In living cells, proteins that function in the same or related pathways work co-operatively by dynamic assembling and disassembling. Especially in the sessile plant lives, biological processes, such as signal transductions and intracellular membrane trafficking, are extensively depended on the interaction of functionally-correlated proteins. Therefore, detection and determination of protein-protein interactions is a critical important approach for the characterization of protein functions.
Pull-down assay is an in vitro method that is widely used for the confirmation or detection of physical interactions between two or more proteins. The principle of the pull-down assay is to utilize affinity ligand to capture interacting proteins.
A standard pull-down assay requires a purified protein with a recombinant affinity tag, which functions as the “bait” and is immobilized to a tag-specific affinity ligand. Then the other protein -- or the “prey” protein, will be incubated with the “bait” protein. Upon physical interactions between these two proteins, the “prey” protein will be captured by the “bait” protein. Following that, the interacting “prey” protein can be eluted using an eluting buffer depending on the affinity ligand. Finally, both the “prey” and “bait” proteins can be resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), and then detected by gel staining for western blotting (Figure 1).
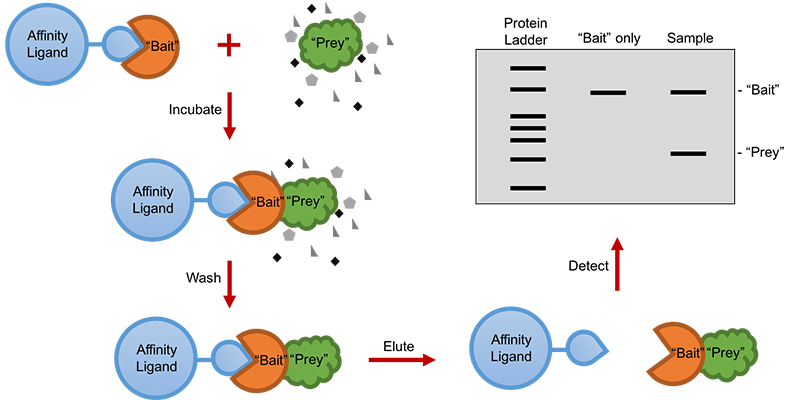 Figure 1. Workflow of a standard pull-down assay.
Figure 1. Workflow of a standard pull-down assay.
Besides confirmation of protein-protein interactions, the pull-down assay can also be used to characterize interacting conditions. For example, using protein domain truncations to perform pull-down assays can help researchers target the functional regions that are critical for protein interactions. Moreover, the pull-down assay can also be used to explore interactive partners of proteins of interest. Specifically, the “bait” protein is incubated with a mixed protein solution, or cell/tissue extractions. After the washing steps, the bound proteins can be eluted and identified by high-throughput approaches such as liquid chromatography - mass spectrometry (LC - MS).
Lifeasible, as a leading plant biotechnology company, has years of experience in plant biochemical assays. We provide highly efficient strategies for plant protein expression and purification, as well as the most optimized protocols for pull-down assays. Featured by stringent quality control and short turn-around time, we proudly offer customized one-stop service that covers every step from gene synthesis to data reporting:
With the very well established technology platforms and excellent teams of scientists and experts, our goal is to provide our customers worldwide with the best quality services. Welcome to contact us for questions, inquires or collaborations.
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025