Pine wilt disease (PWD) is a major worldwide quarantine forest disease caused by the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. North America is the origin of pine wilt disease, while Japan, China, and South Korea in Asia are the most affected areas. Pine wilt disease develops rapidly after infecting pine trees in Asia, which is harmful and difficult to control, resulting in serious economic losses. Pine wood nematode disease can infect 51 pine species and 16 non-pine species under natural conditions. The pathogenic pine wood nematodes cause pine to wilt quickly, and the pathogenic mechanism is complex.
Lifeasible makes full use of our specialized libraries, selection strategies, and maturation techniques to optimize the stability and performance of plant science. With advanced technology and experienced staff, we provide analysis of pine wilt diseases to global clients to support their research.
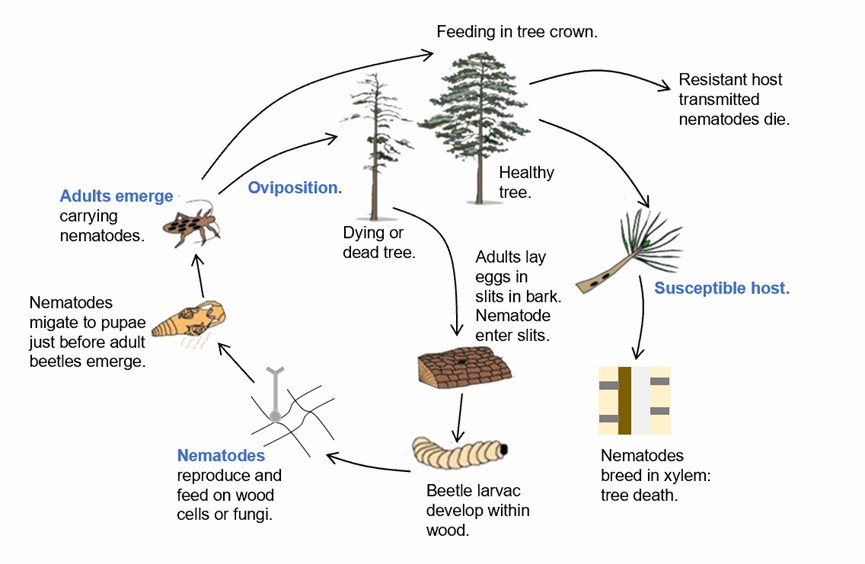 Fig.1 Life cycle of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, and pine wilt disease. (Vicente C, et al., 2012)
Fig.1 Life cycle of the pinewood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, and pine wilt disease. (Vicente C, et al., 2012)
Lifeasible offers a reliable analysis of pine wilt diseases to meet your research demands. With years of experience in plant science, our advanced platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties and conduct research. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025