Endophytic fungi live inside various tissues and organs of healthy plants, and infected plants do not show obvious external disease. Endophytic fungi can act as carriers of exogenous genes that can promote plant growth, resistance to adversity and disease, and increase the allelopathy and resistance of host plants to pathogenic bacteria. The endophytic nature of endophytic fungi can be demonstrated by histological methods, isolation from plant tissues, or direct amplification of fungal DNA from within plant tissues. The isolation and identification of endophytic fungi are the basis of strain research and application.
Lifeasible provides a one-stop service for the isolation, identification, and active substance testing of plant endophytic fungi and is committed to providing customers with comprehensive and accurate information about plant endophytic fungi.
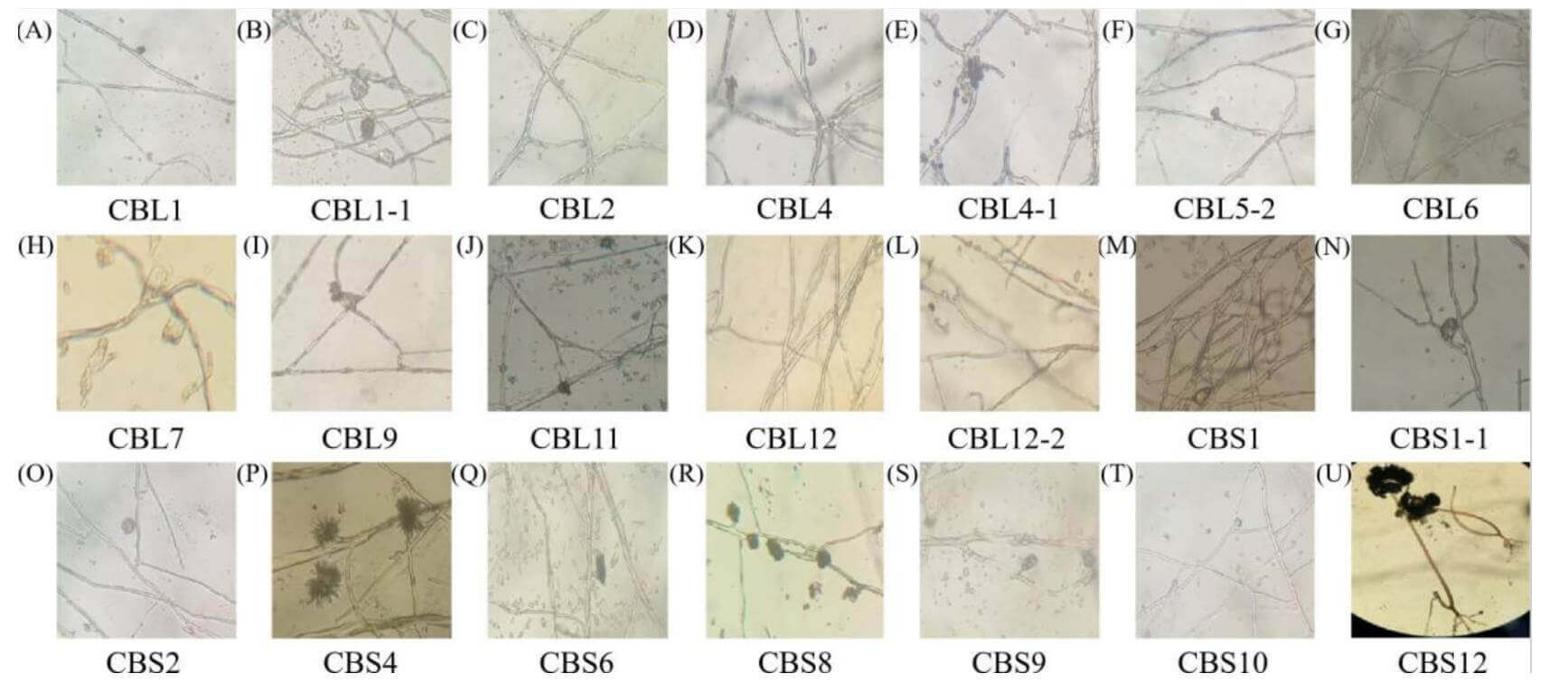 Figure 1. The shape characteristics of the hypha. (Tang Z, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. The shape characteristics of the hypha. (Tang Z, et al., 2020)
- Isolation of plant endophytic fungi. Plant endophytic fungi exist as mycelium in plant tissues and do not produce spores. The growth of endophytic fungi and the number of secondary metabolites species are influenced by the environment. Therefore, conditions such as sterilization time, medium composition, incubation temperature, and aeration conditions during endophytic fungal isolation and culture need to be considered. We used the traditional method of surface sterilization of plant tissue blocks to remove chlamydospores and conidia from the surface of plant tissue and subsequently inoculated the tissue blocks onto the isolation medium. We usually add selective growth inhibitors to the culture medium to inhibit the growth of some bacteria.
- Identification of plant endophytic fungi. We offer a combination of morphological and molecular biological methods for identifying endophytic fungi. We identify and classify fungi by observing and comparing the morphological characteristics of fungal hyphae, spore-producing structures, and spores with the help of optical instruments, electron microscopes, etc. Molecular biology techniques mainly use DNA sequence analysis to study the phylogenetic relationships between different taxa and species levels of endophytic fungi and non-spore-producing endophytic fungal strains. We use the comparative analysis of ITS region sequences of rDNA to respond to the diversity of plant endophytic fungi.
- Detection of secondary metabolites and biological activity of endophytic fungi. The amount of bioactive substances in the fermentation products is generally low. Therefore, the fermentation scale of the strain should be ensured to obtain sufficient active substances before the active substances are isolated. Endophytic fungi can occasionally produce the same or similar physiologically active components as their hosts. We can provide services such as anti-tumor active substance testing, antibiotic-like active substance testing, and hypoglycemic active substance testing. We can provide the following services for endophytic fungal activity testing, including but not limited to the services in the table below.
| Antioxidant activity assay |
DPPH free radical scavenging method |
| ABTS+ free radical scavenging method |
| Anti-tumor activity assay |
Cancer cell proliferation assay |
| Immunomodulatory activity assay |
In vitro lymphocyte proliferation assay |
| Antidiabetic activity assay |
α-glucosidase inhibition assay |
| α-amylase inhibition assay |
Lifeasible can help customers analyze the diversity and biological activity of plant endophytic fungi to support their further research. As your trusted partner, we can meet your needs for endophytic fungal identification and isolation services and provide you with efficient and high-quality services. If you want to know the details, please contact us.
Reference
- Tang Z, et al. Isolation and identification of flavonoid-producing endophytic fungi from medicinal plant Conyza blinii H.Lév that exhibit higher antioxidant and antibacterial activities. PeerJ. 2020 Apr 15; 8: e8978.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Figure 1. The shape characteristics of the hypha. (Tang Z, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. The shape characteristics of the hypha. (Tang Z, et al., 2020)