Fungi and nematodes are among the most abundant organisms in the terrestrial ecosystem. The plant nematode is the second largest phylum in the animal kingdom, encompassing an estimated 500,000 species. Nematodes do not decompose organic matter but are parasitic or free-living organisms that feed on living materials. On the other hand, fungi are the principal decomposers of dead organic matter; they perform fundamental roles in nutrient cycling in the ecosystem. Both fungi and nematodes (as well as all animals) are heterotrophs. They are commonly found co-existing in a diversity of natural and man-made ecosystems, especially in the rhizosphere of plants, including crops, with significant impacts on agriculture and forestry.
Lifeasible provides analysis services of nematode interactions with fungi to help our customers worldwide in plant science research. Our platform is equipped with cutting-edge facilities and professional experts to support research. Here, we provide various services according to customers’ demands.
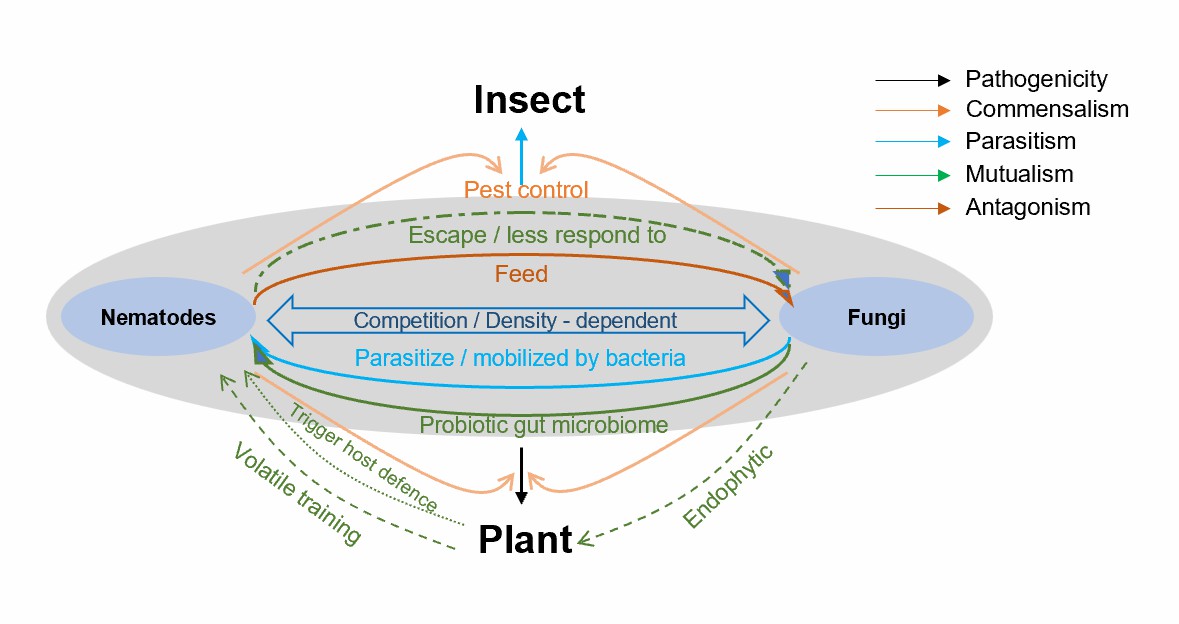 Fig.1 Fungi-nematode interactions in soil.
Fig.1 Fungi-nematode interactions in soil.
Lifeasible provides cost-effective, high-quality, and hassle-free services to our customers worldwide. We provide our clients with direct access to our experts and prompt responses to their questions. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025