Isolation and Identification of Mycorrhizal Fungi
Mycorrhiza is a symbiosis formed by the mycelium of some fungi in the soil and the roots of higher plants. The symbiotic fungi obtain carbon and energy materials from the plant necessary for growth and development. In contrast, the symbiotic fungi expand the absorption range of the root system and enhance the plant's uptake of water and nutrients. Mycorrhizal fungi are widespread in terrestrial ecosystems, and most existing vascular and non-vascular plants can form mycorrhizae with them. Based on the species of fungi and plants involved in the symbiosis and the characteristics of the symbiotic system formed, these mycorrhizae are mainly classified into four categories, namely ectomycorrhizas (ECM), arbuscular mycorrhizae(AM), orchidaceous mycorrhizae(ORM), and ericaceous mycorrhizae(ERM). The analysis of plant mycorrhizal fungal diversity and variability is important for the wide application of mycorrhizal fungi.
Lifeasible provides services for the isolation and identification of plant mycorrhizal fungi and is committed to analyzing the diversity and variability of mycorrhizal fungi in different plants.
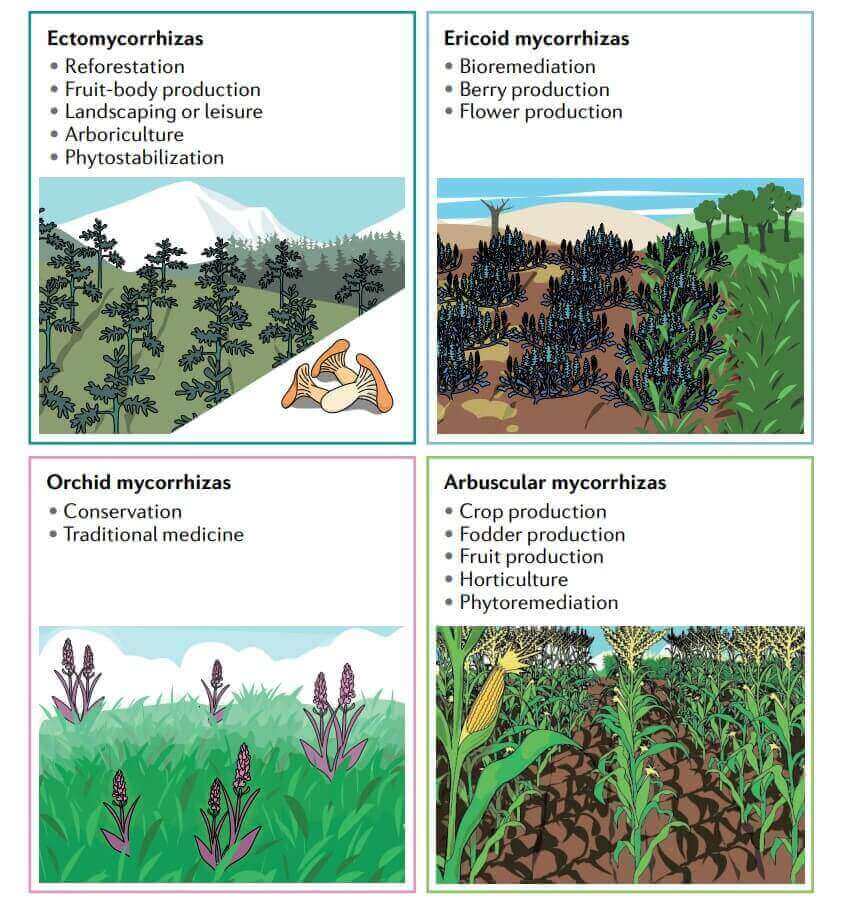 Figure 1. Translational applications of mycorrhizal fungi. (Genre A, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. Translational applications of mycorrhizal fungi. (Genre A, et al., 2020)
- Identification of ectomycorrhizal fungal diversity. Ectomycorrhizas fungi are characterized by the formation of mycorrhizal sets on the root tip surface and epicormic hyphae outside the root. Ectomycorrhizas fungi play an important role in maintaining ecological balance and conserving biodiversity by producing secondary metabolites that promote plant growth and improve plant resistance. We use RFLP, and RAPD techniques to identify ectomycorrhizal fungal in plants using the rDNA ITS region.
- Identification of arbuscular mycorrhizae fungal diversity. Arbuscular mycorrhizae fungi are the most widely distributed, and their interaction with plants improves their utilization of soil resources and enhances their tolerance to various environmental stresses and biological disturbances. We usually use the wet sieve method to isolate the arbuscular mycorrhizae fungal, followed by sequencing and homologous sequence alignment of the target DNA fragments of the mycorrhizal fungi of the bush, and finally, construct a phylogenetic tree.
- Identification of orchidaceous mycorrhizae fungal diversity. Almost all orchids are symbiotic with fungi. Some of the orchidaceous mycorrhizae are saprophytic fungi that can survive and reproduce independently in the soil without relying on the symbiotic relationship between plant roots and mycorrhizae. Most of the fungi that form orchidaceous mycorrhizae fungal belong to the Rhizoctonia, mainly the Sebacinales, Ceratobasidiaceae, and Tulasnellaceae of the Agaricomycetes. We use the special medium for orchidaceous mycorrhizae fungal isolation to isolate mycorrhizal fungi. Then, we classify the resulting fungi basically according to morphological characteristics such as colony morphology, mycelial branching, and spore morphology. Finally, we performed PCR amplification of the ITS region on the rDNA and then compared the sequencing results for analysis.
- Identification of ericaceous mycorrhizae fungal diversity. Plants of the family Ericaceae can form ericaceous mycorrhizae symbioses with soil fungi. Ericaceous mycorrhizae can enhance the host plant's ability to absorb nutrients and resist environmental stresses. We first isolated the samples for mycorrhizal fungi and then cultured the isolates, and then used morphological methods combined with rDNA ITS sequence analysis to identify the isolated ericaceous mycorrhizae.
Deliverables
- NMDS plots of the fungal communities.
- The richness of mycorrhizal fungi operational taxonomic units.
- Rank–frequency plot of mycorrhizal fungal.
- A Bayesian phylogenetic reconstruction figure based on ITS rDNA sequences.
Lifeasible can help customers analyze the diversity and biological activity of mycorrhizal fungi to support their further research. As your trusted partner, we can meet your needs for mycorrhizal fungi identification and isolation services and provide you with efficient and high-quality services. If you want to know the details, please contact us.
References
- Genre A, et al. Unique and common traits in mycorrhizal symbioses. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020 Nov; 18(11): 649-660.
- Senés-Guerrero C, Schüßler A. DNA-Based Characterization and Identification of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Species. Methods Mol Biol. 2016; 1399: 101-23.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Figure 1. Translational applications of mycorrhizal fungi. (Genre A, et al., 2020)
Figure 1. Translational applications of mycorrhizal fungi. (Genre A, et al., 2020)