In nature, Ganoderma lucidum reproduces sexually through the production of spores by the ascospores. When Ganoderma lucidum was introduced and domesticated, it was found that the germination rate of spores was extremely low and this led to the development of a cultivation method using spores or tissue cells of the zygote as explants to form pure mycelium by germination in culture. However, this method usually results in low viability of the explants, a low growth rate of the mycelium at all stages, and low amino acid and polysaccharide content, resulting in slow development and low active ingredient content of the substrates.
Lifeasible offers tissue culture services for Ganodernia lucidum. We have developed a histoculture method for Ganoderma lucidum that allows for rapid mycelial growth and increased API content. This can help you in your research into the artificial propagation of Ganoderma lucidum and better contribute to the sustainable development of the Ganoderma industry.

Introduction to Ganoderma lucidum
Ganoderma lucidum is a valuable herbal medicine belonging to the genus Ganoderma of the family Polyporaceae, in the order Streptomyces. Reishi is a large, dark-colored mushroom with a glossy surface (including a kidney-shaped cap coated in red lacquer) and a woody texture. The color of the pores on the underside depends on the age of the mushroom and can be white or brown. Reishi grows at the base and stumps of various deciduous trees. Recent studies have shown that Ganoderma lucidum contains polysaccharides that boost the immune system and have anti-tumor activity, giving it anti-cancer, anti-aging, analgesic, and hepatoprotective properties, with very low toxicity.
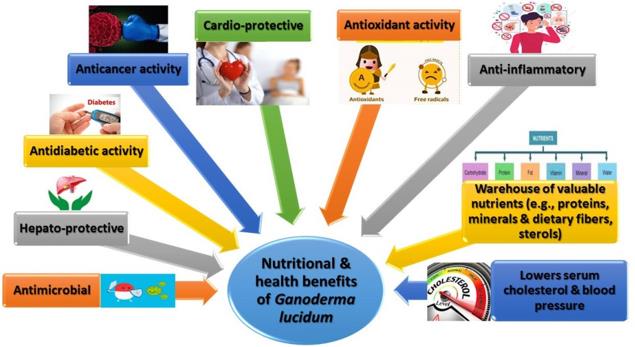 Fig. 1 Nutritional and health benefits conferred by Ganoderma lucidum. (El Sheikha AF, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1 Nutritional and health benefits conferred by Ganoderma lucidum. (El Sheikha AF, et al., 2022)
Our Services
Lifeasible offers tissue culture services for Ganodernia lucidurm. Our tissue cultures produce explants with high viability, fast mycelial growth rates, and high polysaccharide content. We offer a complete tissue culture process for Ganoderma lucidum consisting of the following steps:
- Disinfection: The Ganoderma seeds are collected, immersed in a biological disinfectant solution, and removed.
- Explants are cut, sprayed with a preservation solution, sealed to maintain sterility, and repeated 2-4 times for cooling and activation to obtain activated explants.
We provide a preservative solution containing the following ingredients: zeatin, chlorophyll, astaxanthin, blueberries, glutelin, moringa seed extract, zearalenone, 5-hydroxytryptamine, mannan oligosaccharides, and glycerol.
- The activated explants were inoculated on the mother strain medium and incubated at 20-30℃ 10-20 days to allow the medium to grow full of mycelium to obtain the mother strain.
- Microwave the mother strain to obtain the test strain.
- Inoculating the trial seeds on MS medium for cultivation so that the MS medium is full of mycelium to obtain cultivated seeds.
- Inoculate the cultivated seeds on the bag or wood and cultivate the mushroom in the usual way.
Advantages of Our Services
Through our well-established techniques and experimental procedures, tissue-cultured Ganoderma lucidum has the following advantages:
- High survival rate of explants
- High growth rate of mycelium at all stages
- High levels of amino acids and polysaccharides
- Faster development of fruiting bodies
- High levels of active ingredients in Ganoderma lucidum
Contact Us
Lifeasible provides tissue culture services for Ganoderma lucidum. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us for further information.
References
- Unlu A, et al. Ganoderma lucidum (Reishi Mushroom) and cancer. J BUON. 2016; 21 (4): 792-798.
- El Sheikha AF. Nutritional profile and health benefits of Ganoderma lucidum" lingzhi, reishi, or mannentake" as functional foods: Current scenario and future perspectives. Foods. 2022; 11 (7).
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!



 Fig. 1 Nutritional and health benefits conferred by Ganoderma lucidum. (El Sheikha AF, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1 Nutritional and health benefits conferred by Ganoderma lucidum. (El Sheikha AF, et al., 2022)