Starch is a way for all green plants to store energy, and it is also the most important energy substance. It is in the form of semi-crystalline particles in various substances of various plants. At present, it is known that its common storage organs are mainly seeds (wheat, rice, corn, etc.), tubers (potatoes, yams, etc.), and roots (sweet potato, cassava, etc.) and leaves (quasi-Nanqi, algae, etc.) (Figure 1). Due to its important function, starch has always been a hot spot of scientific research. In recent years, Lifeasible has established a comprehensive analysis platform from anabolism, structural properties, physical and chemical properties, production and processing to modification and denaturation. We provide starch testing and other related services for various types of customers (research institutes, governments, and individuals).
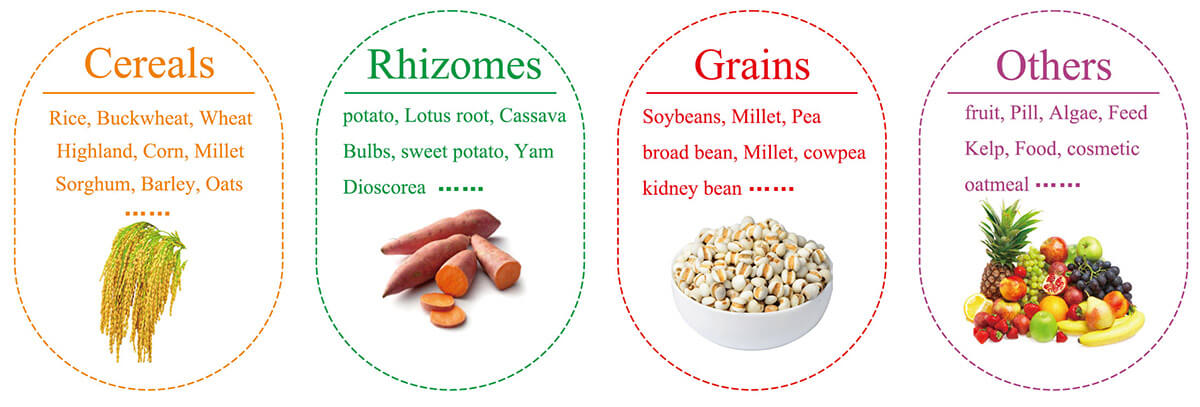 Figure 1. Source species of starch that can be detected.
Figure 1. Source species of starch that can be detected.
Starch analysis technology has huge application prospects, such as breeding and improvement of starch-based crops, evaluation of starch germplasm resources, starch taste quality, starch properties and processing, plant nutrition and metabolism, plant resistance, etc. as shown in the figure 2.
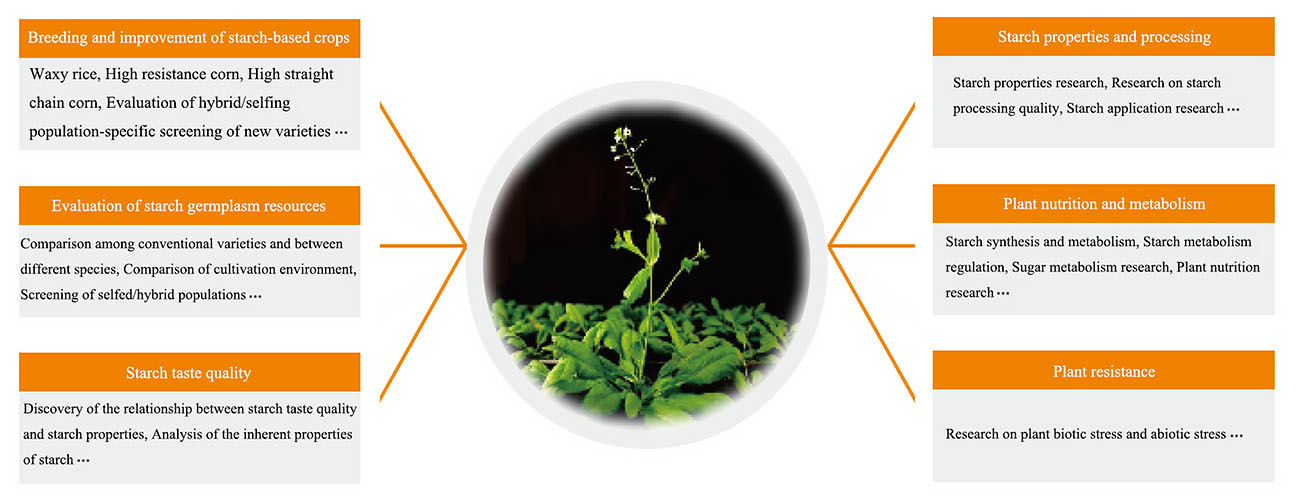 Figure 2. Application prospects of starch analysis technology.
Figure 2. Application prospects of starch analysis technology.
There are five main categories of starch testing items provided by Lifeasible, including starch synthesis and metabolism, starch basic testing, starch characterization testing, starch structural properties testing, and starch physical and chemical properties testing.
| Service name | Sample amount |
|---|---|
| Adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (ADPG) activity determination | 2-5 g |
| Granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS) activity determination | 2-5 g |
| Starch branching enzyme (SBE) activity determination | 2-5 g |
| Soluble Starch Synthase (SSS) Activity determination | 2-5 g |
| α-amylase activity determination | 2-5 g |
| β-amylase activity determination | 2-5 g |
| Saccharose synthase (SS) activity determination | 2-5 g |
| Sucrose Phosphate Synthase (SPS) Activity Determination | 2-5 g |
| Neutral sugar invertase (NI) activity determination | 2-5 g |
| Acid sucrose invertase (Al) activity determination | 2-5 g |
Service parameters: Sample is needed dry ice transport; Detection method is chemical method; Recommended 3 repetitions; Detection period is 15 working days.
| service name | Sample type | Sample amount |
|---|---|---|
| Water content determination | Whole flour/starch | 2-5 g |
| Ash content determination | Whole flour/starch | 10-15 g |
| Crude fat content determination | Whole flour/starch | 20-30 g |
| Determination of crude protein content | Whole flour/starch | 2-5 g |
| Starch digestibility test | Whole flour/starch | 2-5 g |
| Determination of starch phosphorylation level | starch | 2-5 g |
| Determination of starch gum consistency | Whole flour/starch | 2-5 g |
| Starch water solubility index | Whole flour/starch | 2-5 g |
| Starch swelling force measurement | Whole flour/starch | 2-5 g |
Service parameters: Recommended 3 repetitions; Detection period is 15 working days.
| service name | Instrument method | Sample type | Sample amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Determination of total starch content | Enzymatic hydrolysis | starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Determination of amylose content | Lodine binding method | Whole flour/starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Determination of resistant starch content | Enzymatic hydrolysis | Whole flour/starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Starch molecular weight distribution | Gel chromatography | starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Determination of starch chain length distribution | Ion chromatography | Whole flour/starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Determination of starch branching | NMR | starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Starch polymerization degree determination | Ion Chromatography | Whole flour/starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Starch X-ray diffraction analysis | X-ray diffraction | starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| service name | Instrument method | Sample type | Sample amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starch viscosity determination | Fast viscometer | Whole flour/starch | 3-5 g once |
| Determination of starch gelatinization temperature | Differential calorific value scanner | Whole flour/starch | 0.1-0.5 g once |
| Starch thermal stability determination | Thermogravimetric Analyzer | Whole flour/starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Starch infrared scan | Infrared spectrometer | starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Analysis and determination of starch thermal weight loss | Thermogravimetric Analyzer | Whole flour/starch | 0.5-1.5 g once |
| Determination of starch gum consistency | National Standard Law | Whole flour/starch | 1-3 g once |
The overall research process of starch analysis technology is shown in the figure below
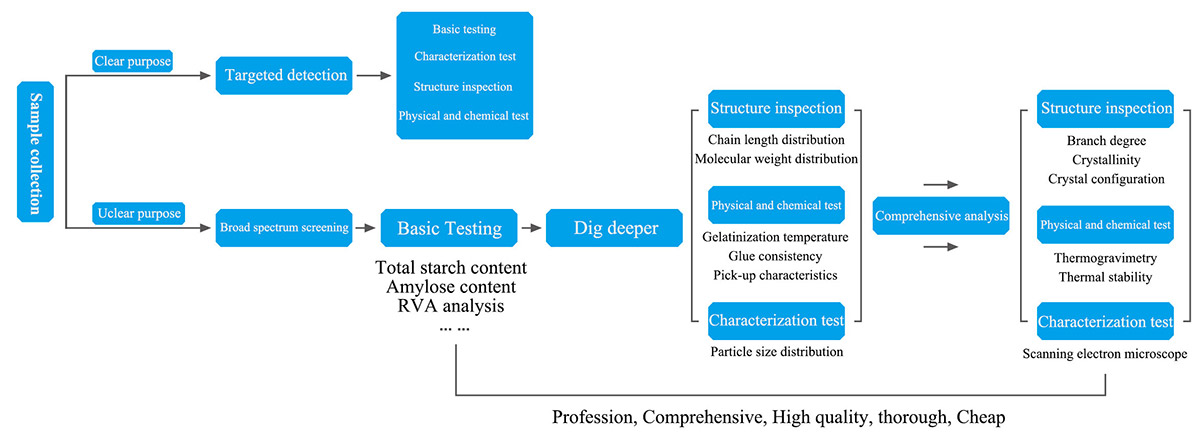 Figure 3. Overall research process of starch analysis technology.
Figure 3. Overall research process of starch analysis technology.
As an expert in crop nutrition evaluation, Lifeasible can provide customers with comprehensive solutions for starch indicator research. We hope that our products and technologies can satisfy our customers. We will look forward to your inquiry. For more information, please contact us.