With the advent of high-throughput genomics, the determination of protein function is increasingly dependent on adequate sequence analysis. Functional annotation of genomes requires correlating an increasing amount of experimental evidence with an exponentially increasing sequence similarity data. However, this is a daunting task and the quality of the results depends on the adequacy of the sequence analysis procedures used. In addition, eukaryotic cells add another layer of complexity due to multiple membrane-bound intracellular compartments. Microalgae are eukaryotic microorganism widely used as a primary model for deciphering the processes occurring in the intracellular compartment of photosynthetic cells. Organelle-specific proteomics studies have begun to map its various subproteomes, and the function of proteins depends largely on their subcellular localization in the cell. Therefore, sequence-based prediction software is necessary to assign protein subcellular localization on a genome-wide scale.
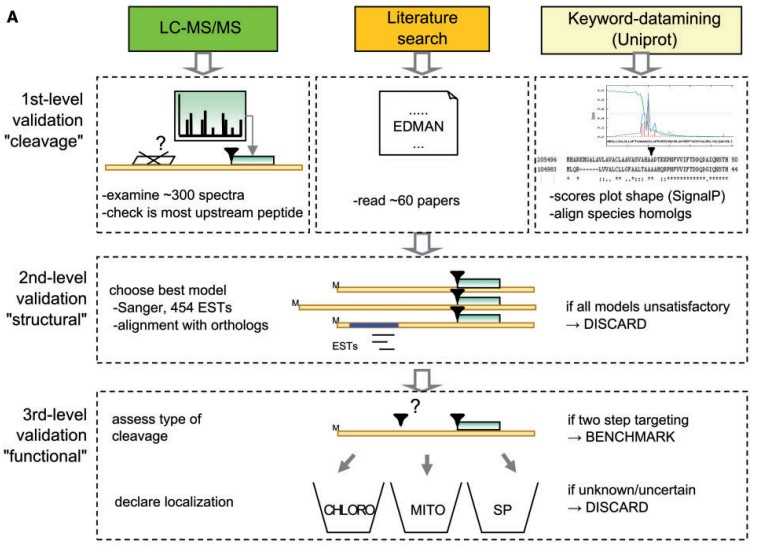 Fig 1. Workflow for collecting green algae proteins with a known targeting cleavage site. (Mukherjee A, et al., 2019)
Fig 1. Workflow for collecting green algae proteins with a known targeting cleavage site. (Mukherjee A, et al., 2019)
There are at least ten major subcellular localizations in eukaryotic microalgae. Traditional tools can incorrectly predict the localization of nuclear-encoded algal proteins, predicting many chloroplast proteins as mitochondrial targets. At Lifeasible, we provide specialized services for the subcellular localization of microalgal proteins to predict the intracellular localization of these proteins in one of three intracellular compartments in green algae: mitochondria, chloroplasts, and the secretory pathway.
The function of a protein is closely related to its subcellular location in the cell. An essential step in microalgal proteomics is determining each proteins subcellular localization. Over the years, our skilled scientists have used various experimental methods for identifying the location of microalgal proteins and computational methods for predicting the subcellular location of microalgal proteins.
Our goal is to help you predict the subcellular location of microalgal proteins based on machine learning to integrate protein interaction and functional information. The currently available prediction methods differ in three main areas of critical importance to the user:
We provide a suitable intracellular targeting prediction tool for your microalgal studies to efficiently identify microalgal proteins localized in chloroplasts and mitochondria. If you are interested in our solutions for the subcellular localization of microalgal proteins, please contact us directly.
Reference