Exosomes are present in all body fluids under both normal and pathophysiological conditions. Exosomes are extracellular vesicles (EVs) with a size range of ~40 to 160 nm (average ~100 nm) in diameter with an endosomal origin. Depending on the cell of origin, exosomes can contain many constituents of a cell, including DNA, RNA, lipids, metabolites, and cytosolic and cell-surface proteins.
The physiological purpose of generating exosomes remains largely unknown and needs investigation. Intercellular communication through exosomes seems to be involved in the pathogenesis of various disorders, including cancer, neurodegeneration, and inflammatory diseases.
Exosomes have potential therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Exosomes can function as potential biomarkers, as their contents are molecular signatures of their originating cells. Due to the lipid bilayer, exosomal contents are relatively stable and protected against external proteases and other enzymes, making them attractive diagnostic tools. Exosomes are being pursued use in an array of potential therapeutic applications. While externally modified vesicles suffer from toxicity and rapid clearance, membranes of naturally occurring vesicles are better tolerated, offering low immunogenicity and high resilience in extracellular fluid.
At Lifeasible, we provide custom one-stop exosome analysis services. From exosome isolation, imaging, identification, characterization, and polyomics analysis to exosome engineering. In addition, we also provide glycochemical analysis for milk exosomes, mannosylated exosome customization services and exosomes development services for immunomodulation. If you have special needs in the field of exosome research, we also provide cosmetic hair growth exosome and calibration exosome antibody development services. Lifeasible can provide efficient and cost-effective solutions for our customers.
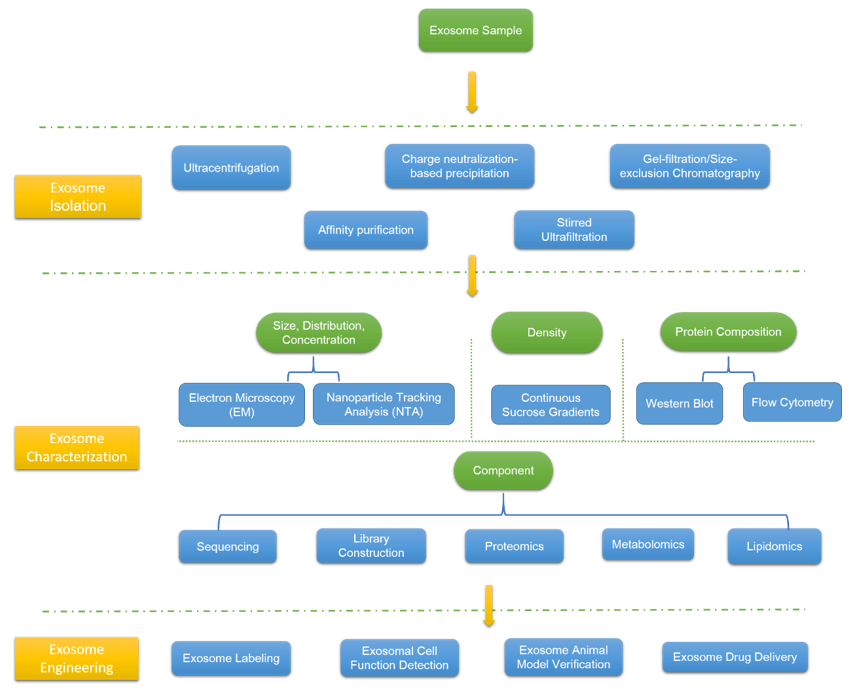
Our exosome platform offers a wide range of services related to exosome isolation and identification and other services that can be tailored to meet the needs of different projects. We work closely with the user for each project to customize the solution for the intended application. We offer exosome services that cover a wide range of plant species.
| No. | Name | No. | Name |
| 1 | Bidens pilosa | 15 | Lycium chinense |
| 2 | Mexican mint | 16 | Paeonia lactiflora |
| 3 | Perilla frutescens | 17 | Semen ziziphi spinosae |
| 4 | Blackberrglily rhizome | 18 | Zingiber officinale |
| 5 | Plumbago auriculataLam. | 19 | Zea mays L. |
| 6 | Salvia leucantha | 20 | Angelica sinensis |
| 7 | Gardenia jasminoides | 21 | Toxicodendron vernicifluum |
| 8 | Platostoma palustre | 22 | Rosmarinus officinalis |
| 9 | Mentha | 23 | Curcuma longa |
| 10 | Sophora flavescens | 24 | Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer |
| 11 | Coleus scutellarioides var. crispipilus | 25 | Citrullus lanatus |
| 12 | Tetradium ruticarpum | 26 | Malus pumila Mill. |
| 13 | Mallotus apelta | 27 | Nothapodytes nimmoniana |
| 14 | Vernonia amygdalina | 28 | Aloe vera |
Exosomes exist in various body fluids of humans and animals, and we can choose exosomes from different sources as needed. Different body fluid collection and storage standards are different. In addition, the amount of samples required for various body fluids varies according to the subsequent projects that need to be carried out. Ultracentrifugation is regarded as the gold standard for exosome isolation, besides, our experts provide alternative methods according to sample and project’s requirements, such as charge neutralization-based precipitation, gel-filtration/size-exclusion chromatography, affinity purification using immunomagnetic beads, stirred ultrafiltration, etc. You could contact our experts to discuss suitable methods.
Once a sample is prepared it needs to be characterized to demonstrate that the vesicles have the size, density, and protein composition consistent with exosomes.
We could provide electron microscopy (EM) to image exosomes directly, which could also determine the size, distribution, and concentration of exosome. For complementary EM, we also provide nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), an indirect method to rapid analysis of large numbers of exosomes, which is mostly automated such that there is minimum human influence.
Besides the characteristic size of exosomes, they have a density that differentiates them from other vesicles and membrane artifacts. We provide continuous sucrose gradients for analysis.
The protein composition of exosomes likely reflects the cell from which it originates. The presence of these exosome marker proteins is a strong indication of the vesicle’s biogenesis. We provide Western Blot and flow cytometry for your choice.
Exosomes naturally transport mRNA, miRNA, and proteins between cells, which form a major component of exosome cargo. They have been regarded as a vital source of biomarkers and therapeutic cargo. Specific detection methods include miRNA sequencing, whole exosome RNA sequencing, library construction, proteome analysis (iTRAQ, TMT, Label-free), exosome lipidomics & metabolomics analysis, etc.
In vitro labeling or in vivo tracing of isolated exosomes can be used to further study the function of exosomes. When the cells and exosomes are incubated together, the cells can engulf the exosomes through the process of endocytosis, then proteins, nucleic acids, and other molecules wrapped by the exosomes will be released, thereby affecting the functional changes of the cells. Add the labeled exosomes to the recipient cell culture medium and co-culture with the recipient cells could observe the functional changes of the cells, such as cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and apoptosis; or inject the exosomes into the animal model could then observe animal phenotype changes and detect animal-related indicators. The experimental content includes exosome labeling, exosomal cell function detection, exosome animal model verification, etc.
For detail, please feel free to contact our experts.