From a structural point of view, liposomes are sub-stable structures consisting of one or more lipid bilayers around an aqueous compartment, where the hydrophilic (or polar) head group is oriented towards (external and internal) the aqueous phase. Aqueous solutions' structure and size depend on the preparation conditions (i.e., sonication, stirring, extrusion, electroformation, or microfluidization). Liposomes are mainly between 25 and 2500 nm in size, and depending on the number of bilayers, they can be classified as monolayers (ULV), multilayers, or oligolayers.
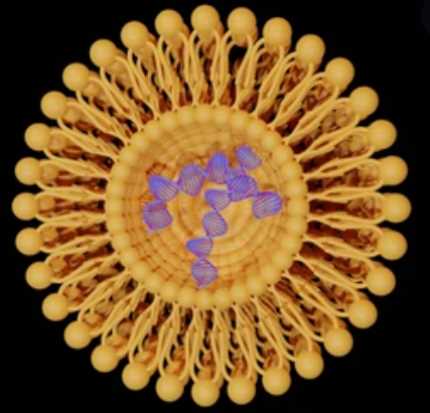
The stability of liposomes is usually examined as physical stability and chemical stability. Physical stability is essential for the storage, safety, and application of liposomes, and their physical stability can be assessed based on colloidal stability. We can analyze the liposome thermodynamic stability by monitoring the change in particle size. The evaluation of chemical stability includes the lipid composition of the liposomes as well as the chemical stability of the contained molecules. Stability studies (after exposure to different pH) can be performed to analyze the chemical stability of liposomes by testing the particle size, zeta potential, etc. And physical and chemical stability tests of liposomes can help to establish suitable storage conditions and retest periods.
Lifeasible provides professional liposome stability testing. Depending on our current experimental equipment, we can provide customers with liposomes' physical and chemical stability testing, including the effect of sugar concentration, salt concentration, pH, heating temperature and time, storage temperature and time, etc., on liposomes. Usually, this effect can be fed back by zeta potential, particle size, and retention rate.
Our experimentalists examine the effect of different concentrations of sucrose on the morphology, zeta potential, particle size, and retention of liposomes.
The effect of different concentrations of salt solutions (e.g., NaCl) on the zeta potential, and mean particle size product of liposomes can be examined according to customer requirements.
We can examine the effect of different pH on the properties of liposomes and test whether the zeta potential, retention rate, encapsulation rate, and average particle size of liposomes change to determine the suitable acid-base environment.
Liposomes are placed in constant-temperature water baths to see if flocculation and precipitation occur and to test for changes in mean particle size and absolute zeta potential to determine the maximum temperature they can withstand.
The effect of different temperatures for 15 min on the stability of the liposomes was investigated.
To examine the effect of storage temperature and time on the stability of liposomes, the particle size, the absolute value of zeta potential, and the retention rate of liposomes are tested.
If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us anytime.