DNase I footprinting assay is a detection method that accurately identifies the binding sites of DNA binding proteins (such as transcription regulatory proteins) on DNA molecules. Transcription regulatory proteins regulate the transcription of target genes by binding to their promoter regions. At present, the EMSA (Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay) and DNase I footprinting assay are important sets of in vitro research tools. EMSA determines whether transcription factors are directly bound to DNA, while DNase I footprinting assay can accurately identify the DNA sequence to which they bind, thereby helping us to study the mechanism of gene transcription regulation.
The classic DNase I footprint analysis experiment requires the use of isotopes for labeling, which is not only dangerous, but also time-consuming, requires high technical requirements for the operator, and has a low success rate. In this case, our company uses "fluorescent labeling" combined with the ABI sequencer method to perform DNase I footprinting assay. The DNA can be accurately quantified, and the experiment can be operated on a conventional laboratory bench. The repeatability of the fluorescent labeling method is much better than isotope operation. Moreover, the operating system of ABI sequencer is very mature, with high sensitivity and good repeatability. Therefore, our DNase I footprinting assay is more sensitive, the protected area obtained is clearer, and the quality of the experimental picture is better.
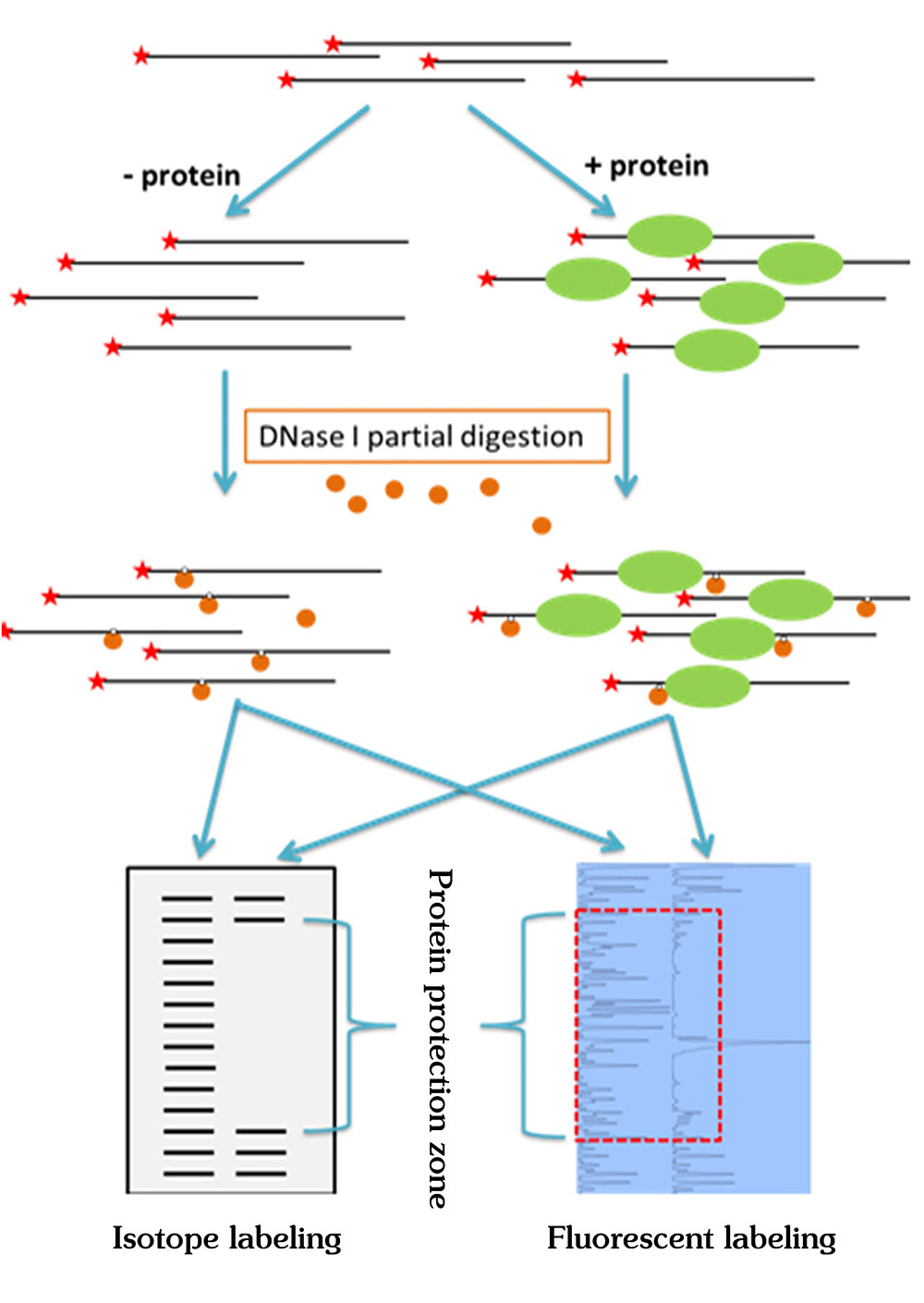 Figure 1. The principle of DNase footprinting assay and comparison between isotope labeling method and fluorescent labeling method.
Figure 1. The principle of DNase footprinting assay and comparison between isotope labeling method and fluorescent labeling method.
Lifeasible provides DNase footprinting testing service with high quality and short turnaround time. The experimental operation process of DNase footprinting assay is as shown below.

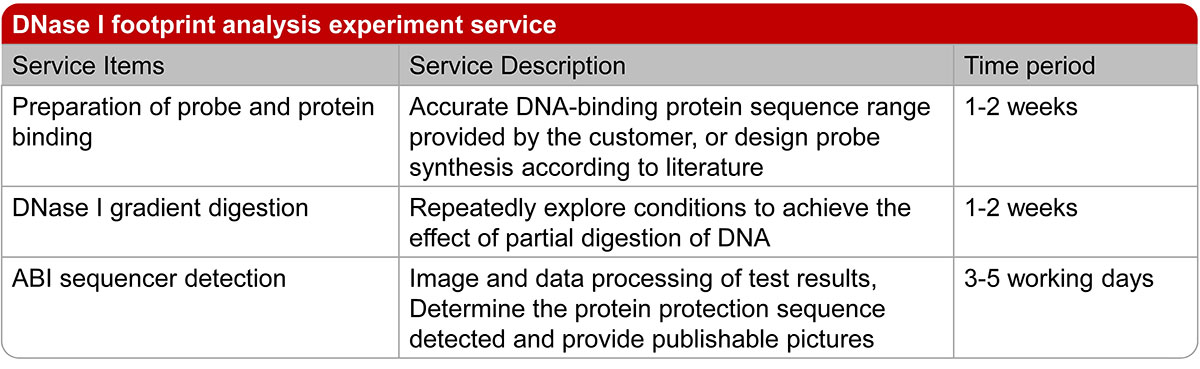 Figure 2. The experimental operation process and lead time of DNase I footprinting assay.
Figure 2. The experimental operation process and lead time of DNase I footprinting assay.
Information customer needs to provide:
Delivered result: Detailed experimental procedures, Experimental raw data, DNase I footprinting assay picture, and complete experiment report.
Lifeasible has been deeply involved in the field of molecular biology and protein detection for many years, and has achieved gratifying scientific research results in DNase footprinting analysis. Our company's latest analysis technology can help customers obtain satisfactory experimental results and publishable paper diagram. Please don't hesitate to contact us.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025