Nematodes are ubiquitous organisms that significantly impact ecosystems, economies, agriculture, and human health. Nematodes and their bacterial associates exist in marine, freshwater, soil, and plant or animal host environments. Nematode-bacterium associations can be beneficial (mutualistic) or harmful (pathogenic/parasitic) and can range from facultative, temporary interactions to stably maintained long-term symbioses. Bacteria can be a potential food source for nematodes. As well as being a food source, bacteria can be pathogens of nematodes.
Lifeasible provides an analysis of nematode interactions with bacteria with decades of experience. Our experts will answer your questions comprehensively and carefully and help you solve the problems in your studies. We guarantee satisfied and reliable results for our customers all over the world.
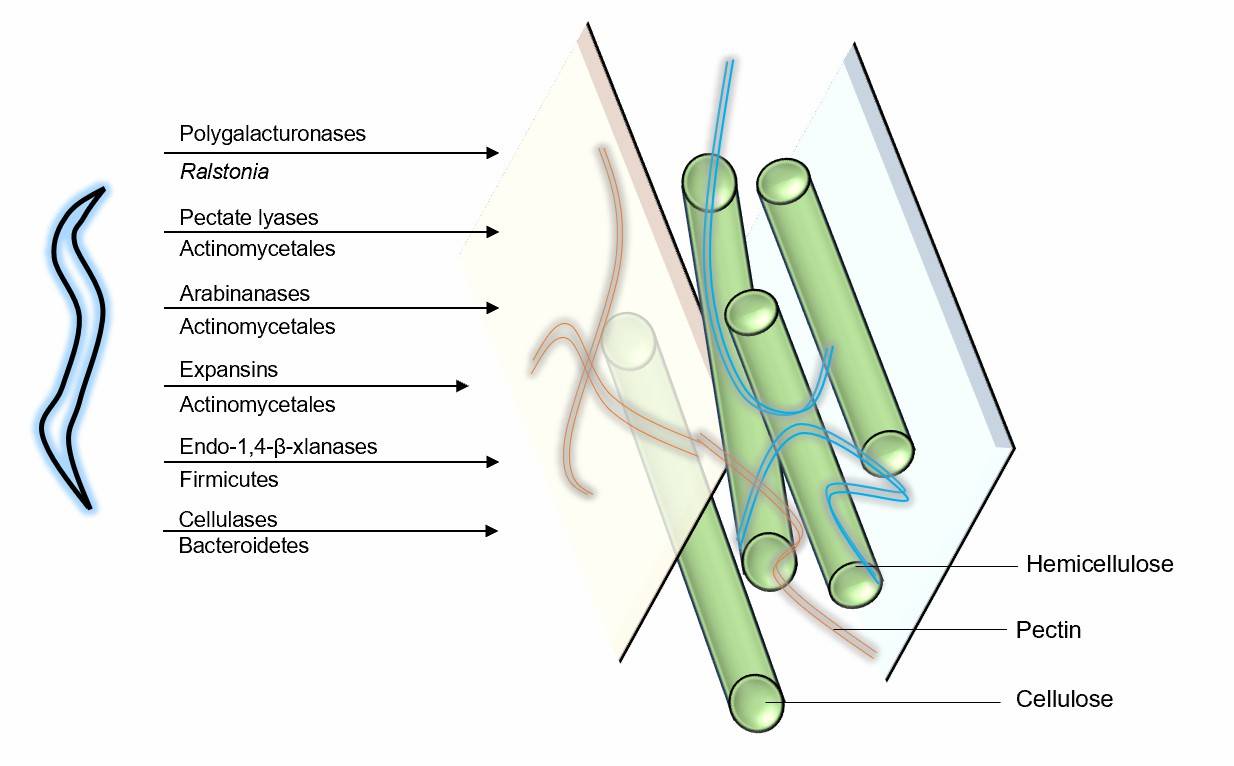 Fig.1 A multi-pronged assault between nematode and bacteria.
Fig.1 A multi-pronged assault between nematode and bacteria.
Lifeasible offers analysis services with customized delivery strategies and precise design. Our advanced technical platforms help our clients solve the problems they may encounter in research based on decades of experience. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025