Terpenoids, an umbrella term for terpenes and their derivatives are likely the most diverse plant secondary metabolites, with more than 60,000 compounds already identified. Terpenes are formed by condensing two or more activated isoprene units (C5 building blocks), either isopentenyl pyrophosphate or its isomer dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. Depending on the number of C5 building blocks involved, this condensation can lead to the formation of a C10 (monoterpene), C15 (sesquiterpene), or C20 (diterpene) terpene. Sesqui- and diterpene units can, in turn undergo head-to-head condensation to form C30 (triterpenes) or C40 units (tetraterpenes).
Lifeasible offers comprehensive services covering various cutting-edge technologies to advance your projects. Our scientists have developed a series of innovative solutions to help analyze the role of terpenoids in the biological control of plant nematodes.
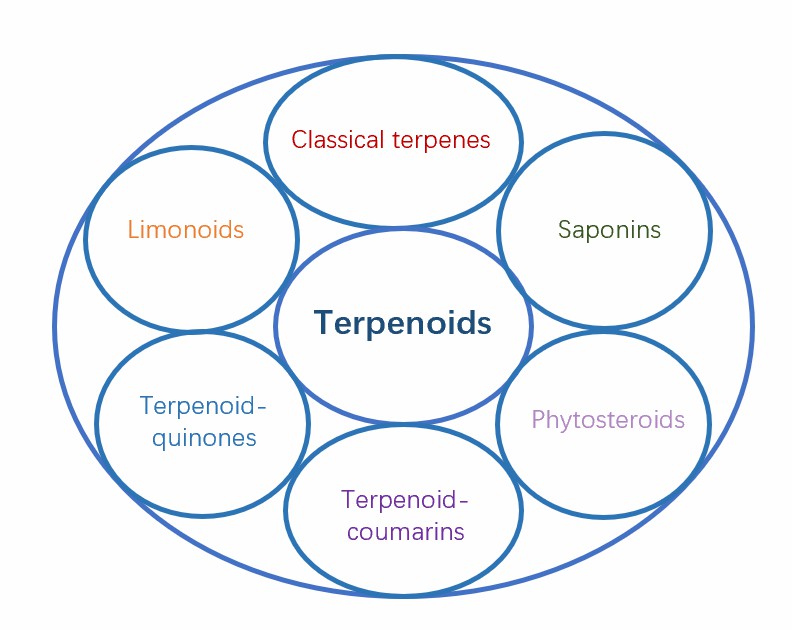 Fig.1 Types of various terpenoids.
Fig.1 Types of various terpenoids.
Lifeasible has extensive experience and expertise in plant science. We are committed to providing you with timely and high-quality deliverables. At the same time, we guarantee the cost-effectiveness, completeness, and simplicity of the report. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025