Fungi, an essential class of eukaryotes, have developed mechanisms to sense various light signals during evolution. At the same time, many physiological responses and growth and development processes of fungi are regulated by light. Mycelial growth, pigment formation, induction of asexual or sexual reproduction, and regulation of fungal cycle rhythm are all controlled by light. Fungal photoreceptors are mainly classified into blue, red, and green photoreceptors. Lifeasible can find new photoreceptor genes through transcriptomics, screen for photoreceptor-regulated target genes, and analyze the effect of photoreceptors on fungal pathogenicity.
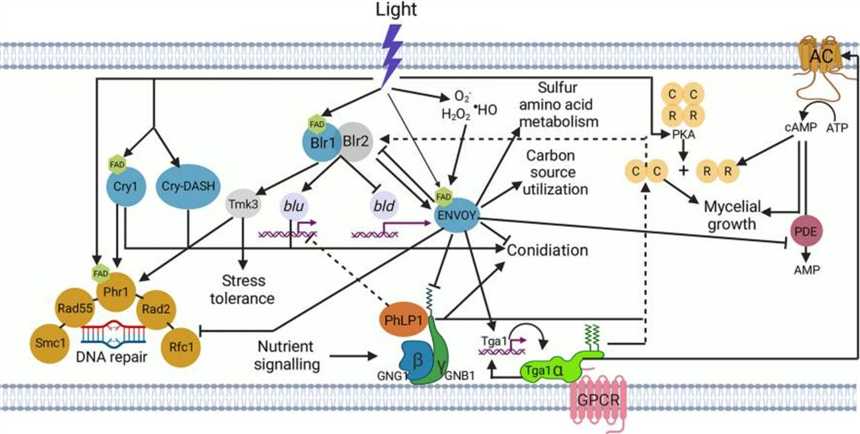 Figure 1. Trichoderma atroviride light signal perception and transduction. (Pola-Sánchez E, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Trichoderma atroviride light signal perception and transduction. (Pola-Sánchez E, et al., 2021)
- Search for new photoreceptor genes.
In the study of fungal light response, how fungi sense light is the focus of research. Current reports on photoreceptors in large fungal species are limited to WC-1 and WC-2 homologous proteins. With the publication of many large fungal genomic data, we can search for new fungal photoreceptor genes through transcriptomic analysis.
- Screening for photoreceptor-regulated target genes.
The acceptance and conduction of light signals by fungi depend on photoreceptors. Studies have shown that photoreceptor transduction in fungi has different pathways, and it is essential to study the mechanism of photoreceptor action. We can explore the target genes and signaling pathways regulated by photoreceptors in different macro fungi through transcriptomic analysis, the interaction mechanisms between various light signaling pathways, and other functions of photoreceptors.
- Analysis of the regulation of fungal pathogenicity by photoreceptors.
Fungi are an essential cause of plant diseases, and the occurrence or prevalence of various diseases in nature often depends on the interaction between the pathogen, the host, and the environment. Light is one of the important environmental factors that can affect fungal pathogenicity in several ways, yet the molecular mechanism of how light regulates fungal pathogenicity is unclear. Through transcriptomic studies, we can resolve the important determinants of pathogenic fungal pathogenicity involved in the downstream regulation of photoreceptor signaling pathways.
- Analysis of changes in the expression profile of mutant strains in response to light.
We can use the transcriptomic results to analyze the transcriptional changes in the expression profile of the mutant strain in the presence of light regulation and to identify the photoreceptors of the strain.
Lifeasible can analyze the mechanism of action of different light signaling pathways in fungi through transcriptome, the possible interaction mechanism between various light signaling pathways, and the mechanism of downstream regulation of light-responsive gene expression by various light signals. As your trusted partner, we can meet your fungal phylogenetic analysis needs and provide you with efficient, high-quality services. If you want to know the details, please contact us.
Reference
- Pola-Sánchez E, et al. (2021). "A Global Analysis of Photoreceptor-Mediated Transcriptional Changes Reveals the Intricate Relationship Between Central Metabolism and DNA Repair in the Filamentous Fungus Trichoderma atroviride." Front Microbiol. 12: 724676.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Figure 1. Trichoderma atroviride light signal perception and transduction. (Pola-Sánchez E, et al., 2021)
Figure 1. Trichoderma atroviride light signal perception and transduction. (Pola-Sánchez E, et al., 2021)