Senescence is an irreversible growth and stagnation phenomenon that occurs during plant growth and development and is the process of accumulating random damage to an organism's DNA, proteins, and other macromolecules. Senescence ultimately leads to cell death, characterized by irreversible cell proliferation, altered gene expression patterns, increased resistance to apoptosis, and changes in specific cellular functions, accompanied by telomere shortening.
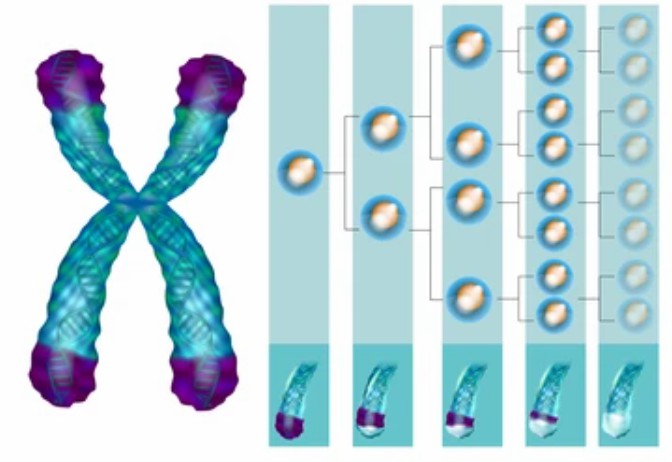 Fig. 1 The phenomenon of telomere shortening that accompanies cell division.
Fig. 1 The phenomenon of telomere shortening that accompanies cell division.
As a leading biotechnology company, Lifeasible has extensive expertise in analyzing plant telomeres regulating senescence. Our advanced methodologies enable us to unravel the intricate mechanisms underlying telomere-regulated senescence in plants.
We further help our customers explore the mechanisms by which telomeres regulate plant senescence. The shortening of telomeres leads to the initiation of DNA damage signals, which in turn causes cellular senescence. Telomeres shorten with each round of cellular replication due to the end-replication of chromosomes, and the shortening of telomere length triggers cellular senescence, which in turn leads to oxidative damage, gene overexpression, chromatin alterations, and DNA damage, among other stresses.
At Lifeasible, we can provide invaluable insights into the plant telomeres and their role in senescence regulation with our expertise in this field. If you are interested in our services or have some questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Mechanisms Regulating Plant Chloroplast Biogenesis
April 15, 2025