Based on cutting-edge metabolomics technology platforms, Lifeasible provides metabolomics services to screen the bioactive substances in mushrooms and their metabolic pathways. It also improves the content of important active substances in mushrooms through molecular technology.
Introduction to Metabolomics of Mushroom Bioactive Substances
Mushrooms are of importance in medicine, biocontrol, food, biological, chemical, and other industries due to their high content of bioactive compounds such as polysaccharides, alkaloids, terpenoids, sterols, and proteins. There are a variety of mushrooms whose secondary metabolites also have drug-like structures and may be considered the natural inspiration for major drug discovery. Less information is available on the purification of biologically active mushroom secondary metabolites and related secondary metabolic regulation, and the fractionation and isolation of metabolites is a daunting task. A systematic and comprehensive analysis of the metabolites produced by mushrooms with the help of metabolomics techniques would be very helpful for future pharmacological studies and drug applications.
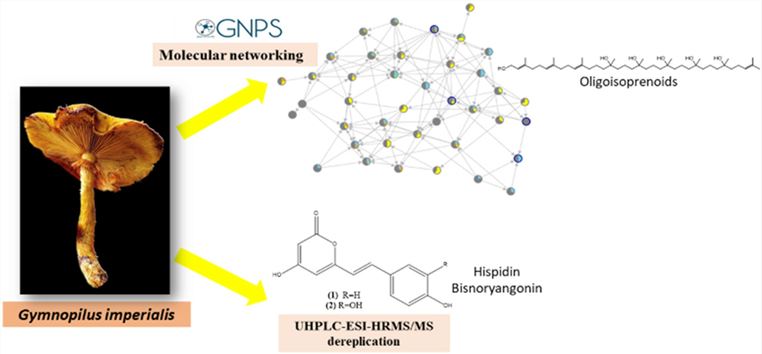 Fig. 1. Metabolomics of the wild mushroom Gymnopilus imperialis by UHPLC-HRMS/MS analysis and molecular network. (Caldas L A, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1. Metabolomics of the wild mushroom Gymnopilus imperialis by UHPLC-HRMS/MS analysis and molecular network. (Caldas L A, et al., 2022)
Services
Many metabolites, such as primary and secondary metabolites, are present in mushrooms. Our experts are actively involved in studying mushroom bioactive metabolites and are committed to providing essential data on the range of bioactive compounds found in these fascinating fungi. Lifeasible offers advanced mass spectrometry-based metabolomics technologies to screen hundreds of mushrooms simultaneously for dereplication studies and extractions of bioactive compounds.
We employ LC-MS/MS, GC-TOF-MS, and UHPLC-MS/MS techniques to identify a wide range of metabolites produced by mushrooms, including volatile oils, flavonoids, alkaloids, ascorbic and organic acids, fats, polysaccharides, tocopherols, glycosides, minerals, proteins, carotenoids, terpenoids, lectins, enzymes, phenolics, and folic acid, etc. In addition, we provide global, interactive, and online de-duplication platforms for the rapid annotation of metabolites and the creation of molecular networks to help rapidly identify metabolites that may have biological potential.
Our metabolomics approach is widely used for the discovery and novel metabolites of a variety of mushrooms, such as Agaricus, Amanita, Calocybe, Cantharellus, Cordyceps, Coprinus, Cortinarius, Ganoderma, Grifola, Huitlacoche, Hydnum, Lentinus, Morchella, Pleurotus, Rigidoporus, Tremella, Trametes sp.
Mushroom Metabolomics Workflow
- Sample extraction. Metabolite samples are usually extracted with water and organic solvents.
- Sample purification. We offer solid phase microextraction (SPME), solid phase extraction (SPE), and affinity chromatography to remove other components from the extracted samples.
- Metabolite analysis. We offer GC-MS, LC-MS, CE-MS, NMR, and FTIR/MS for the separation and analysis of metabolites in samples containing impurities.
- Analysis of metabolite structure and function. The data obtained from the analysis are combined with metabolome databases and websites to resolve and analyze the structure and function of metabolites by chemometrics.
The combination of metabolomics and signature-based molecular network technologies can highlight and cluster mushroom metabolite signatures together, enabling efficient de-duplication of compounds and greatly reducing the difficulty of new metabolite discovery. We can perform a systematic and comprehensive analysis of metabolites produced by a wide range of mushrooms to facilitate your research on new drugs or lead compounds in the medical field. If you are interested in our services, please contact us.
Reference
- Caldas L A, et al. (2022) Metabolomics of the wild mushroom Gymnopilus imperialis (Agaricomycetes, Basidiomycota) by UHPLC-HRMS/MS analysis and molecular network[J]. Fungal Biology. 126(2): 132-138.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!


 Fig. 1. Metabolomics of the wild mushroom Gymnopilus imperialis by UHPLC-HRMS/MS analysis and molecular network. (Caldas L A, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1. Metabolomics of the wild mushroom Gymnopilus imperialis by UHPLC-HRMS/MS analysis and molecular network. (Caldas L A, et al., 2022) 