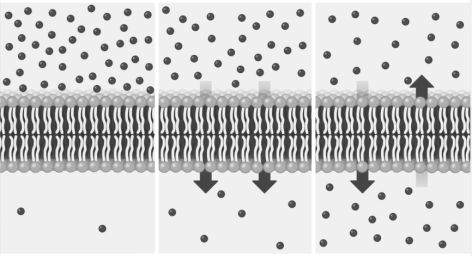
Small liposome molecules need to pass through a series of biological membranes to function. Therefore, the prediction of membrane permeability of small molecules is very important. Liposomes can mimic the structure of natural biological membranes, and their good stability and cellular affinity are often used as quasi-stationary or stationary phase in capillary electrophoresis (CE) analysis. Liposome capillary electrophoresis, which uses liposome solution as the running medium, can be a simple, effective, and stable model for in vitro screening small molecules.
Micellar capillary electrochromatography (MEKC) is a fast-developing and widely used electrokinetic chromatography technique, which is often used to simulate the hydrophobicity of compounds evaluated by biological membranes due to its hydrophobic and hydrophilic moieties. The separation principle is based on adding a quasi-stationary phase (commonly used surfactants, charged micelles, or microemulsions with their mobility) to a buffer solution and separating compounds according to their electrophoretic differences and differences in partitioning properties in the micelles. The MEKC method is often used as an alternative method to assess the lipophilicity of compounds due to its simplicity, rapidity of operation, and small sample size.
Lifeasible uses liposome electrokinetic chromatography (LEKC), in which liposomes are added to buffers as quasi-mobilized phases, and immobilized liposome capillary column chromatography (ILCCC), in which liposomes are covalently immobilized on the inner walls of capillaries, to study the interaction between small molecules and mimic membranes and thus evaluate the membrane permeability of small molecules.

If you are interested in our services, or if the service you want is not listed, please feel free to contact us, and we will get back to you as soon as possible.