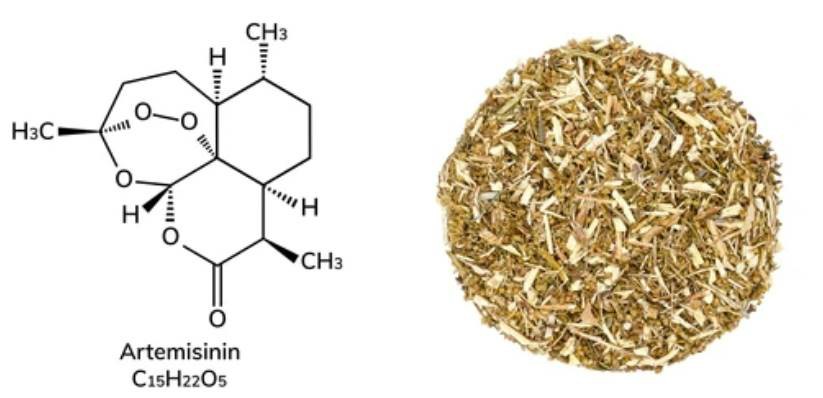
Malaria is one of the most challenging diseases. Artemisinin, extracted and isolated from the plant Artemisia annua, is currently the drug of choice for treating malaria. Artemisinin is produced from Artemisia annua, a plant that grows only in summer and has a short growing season. The low levels of artemisinin in wild Artemisia plants and the complexity of their structure make chemical synthesis both rationally and economically unfeasible, resulting in short supply of artemisinin and costly treatment.
Lifeasible is dedicated to providing effective solutions to bottlenecks in agricultural research. Using new synthetic biology techniques, we can simply solve the challenges of artemisinin production. We continue to study the artemisinin biosynthesis pathway in depth, using breeding methods, cell tissue culture, genetic transformation of Artemisia annua, and transferring heterologous or endogenous genes related to artemisinin biosynthesis into Artemisia annua for enhancing artemisinin content. We have provided effective technical support and research strategies in the large-scale production of artemisinin.
Our constructed transgenic moss can be grown in the liquid and solid mediums under LED light. A large amount of artemisinin can be produced within a short period of culture. In addition, the modified mosses do not require precursor engineering or subsequent chemical synthesis, making artemisinin production from transgenic mosses simpler and more efficient.
We transferred the genes related to artemisinic acid synthesis from Artemisia annua to the genome of tobacco chloroplasts to give them the ability to synthesize "artemisinic acid", which can be extracted in greater quantities due to the large leaf size and the presence of chloroplasts on the leaf surface. This method helps to increase artemisinin production and provides a good basis for low-cost drug production from large leafy crops.
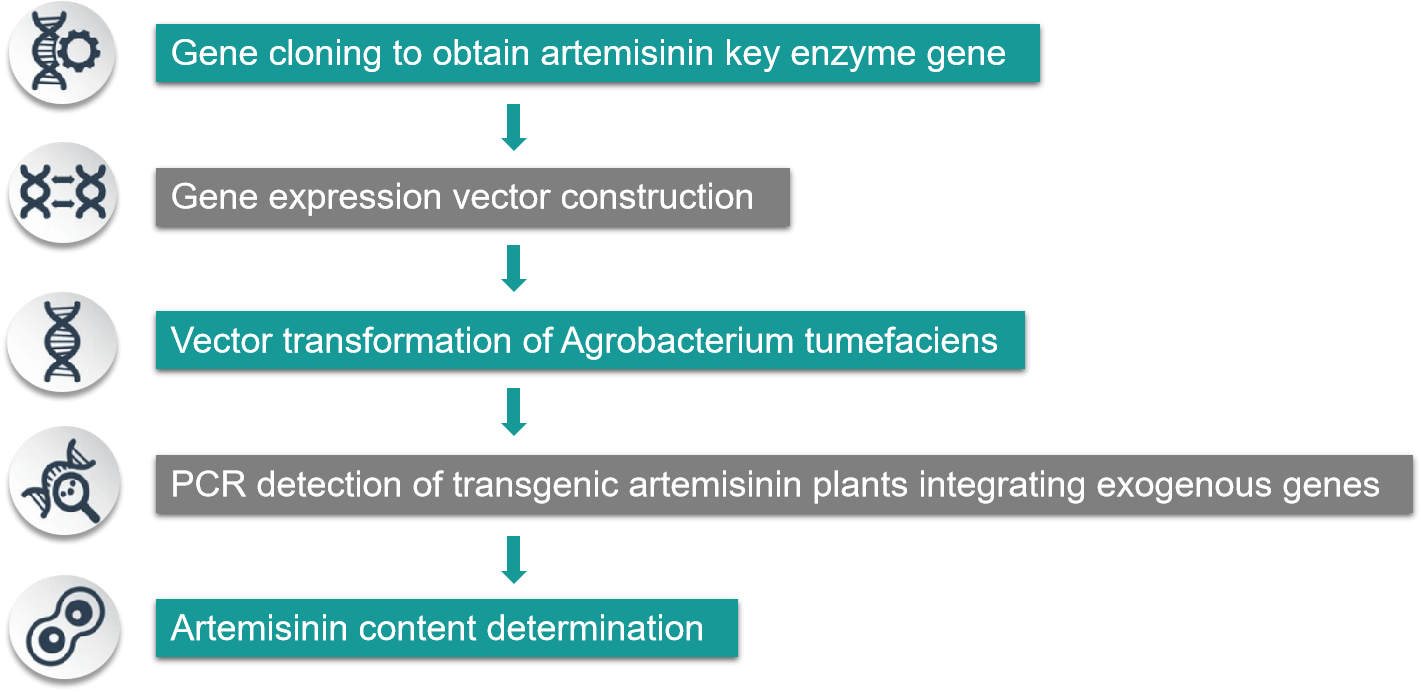
We used Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid-derived binary vector system to construct antisense SS expression vectors and subsequently transformed Artemisia ex vivo and regenerated transgenic plants to reduce steroid synthesis and direct carbon flow to artemisinin synthesis by blocking endogenous SS gene expression in Artemisia ultimately increasing artemisinin content.
Lifeasible uses synthetic biology technology to provide a stable example of building a plant platform that can be extended to the industrial production of other complex, high-value plant compounds while we continuously optimize the reaction process to minimize any unnecessary products and ensure that the metabolic process is as efficient as possible. If you are interested in us, please feel free to contact us.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox