Mushrooms are widely cultivated for their nutritional and medicinal value. However, research on its genetics is limited by the lack of knowledge of the details of the organization of its genetic material. Often mushroom genetics is hampered by small chromosome sizes, the lack of known sexual stages in many medically and industrially important species, and mitosis in the nucleus. The molecular karyotype of some mushrooms has yet to be fully elucidated. In higher organisms, karyotypes are established cytologically as a complement to genetic studies and as taxonomic characters of great value. With the development of high molecular weight DNA separation techniques, pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) techniques have been developed. Much of the initial development of these systems employed methods that served as standards for separating yeast brewer's yeast and poncey yeast chromosomes.
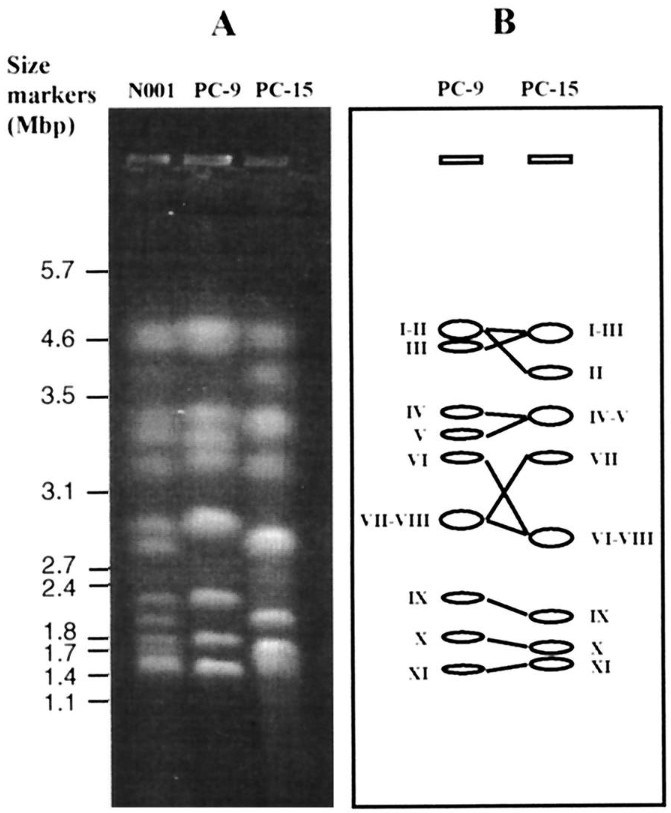 Fig. 1. Molecular karyotype of P. ostreatus N001. (Larraya LM, et al., 1999)
Fig. 1. Molecular karyotype of P. ostreatus N001. (Larraya LM, et al., 1999)
Services
Our experts use various analytical techniques to analyze different chromosome numbers and genome sizes, including microscopy, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP), and pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). Most the mushroom chromosomes are small enough to be isolated using PFGE. Here, Lifeasible offers cutting-edge PFGE techniques to analyze the molecular karyotype of mushrooms and the genetic assignment of fungal chromosomes. We can help you obtain the genome structure of your mushrooms and use cloning gene probes and genetics to combine these data with genetic linkage mapping of mushroom strains to design breeding and cloning strategies for specialty mushrooms.
Lifeasible develops customized pulsed field electrophoresis processes to determine the molecular karyotype of different mushrooms. The pulsed field electrophoresis conditions are optimized specifically for isolating different mushroom chromosomes.
- Microbial strain and culture.
- Protoplast preparation and mycelium regeneration.
- Incompatibility testing.
- DNA manipulation.
- Microsatellite analysis.
- Chromosome size DNA preparation.
- Pulsed field electrophoresis separation of chromosomes.
- Identification of chromosome-specific DNA probes.
Advantages of Our Services
- Allowing the identification of multiple chromosomes per haploid genome in mushroom strains.
- Each chromosome is individualized by chromosome-specific probes.
- Chromosome sizes cover the full range for which specialty mushrooms have been described.
- Optimization of the pulse conditions allowed reproducible resolution of the chromosomes.
Mushroom chromosomes are too small to be resolved and counted reliably with a light microscope. We provide comprehensive electrophoretic karyotype data to fill this major gap in the knowledge of fungal biology. Our electrophoretic karyotypes are widely used in basidiomycetes such as Agaricus bisporus, Pleurotus, Coprinus cinereus, and Schizophyllum commune. The genomic karyotype of each mushroom was prepared using a standardized staining program that reveals the characteristic structural features of each chromosome. If you are interested in our services, please contact us.
Reference
- Larraya LM, et al. (1999) Molecular karyotype of the white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 65(8):3413-7.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!


 Fig. 1. Molecular karyotype of P. ostreatus N001. (Larraya LM, et al., 1999)
Fig. 1. Molecular karyotype of P. ostreatus N001. (Larraya LM, et al., 1999) 