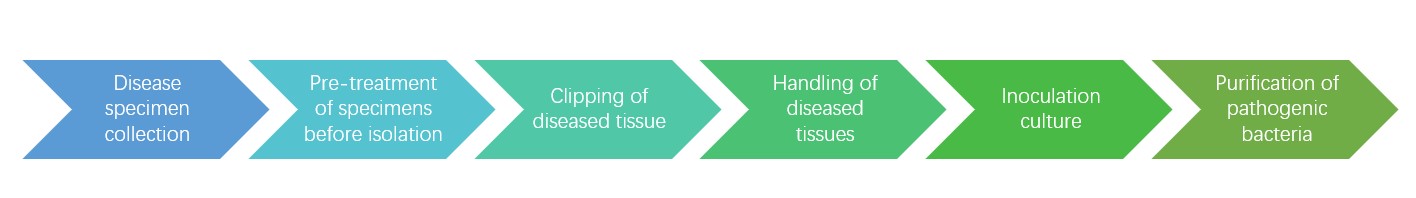 Figure 1. Plant pathogenic fungal isolation process.
Figure 1. Plant pathogenic fungal isolation process.
- DNA-DNA hybridization technology. DNA-DNA hybridization technique applied to fungal identification refers to the hybridization percentage and the thermal stability of the hybridization complex. The difference between species can be reflected by the difference in the thermal elution temperature of the hybrids. The fungi genome is relatively small compared to animals and plants, and there are fewer repetitive sequences. We can use DNA-DNA hybridization technology to help our clients achieve the identification of plant pathogenic fungi.
- Restriction fragment length polymorphism. Restriction fragment length polymorphism refers to the difference in length of enzyme segments containing homologous sequences after restriction endonuclease enzymatic digestion of different individual genomes. Restriction endonucleases recognize recognition sites consisting of specific bases on sequences and cut at the recognition sites, degrading very long molecules into fragments of varying lengths. The number and length of fragments reflect the distribution of restriction endonuclease cut sites. For a particular DNA/restriction endonuclease combination, the number and length of fragments degraded are deliberate and, therefore can be used as a unique fingerprint for a particular genome. We can use RFLP technology to help our customers achieve taxonomic identification of plant pathogenic fungi.
- Polymerase chain reaction. Polymerase chain reaction enables direct sequencing of genomes, cloning, rapid detection of gene mutations, oligonucleotide probe synthesis, and detection of gene sequence polymorphisms. We can provide specific PCR, simplex primer PCR, immunocapture PCR, random amplification polymorphism technique, and amplified fragment length polymorphism to help our customers to achieve the identification of plant pathogenic fungi.
Lifeasible can help customers isolate and identify plant pathogenic fungi using various molecular techniques based on DNA data. As your trusted partner, we can meet your needs for mycorrhizal fungi identification and isolation services and provide efficient and high-quality services. If you want to know the details, please contact us.
Reference
- Yu X, et al. Identification and Pathogenicity of Fungi Associated with Leaf Spot of Muskmelon in Eastern Shandong Province, China. Plant Dis. 2022 Mar; 106(3): 872-890.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Figure 1. Plant pathogenic fungal isolation process.
Figure 1. Plant pathogenic fungal isolation process.