For mapping sites where proteins directly interact with RNA accurately, several technologies have been developed. Photoactivatable ribonucleoside enhanced cross-linking and immunoprecipitation (PAR-CLIP) is a modified CLIP protocol allowing the identification of cross-linking sites at a single-nucleotide resolution. Lifeasible is a global leading biotechnology company, providing PAR-CLIP platform for RNA-protein interaction study.
In PAR-CLIP, the photoreactive ribonucleoside analogs, such as 4-thiouridine (4-SU) and 6- thioguanosine (6-SG), are usually incorporated into nascent RNA transcripts by living cells. UV irradiation at 365 nm can induce efficient cross-linking of photoreactive nucleoside-labeled cellular RNAs to interacting RBPs. Cross-linking the 4-SU and 6-SG analogs lead to thymidine (T) to cytidine (C), and guanosine (G) to adenosine (A) transitions respectively (Figure 1). Therefore, PAR-CLIP can identify binding site with high accuracy.
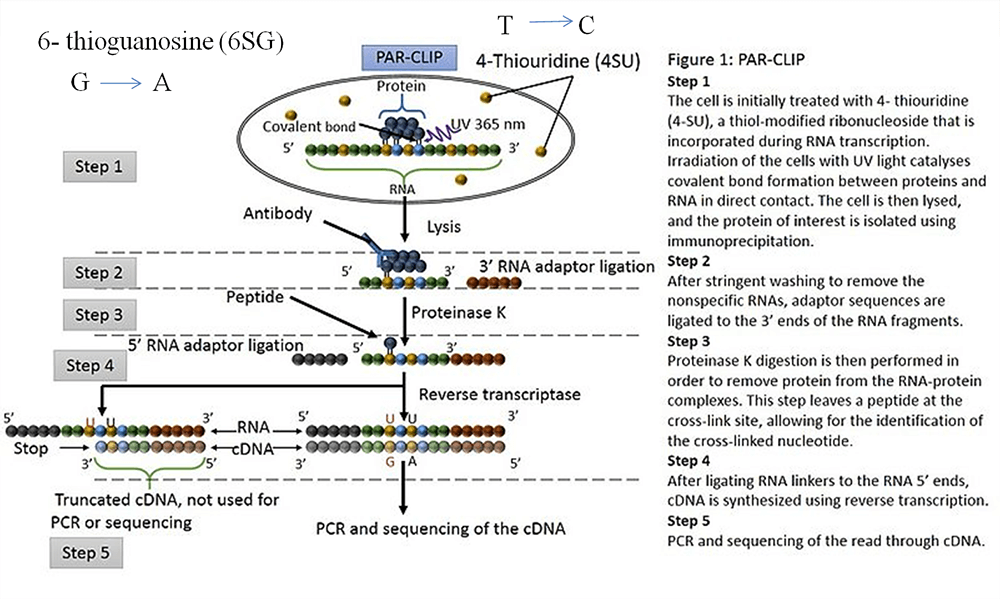 Figure 1. The workflow of a PAR-CLIP assay (Wikipedia)
Figure 1. The workflow of a PAR-CLIP assay (Wikipedia)
With years of experience in molecular biology technologies, Lifeasible has contributed great effort in optimizing the protocol for PAR-CLIP. We are determined to provide the professional and customized one-stop services for PAR-CLIP assay (Figure 1) that cover:
Working closely with Lifeasible, you will benefit from PAR-CLIP services with high sensitivity, reliable quality, and competitive price. Moreover, with valuable national and international tie-ups with renowned companies, we could provide you with innovative solutions, guaranteeing the success of your project. Welcome to contact us for questions or inquiries.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Mechanisms Regulating Plant Chloroplast Biogenesis
April 15, 2025