Ultra-low temperature detoxification is a new and efficient detoxification technology based on ultra-low temperature preservation. Compared with traditional detoxification methods, ultra-low temperature detoxification has the advantages of high detoxification rate, independent of stem tip size and ultra-low temperature treatment method, and short production cycle of detoxified seedlings. More importantly, stem tip ultra-low temperature treatment can simultaneously achieve the dual objectives of detoxification and long-term conservation of plant germplasm resources.
After ultra-low temperature treatment of the stem tip, the vast majority of cells are frozen to death, with only the apical layers of the meristem and local cells of the first and second leaf primordia being viable. Most of the cells that are viable are non-toxic, and the resulting complete plants are likely to be non-toxic.
The plant tissues were first trimmed to remove unwanted parts, leaving stem segments and axillary buds, and then rinsed with tap water. Disinfection was performed on an ultra-clean bench by soaking in 70% alcohol for 10~30s and rinsing with sterile water 2~3 times. Then according to the oldness and tenderness of the material and the firmness of the branches, soak the stem in 2% sodium hypochlorite for 10~15min or in 0.1% mercuric chloride for 5~10min, respectively. Disinfection was carried out by constant stirring to bring the plant material into full contact with the disinfectant. Finally, rinse with sterile water 3~5 times and insert into rooting medium to establish the sterile seedling system (Fig.1).
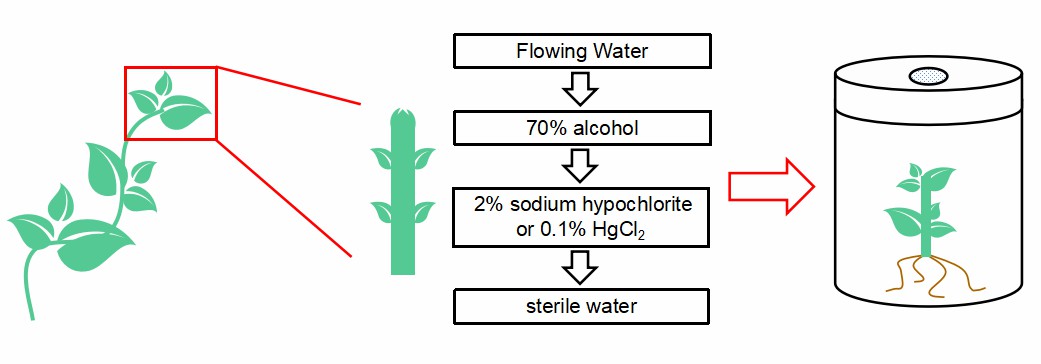 Fig 1. The procedures of establishment of sterile seedling system
Fig 1. The procedures of establishment of sterile seedling system
The material is precultured to make the cells moderately dehydrated and reduce the free water content in the cells, which can improve the freezing resistance of the cells and the survival rate. The stem tip can be cut in size of 2~3 mm and then precultured in medium with high sucrose concentration of 0.3 mol/L for one day with 16 h of light and 2000 lx light intensity (Fig.2).
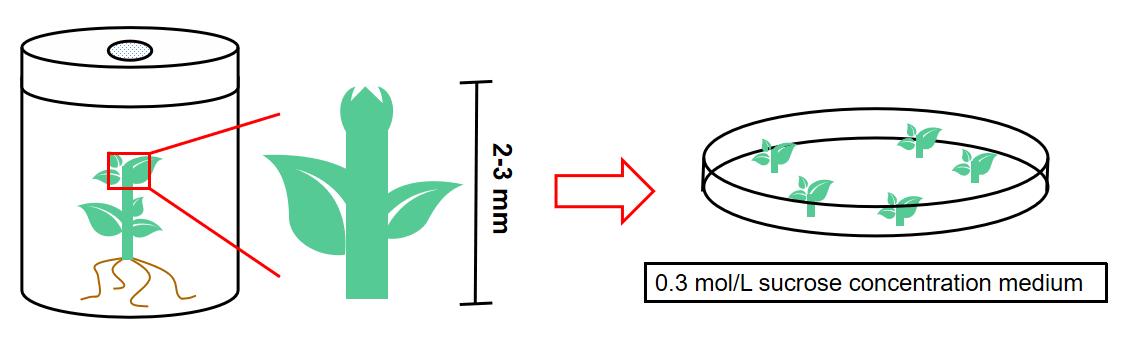 Fig 2. The procedures of pretreatment of stem tips
Fig 2. The procedures of pretreatment of stem tips
15 μL of PVS (plant vitrification solution) was added to a 0.03 mm thick 1.0 cm × 4.0 cm aluminum foil, and then the pre-cultured stem tips were loaded into the PVS droplets and treated at room temperature for 20 min. The aluminum foil wrapped with stem tips was dipped in liquid nitrogen, and then the aluminum foil strips were placed in a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube, which was then placed in liquid nitrogen for 1 h at ultra-low temperature.
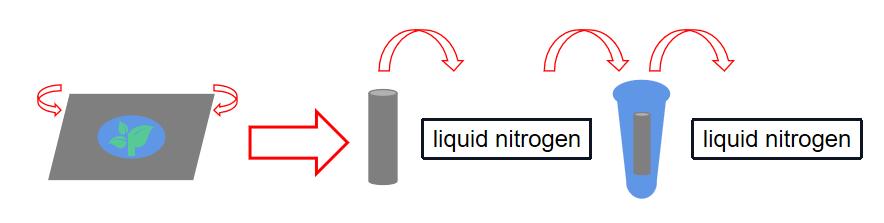 Fig 3. The procedures of liquid nitrogen ultra-low temperature treatment
Fig 3. The procedures of liquid nitrogen ultra-low temperature treatment
The materials frozen in liquid nitrogen for 1 h were then placed in a water bath at 25~40°C for 1~3 min to thaw. Remove the aluminum foil strip wrapped around the stem tip from the centrifuge tube in a sterile ultra-clean bench, and then quickly place it into liquid MS medium with 1.2 mol/L sucrose concentration for 2~3 washes for 10 min each time. Aspirate the washing medium left on the surface of the material with sterile paper, and inoculate it into solid recovery medium (MS + 0.1 mg/L NAA + 0.5 mg/L 6-BA + 1.0 mg/L GA3). The culture conditions were selected to be in darkness for 7 d, then in low light at 1000 lx for 7 d, and finally in normal light at 2000 lx. Complete plants were obtained in 1 month.
 Fig 4. The procedures of stem tip recovery
Fig 4. The procedures of stem tip recovery