Analysis of Nematicide Inhibition of Nematode Neurobehavior
The metabolic activities, digestion, reproduction, endocrine, sensory, and muscle movements of plant nematodes are all governed by neurons, and some genes involved in neurotransmission were first identified in Caenorhabditis elegans. In addition, nematodes have neurotransmitters similar to those found in mammals, such as acetylcholine, dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and glutamate. Carbamates, organophosphate nematicides, and avermectins act on acetylcholinesterase and glutamate-gated chloride channels, respectively.
Lifeasible analyzes nematicide inhibition of nematode neurobehavior to help our customers worldwide in plant science research. Our platform is equipped with cutting-edge facilities and professional experts to support research. Here, we provide various services according to customers' demands.
Analysis of Acetyl Cholinesterase Inhibitors
- Acetylcholine (ACh) is the main neurotransmitter involved in the motor function of most organisms and nematodes as well. Plant nematodes regulate normal muscle movement by hydrolyzing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the body via acetyl cholinesterase (AChE) to terminate the transmission of nerve impulses.
- By forming covalent bonds with serine residues in the active site of nematode acetylcholinesterase, nematicides prevent acetylcholinesterase from decomposing acetylcholine, which causes the nematode's nerves from being excited for a long time, resulting in muscle paralysis and abnormal movement of the nematode, which then makes it difficult to feed and die.
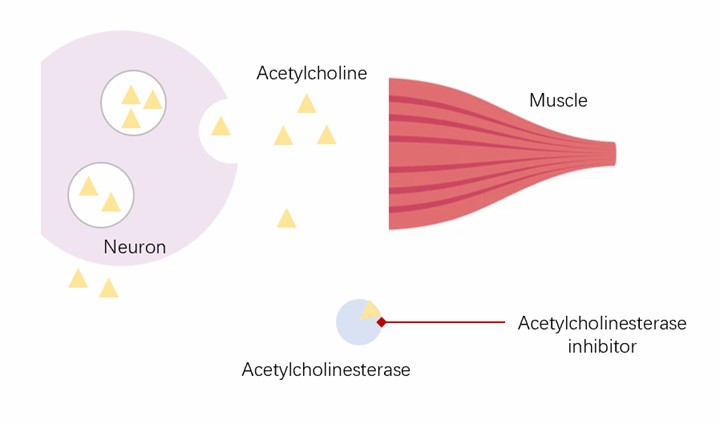 Fig.1 Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors prevent acetylcholinesterase from breaking down acetylcholine.
Fig.1 Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors prevent acetylcholinesterase from breaking down acetylcholine.
- Lifeasible provides analysis of acetyl cholinesterase inhibitors, including carbamates, organophosphates, and others. We provide toxicological index measurements, including lethality, reproductive indexes such as brood size, generation time, number of eggs conceived, developmental indexes such as body length, behavioral indicators such as locomotor behavior, learning behavior, foraging behavior, feeding behavior, etc.
- In addition, we help our customers to explore nematode resistance analysis, such as indoor bioassays of resistant and sensitive populations, AChE activity assays, insecticide inhibition tests against AChE, and others.
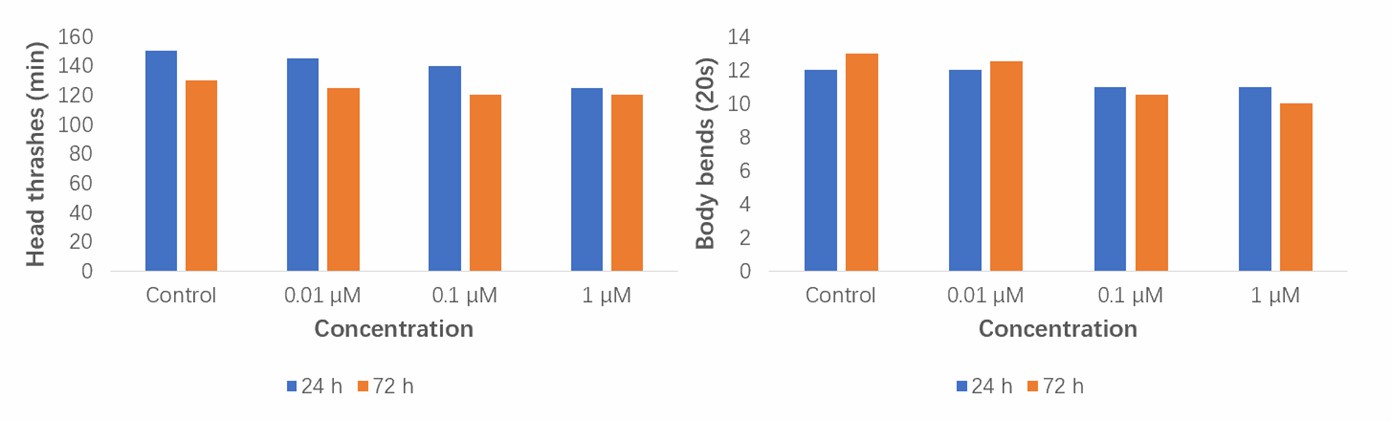 Fig.2 The neurobehavior changes in nematodes treated with 0.01, 0.1, and 1 µM nematicides for 24 and 72 h, respectively.
Fig.2 The neurobehavior changes in nematodes treated with 0.01, 0.1, and 1 µM nematicides for 24 and 72 h, respectively.
Analysis of Glutamate-Gated Chloride Channel Variant Modulators
- Glutamate is an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate and invertebrate nervous systems, acting on glutamate receptors on cell membranes. In invertebrates such as insects and nematodes, there is an inhibitory glutamate receptor to which glutamate can bind to open chloride channels, hence the name glutamate-gated chloride channels.
- Studies in nematodes have revealed that glutamate-gated chloride channels regulate nematode locomotion, feeding, signal perception, and reproduction, in addition to neuroexcitation.
- We help our clients analyze glutamate-gated chloride channel variant modulators, mainly avermectin (AVM). We offer studies on the toxic effects of low doses of AVM on nematodes, including the determination of female egg production, developmental progress, nematode jitter frequency, and offspring sex ratio. In addition, we also help to analyze the screening service of nematode differentially expressed genes under AVM treatment.
Lifeasible has a long-term commitment to the development and application of plant nematodes. We are pleased to use our extensive experience and advanced platform to provide satisfactory service and qualified products to meet the needs of our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors prevent acetylcholinesterase from breaking down acetylcholine.
Fig.1 Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors prevent acetylcholinesterase from breaking down acetylcholine. Fig.2 The neurobehavior changes in nematodes treated with 0.01, 0.1, and 1 µM nematicides for 24 and 72 h, respectively.
Fig.2 The neurobehavior changes in nematodes treated with 0.01, 0.1, and 1 µM nematicides for 24 and 72 h, respectively.