Plant nematodes are easy to spread and highly pathogenic, and their populations are growing rapidly, making control difficult. Among the many control measures, chemical control has the advantages of being rapid, efficient, and economical and remains the main means of nematode control. While nematodes have digestive, reproductive, nervous, and excretory systems, they do not have discrete circulatory or respiratory systems. Internal and external gas exchange occurs by diffusion through the body wall, and metabolic studies have shown that both free-living and plant-parasitic nematodes metabolize energy through glycolysis and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and have the glyoxylate cycle in many nematode populations.
Powered by our professional scientists and their years of field experience, Lifeasible can help our clients analyze for nematicide inhibition of nematode respiratory behavior. With our cutting-edge platforms, we can provide analysis of mitochondrial complex II electron transfer inhibitors, succinate-coenzyme Q reductase inhibitors, and so on.
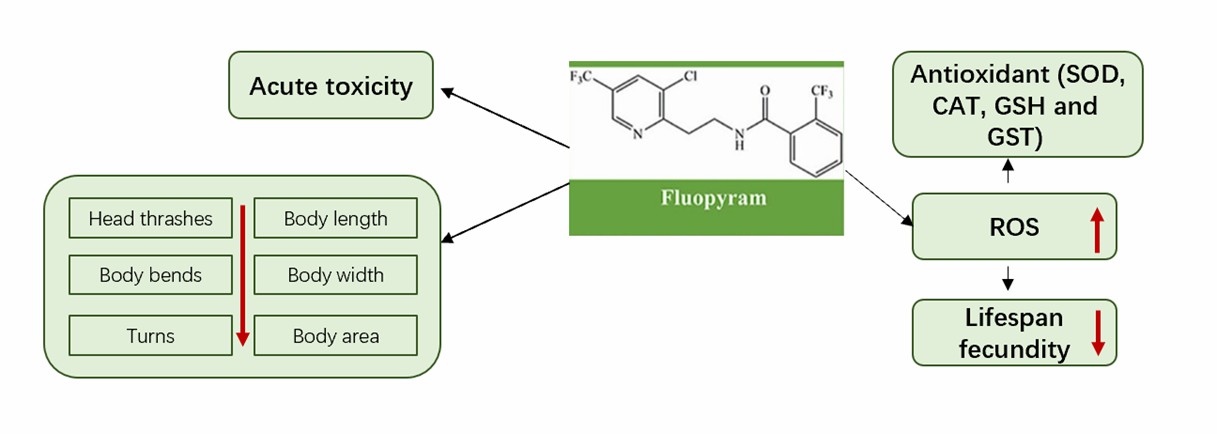 Fig.1 Toxicity induced by fluopyram in nematodes.
Fig.1 Toxicity induced by fluopyram in nematodes.
Lifeasible offers the analysis services involved in nematicide inhibition of nematode respiratory behavior for your research convenience. Our goal is to help our clients achieve meaningful results through powerful and consistent approaches. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Mechanisms Regulating Plant Chloroplast Biogenesis
April 15, 2025