Sweet proteins are a class of plant-derived, naturally occurring proteins that are mostly sweet, sometimes thousands of times sweeter than sugar, and have no appreciable caloric value. They deliver sweetness without affecting blood sugar levels by stimulating sweet taste receptors on the tongue, making them a potential replacement for traditional sugar and artificial sweeteners. So far, eight sweet proteins have been identified, namely miraculin, monellin, thaumatin, mabinlin, pentadin, curculin, neoculin, and brazzein. Some of these proteins have been extensively studied for their potential use as sugar substitutes in food and beverages and their therapeutic properties.
Sweet protein comprises about 50-200 amino acids and has a molecular weight of about 6,500 to 30,000 Da. Although these proteins display the same property (inducing sweet taste), they share no sequence identity and structural similarity. The spatial structures of many sweet proteins have been resolved by X-ray diffraction or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), showing diverse spatially folded structures.
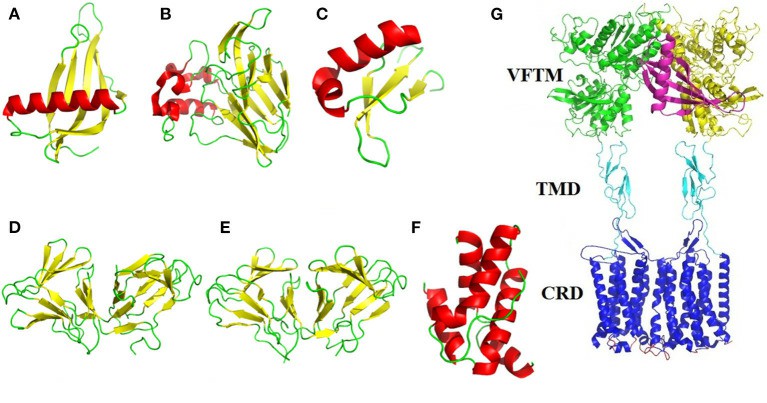 Figure 1. The structure of the sweet protein. (Zhao X et al. 2021)
Figure 1. The structure of the sweet protein. (Zhao X et al. 2021)
From A-F are thaumatin, brazzein, curculin, neoculin, mabinlin. G is a schematic diagram of the interaction between monellin (purple) and sweet receptor T1R2/T1R3.
As a world-leading biotechnology company, Lifeasible focuses on sweet proteins for many years and has a deep understanding and unique insights into sweet proteins. With our comprehensive technology platform and professional knowledge, our team of scientists provides a wealth of CRO services for researchers interested in sweet protein, mainly involving the development of sweet protein transgenic plants and the development of sweet protein production strains.

The development of sweet protein transgenic plants is of great significance to experts in the fields of plants, agriculture, food, and proteins. The development of sweet protein transgenic plants can not only breed high-quality new varieties of crops, fruits, vegetables, etc. with high sweetness and good quality but also provide a new way for mass production of sweet protein. We provide transgenic plant development services for 8 sweet proteins, including gene cloning and transformation, molecular characterization, protein expression analysis, sensory evaluation, etc.

The development of sweet protein-producing strains is crucial to expand the practical application of sweet proteins. The 8 sweet proteins are all extracted from natural plant species, and most of these plants are difficult to grow on a large scale. This undoubtedly limits the application of sweet protein in the food and medical industries. We provide sweet protein production strain development services for 8 kinds of sweet proteins, including target strain selection, gene expression optimization, expression vector construction, culture condition optimization, recombinant sweet protein analysis, etc.
Lifeasible is dedicated to accelerating sweet protein research for customers around the world. With more than twenty years of experience, advanced technology, and complete equipment, we provide customized solutions for our customers. If you have any questions or inquiries, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox