Comparative transcriptomics is a comparison by measuring the transcriptome, focusing on changes at the gene sequence level. It is usually studied mostly in terms of evolutionary so-called phylogenetic relationships, divergence times, etc. Comparative transcriptome studies between different strains can be used to study rapidly evolving genes and adaptation-related genes. Comparative transcriptomic analysis can be applied in cases where genomes are too large, and species DNA is challenging to extract. Lifeasible can provide comparative transcriptomic analysis of fungi to help customers gain insight into the expression patterns of conserved fungal genes.
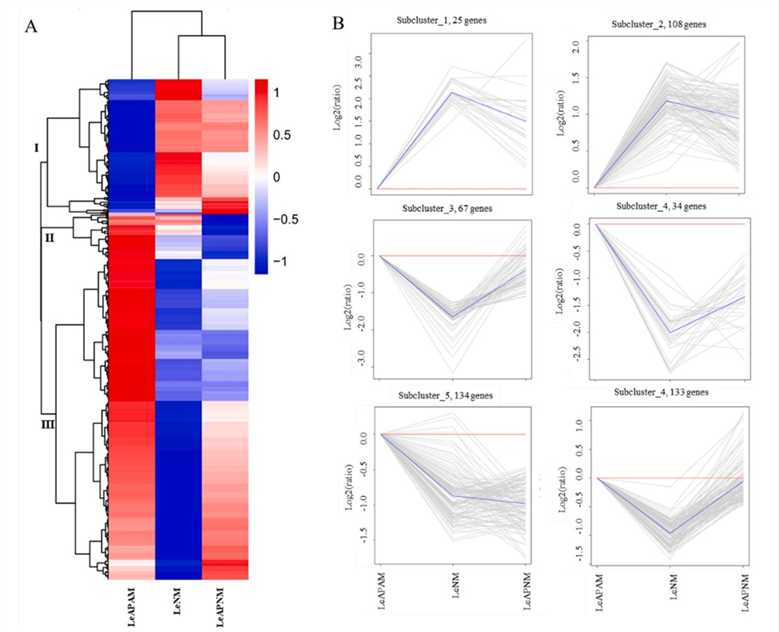 Figure 1. Cluster analysis of differential gene expression patterns among different samples. (Yan D, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Cluster analysis of differential gene expression patterns among different samples. (Yan D, et al., 2021)
- Orthologous gene clustering analysis.
Orthologous genes refer to genes from different species that have evolved from the species and retain the same function as the original gene. We use the orthotics method for the analysis of fungal orthologous genes. An orthogroup contains genes of common ancestry for all species and contains both orthologous genes and paralogous genes. Ortholog groups do the inference, sequence similarity scores are calculated between sequences of multiple species using BLAST, and then the MCL clustering algorithm is used to identify highly similar sequence groups in this dataset.
- Identification of single-copy genes.
Among the orthologous genes, single-copy genes are of great importance. Single-copy genes can serve as a gold standard for understanding the phylogenetic position and divergence time of species because they are mainly neutral mutations. Based on the similarity of fungal sequences, we use blast to obtain orthologous genes and then cluster each homologous direct lineage gene by a clustering algorithm to distinguish multi-copy genes from single-copy genes.
- Phylogenetic construction.
We perform fungal phylogenetic construction by obtaining single-copy gene sequences, extracting conserved loci, selecting models, and finally using most models for phylogenetic relationships.
- Divergence time estimation.
Single-copy genes change at a relatively constant rate of evolution and are a molecular marker similar to a timer. We can derive the differentiation relationships among fungi by model extrapolation. We usually know the phylogenetic relationships of fungal species by constructing phylogenetic trees, marking the node times, and adjusting the divergence time model according to the species relationships.
Lifeasible can provide a comparative transcriptomic analysis of fungi, revealing the extent of genetic relatedness between fungal species. As your trusted partner, we can meet your fungal phylogenetic analysis needs and provide you with efficient, high-quality services. If you want to know the details, please
contact us.
Reference
- Yan D, et al. (2021). "Comparative transcriptome analysis of abnormal cap and healthy fruiting bodies of the edible mushroom Lentinula edodes." Fungal Genet Biol. 156: 103614.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Figure 1. Cluster analysis of differential gene expression patterns among different samples. (Yan D, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Cluster analysis of differential gene expression patterns among different samples. (Yan D, et al., 2021)