Research on the pathogenesis of nematodes has been a hot topic in nematode research. The last decade or so has been rich in research in this area, with researchers exploring it from different angles and making many advances. At the same time, many studies have shown that plant endogenous microorganisms have an important influence on the nematode's vital activity and that they can indirectly enhance or diminish the nematode's pathogenicity. Nematode infestation affects the community changes of endogenous microorganisms in trees, the significant differences in the microbial communities of different resistant trees, etc.
Lifeasible is a leading provider of comprehensive, high-quality services for analyzing pathogenic effects of plant endogenous microorganisms. We hope to partner with you to explore new frontiers in plant science and accelerate your discovery.
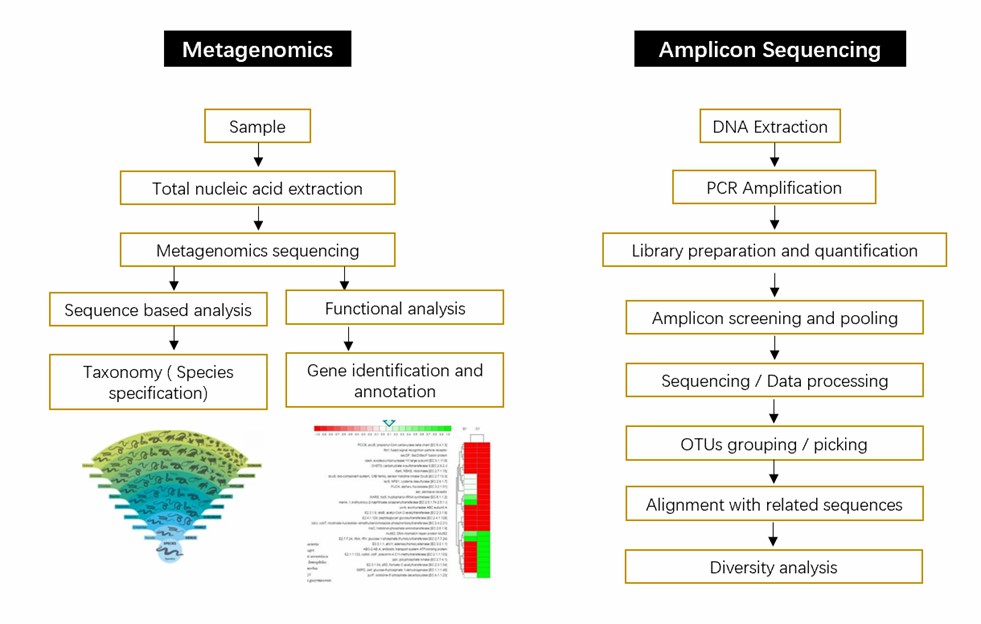 Fig.1 Detailed flowchart-based methodology for metagenomics and amplicon sequencing methods.
Fig.1 Detailed flowchart-based methodology for metagenomics and amplicon sequencing methods.
Lifeasible provides analysis of the pathogenic effects of plant endogenous microorganisms to our clients worldwide. With years of experience in biological services, our advanced platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties in plant research. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025