Lifeasible offers tissue culture services for morels. The cultivation of morels is affected by the season and the quality of the strains. Our tissue separation of high-quality wild morel obtains high-quality parent strains which can realize the perennial supply of high-quality morel strains. Cooperating with us can greatly increase your morel production and reduce potential heavy metal and pesticide pollution.
About Morels
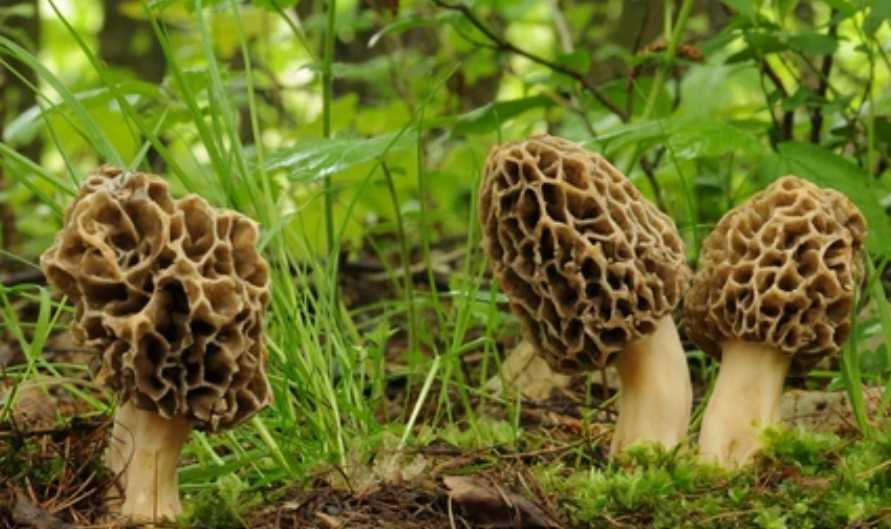
Morels (Morchella spp.) are naturally growing and commercially important edible mushrooms with a delicate taste and a unique appearance that make them one of the world’s most sought-after mushrooms. They have a characteristic shape, with a spongy, honeycomb-like cap that is attached to a stem. With a hollow interior and a spongy texture, they are described as having a unique savory and “meaty” flavor. They are usually consumed fresh or processed as a flavoring agent. The nutritional profile of morel mushrooms is mainly composed of carbohydrates, proteins, fatty acids, vitamins, minerals, and organic acids, which are responsible for their complex sensory attributes and health benefits. Bioactive compounds in morels include polysaccharides, phenols, tocopherols, and ergosterol, which contribute to antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immune protection, gut health, and cancer-fighting abilities.

Our Services
Lifeasible provides morel tissue culture services and provides key technical support for morel research, agricultural cultivation, and industrialization of morels. Our services include but are not limited to the following:
- We provide morel tissue culture services.
Helping you culture morel mushrooms, developing related biotechnology processes, and accelerating your research progress.
- We provide high-quality parent strains for the agricultural cultivation of morels.
Through tissue isolation, we will customize the type of parent strains you want from the morel samples you provide or our collections, increase the agricultural cultivars of morel, and improve the yield and quality of morel.
- We provide materials related to morel tissue and cultivation.
Including but not limited to exogenous nutrition bags, medium, petri dishes, etc.
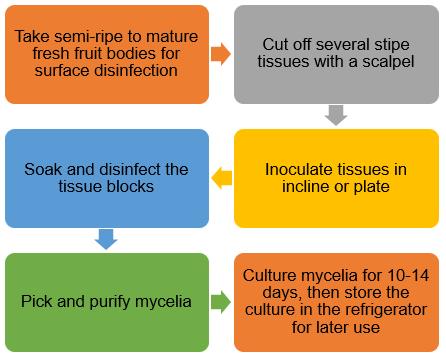
The Process of Morel Tissue Culture
Advantages of Our Services
- Our morel strains are not easy to degenerate, or mutate, and have stable properties.
We carried out fruiting and comparative tests when isolating morel strains to ensure the quality of our strains.
- Our morel strains are rich in variety, excellent in quality, and high in yield stability.
We select a variety of high-quality wild morels for tissue isolation to obtain high-quality parent strains, and then screen through different media and environments to increase the diversity and quality of the strains.
- Our morel-related materials can improve the success rate of experiments and ensure the output of morel.
Our medium and exogenous nutrient bags contain a variety of nutrients for the growth of morels, which are suitable for the growth of morels at different stages and can ensure the transformation of morels from vegetative growth to reproductive growth.
Contact Us
Lifeasible offers morels tissue culture services. Morels are delicious, nutritious and exhibit a variety of biological activities. Through our services, we can help you screen and cultivate high-quality morel strains, promote morel scientific research and agricultural planting, and expand the application of morel-related food, medicine, and nutritional health products. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for a more detailed service description.
References
- Li, Y.; et al. Cultivation, nutritional value, bioactive compounds of morels, and their health benefits: A systematic review. Frontiers in Nutrition. 2023, 10: 1159029.
- Liu, Q.; et al. Artificial cultivation of true morels: current state, issues, and perspectives. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology. 2018, 38(2): 259-271.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!




