Cultured meat has emerged as a breakthrough technology for the global food industry. It is considered a potential solution to alleviate serious environmental, sustainability, global public health, and animal welfare issues in the near future. In recent years, advances in regenerative medicine tissue engineering have helped scientists obtain muscle tissue from slices of living samples and perform cell culture, paving the way for in vitro meat production. In vitro meat culture using skeletal muscle tissue engineering, stem cells, cell co-culture, and tissue culture is practical and avoids livestock issues such as animal hazards and environmental contamination. Cultured meat desires to be biologically equivalent to conventional meat and need to mimic the key qualities required for conventional meat, such as appearance, odor, texture, and flavor.
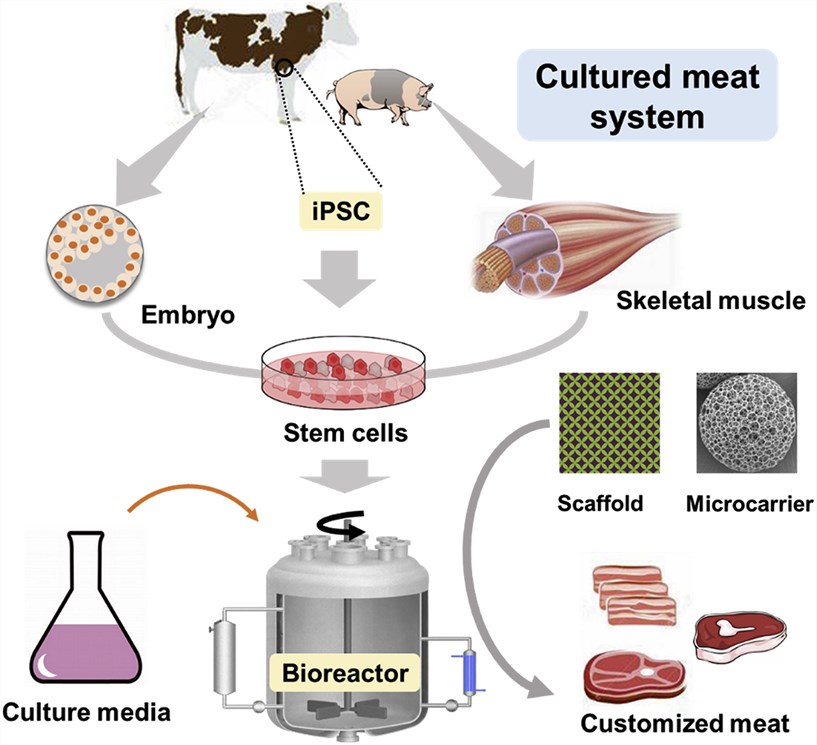 Fig.1. Production flow chart of cultured meat. (Zhang G et al., 2020)
Fig.1. Production flow chart of cultured meat. (Zhang G et al., 2020)
The production of cultured meat depends heavily on large-scale cell culture techniques. We offer an abundance of well-characterized stem cell lines for cultured meat. However, significant effort is still required to achieve sustainable large-scale production. For mass culturing of wall-dependent cells, microcarriers are used to establish suspension cultures. We offer microcarriers for cultured meat as a candidate for cell culture.
As an ideal partner for cultured meat production, Lifeasible offers the following two strategies for manufacturing cultured meat:
We use explants harvested from animals and proliferated in a culture medium. The presence of additional adipose tissue, circulatory system, etc., in the developing muscle, leads to the formation of tissues that resemble conventional meat in structure, composition, and sensory properties.
We proliferate and immobilize embryonic myogenic or stem cells collected from living animals on a substrate or scaffold in a bioreactor growth medium. Here, the tissue structure of cultured meat is created using edible (e.g., collagen and elastin) scaffolds.
One of the most important components of meat is its characteristic texture, which provides consumers with a delicious taste. The texture of the meat tissue affects the "mouthfeel" that the meat provides. Current cultured meat products are too loose to produce a true chewing sensation. The challenges of creating an appealing texture in the production of cultured meat that mimics fresh meat are far greater than those involved in preparing ground or finely ground meat products. Working closely with biotechnologists, Lifeasible is committed to developing customized solutions to reshape the structure of cultured meat to vividly replicate the dense and elastic structure of real meat. Our solutions include:
With decades of knowledge in cell culture, stem cell biology, tissue engineering, fermentation, and chemical and biological process engineering, Lifeasible is a leading manufacturer of cultured meat. Faced with challenges in cultured meat production (cell lines, cell culture media, bioprocess design, and scaffolds), our labs are conducting research across these disciplines to establish industrial-scale production of cultured meat. We guarantee you access to our solutions at competitive prices, with short turnaround times and reliable results. Feel free to contact us for more information.
Reference