Food security is one of the most important issues facing the world today. Any strategy to address this issue must include improving crop yields and quality. In recent years, data from many genome-wide high-throughput sequencing and microarray analysis projects have provided a rich resource of candidate genes, among which microRNAs (miRNAs) have become increasingly attractive. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs (20-24 nt) that mediate gene expression through complementary binding to their target transcripts for mRNA cleavage or protein translational repression. miRNAs play essential roles in various aspects of plant life, including plant development, plant architecture, and biotic and abiotic stress responses. An increasing number of yield-related agronomic traits have also been found to be associated with miRNAs, making miRNAs promising targets for crop improvement. miRNAs and their targets have great potential for crop improvement, either by enhancing plant adaptation to external environmental stresses (plant tolerance to abiotic stress and plant protection against biotic stresses) or by increasing the intrinsic yield potential of plants (manipulation of plant development and modification of plant structure).
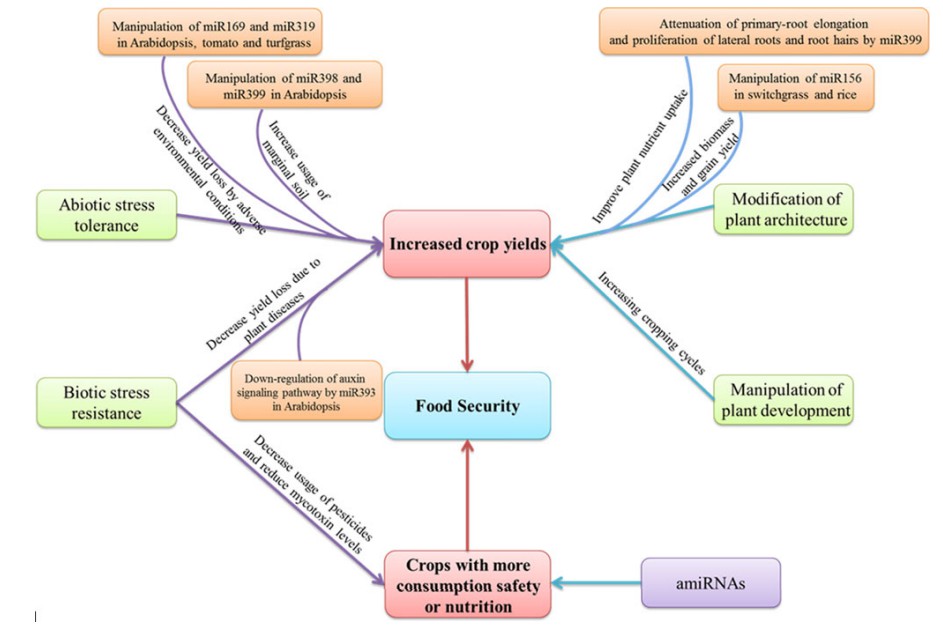 Fig. 1. Potential applications of miRNA-based gene regulation for crop improvement. (Zhou et al., 2013)
Fig. 1. Potential applications of miRNA-based gene regulation for crop improvement. (Zhou et al., 2013)
Lifeasible has been at the forefront of plant biotechnology development for many years, providing microRNA-based gene modification solutions. It directly contributes to agricultural productivity by overexpressing or knocking out specific miRNAs or their targets to develop high-quality crop varieties with enhanced biotic and abiotic stress tolerance and increased biomass yield. In addition, this technology can increase marginal soil use and reduce pesticide use.
We offer the following different strategies to develop mirRNA-based technologies to genetically engineer crops to produce new varieties with desirable agronomic traits. Considering the advantages and disadvantages of each approach, we design customized strategies for each specific study and miRNA of interest.
| Biotechnology Tools | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Transgenesis, cisgenesis and intragenesis | Efficient tissue‐specific or induced expression of MIR genes and accumulation of miRNA | Transgenic approach. As consequence of the wide-acting network of the miRNAs, its constitutive overexpression often results in pleiotropic effects |
| Artificial MIR genes | Modulation of target mRNA is usually more specific compared to RNAi strategies using dsRNA or siRNA | Transgenic approach, backbone selection, potential off‐targets, and pleiotropic effects |
| Viral vector‐mediated miRNA delivery | Transgene‐free approach and suitable for proofs of concept | Restricted host plant range, adult plant resistance, very limited to nucleic acids length, and viral infection usually restricted to young tissue or meristems |
| Endogenous (eTM), circular (circRNAs), and artificial short tandem target mimicry (STTM) | Efficient sequestration of miRNAs, eTMs show themselves better than STTM, high stability of circRNAs and expression driven by specific promoters allows | Transgenic approach and backbone selection |
Lifeasible is committed to developing various tools for the functional analysis of miRNAs. We use these biotechnologies and miRNA-based gene modification techniques to unravel the complex molecular mechanisms of agronomic trait regulation and to provide potential breeding materials for crop improvement and breeding. Together with the CRISPR/Cas gene editing system and many other breeding techniques that can produce transgene-free plants, we aim to facilitate precision crop breeding. Contact us today to learn more about our solutions.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox