Non-human primates (NHPs) are highly similar to humans in terms of tissue structure, immunity, physiology, and metabolism, can solve the research translation dilemma faced by rodent models, and are irreplaceable materials for biological and medical research and drug testing. Commonly used NHPs include rhesus monkeys, crab-eating monkeys, macaques, and tree shrews, which play a pivotal role in neurobiology, reproductive biology, viral immunology, and behavioral ecology.
With the completion of more and more primate genome sequencing and the development of gene editing technologies, researchers have successfully established animal models of major diseases such as neurological diseases, AIDS, cardiovascular diseases, and tumors. To study human disease evolution and develop novel therapeutics, CHIP-seq has been widely applied to NHPs more comprehensively and deeply.
As a world-renowned sequencing company, Lifeasible provides non-human primate ChIP-seq solutions for biologists, geneticists, and medical scientists. To promote the research progress of non-human primates from the direction of epigenetics and then help us overcome various human diseases.

After receiving the immunoprecipitation-enriched DNA samples from our customers, we perform a series of operations such as purification, library construction, and up-sequencing of the samples. After bioinformatic analysis, we obtain genome-wide information on DNA segments that interact with histones, transcription factors, etc.
Epigenetic modifications are critical for developmental status. To explore changes in epigenetic modifications during aging, we used rhesus macaques of different ages as our study subjects. We performed deep sequencing of H3K4me2 in the prefrontal cortex using ChIP-seq technology. We found that H3K4me2 increased in promoter and enhancer regions during postnatal development and aging.
We used ChIP-seq to detect five histone modifications (H3K4me1, H3K4me3, H3K36me3, H3K27ac, and H3K27me3) annotate regulatory elements in human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan, and macaque lymphoblastoid cell lines. Then, the evolutionary conservation patterns of regulatory elements in primates were analyzed in combination with WGS, WGBS, ATAC-seq, and RNA-seq.
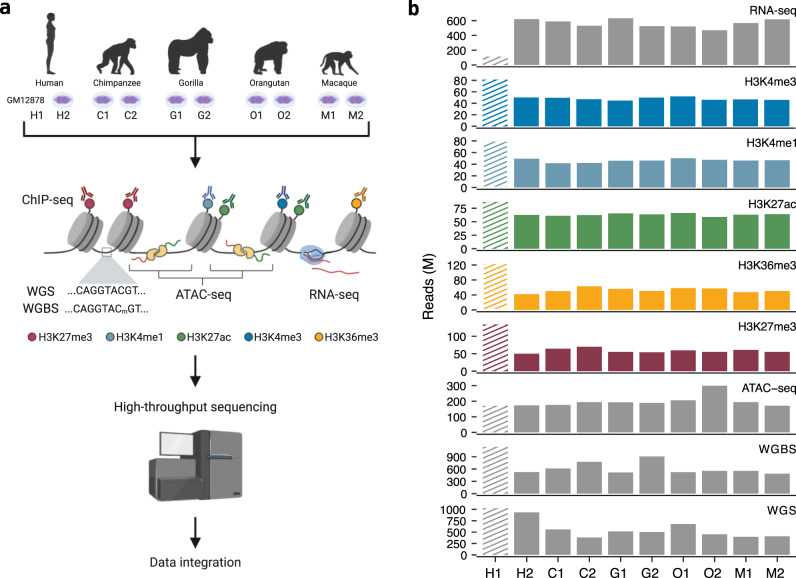 Figure 1. Experimental protocol and sequencing data. (García-Pérez, R, et al. 2021)
Figure 1. Experimental protocol and sequencing data. (García-Pérez, R, et al. 2021)
We first immunoprecipitated macaque brain frontal cortex samples using H3K4me3 antibody and then performed deep sequencing of ChIP DNA using ChIP-Seq. Analysis of ChIP-Seq data revealed a large number of transcriptional start sites. This technique provides a simple way to generate reasonably reliable transcription start site maps for large genomes.
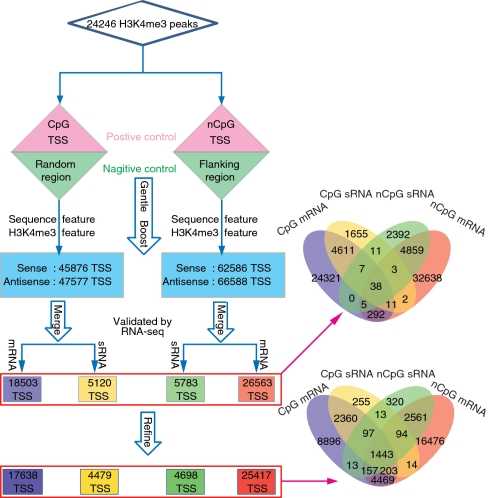 Figure 2. Flow chart for predicting transcription start sites by ChIP-seq. (Liu, Y, et al. 2011)
Figure 2. Flow chart for predicting transcription start sites by ChIP-seq. (Liu, Y, et al. 2011)
It is recommended to provide two sample preparations, if possible, to ensure the quality and continuity of the experiment.
Lifeasible's animal-oriented sequencing technology platform can provide customers with one-stop non-human primate ChIP-seq services to obtain epigenetic information about non-human primates and help understand the regulatory mechanisms of epigenetic modifications in primate development, evolution, aging, and disease. Please feel free to contact us with questions, inquiries, or collaborations.
References