Dietary fiber is the edible parts of plants or analogous carbohydrates that cannot be digested or absorbed by human bodies. Dietary fiber is an essential food ingredient with a nutritional value of 2 kcal/g, which is much lower than the nutritional value of digestible carbohydrates (4 kcal/g). Dietary fibers have been shown to promote numerous beneficial physiological properties such as decreasing the intestinal transit time, lowering cholesterol and blood glucose levels, trapping harmful substances (e.g., mutagenic and carcinogenic agents), stimulating the proliferation of the intestinal flora, alleviating constipation, and many others. Because of these obvious benefits for human health, food products that contain dietary fibers (either naturally occurring or as food additives) have become increasingly popular worldwide. Following this trend, there is an arisen demand for developing advanced methods to precisely measure the contents of dietary fibers in food.
Lifeasible is a leader in food nutritional analysis with a state-of-the-art platform for dietary fiber analysis. We provide various advanced official analytical methods related to dietary fiber analysis adopted by AOAC and AACC, including:
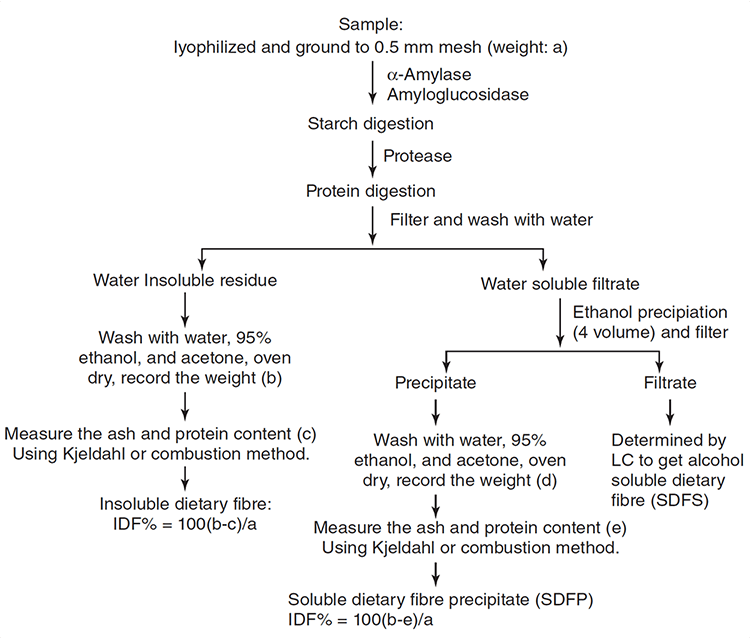 Figure 1. Flow chart of soluble, insoluble and total dietary fiber determination by an enzymatic/gravimetric/LC method of AOAC 2011.25/AACC 32-50.01 (Guo et al., 2014).
Figure 1. Flow chart of soluble, insoluble and total dietary fiber determination by an enzymatic/gravimetric/LC method of AOAC 2011.25/AACC 32-50.01 (Guo et al., 2014).
With cutting-edge equipment, advanced technologies, and excellent experts, lifeasible provides reliable dietary fiber analysis services to help you precisely label of your product to comply with health claims. Our dietary fiber analysis service is featured with:
Welcome to contact us for further information, questions, and inquiries.
Reference:
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025