Plant Organelle Isolation
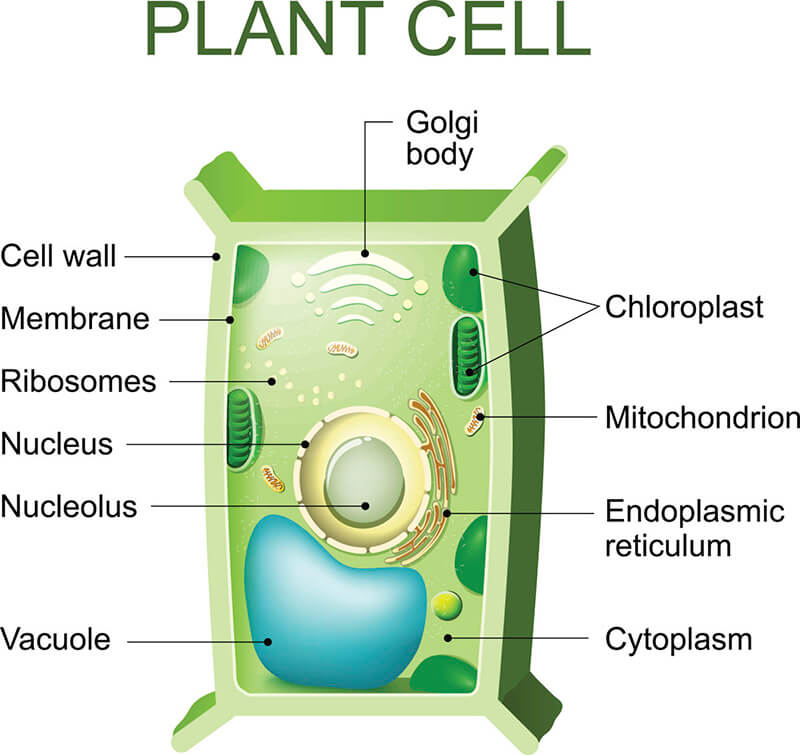
Plant cells contain several types of intracellular membrane-bound structures, known as organelles, such as nucleus, mitochondrion, lysosome, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplast, contractile vacuole, peroxisome, ribosome, and so on. Each organelle has its specific function (Table1). Isolation of subcellular organelles from plant cells is prerequisite for various plant biological topics, including functional and structural genomics, as well as proteomic profiling. Lifeasible, as a leading plant biotechnology company in the world, provides one-stop services for separation of different types of plant organelles. Our sample-to-report services cover every key step from sample homogenization and purification, to organelle enrichment and integrity detection.
Table 1. The specific functions and some marker enzymes for major organelles.
| Organelle |
Function |
Marker enzyme |
| Nucleus |
DNA storage; control of all activities of the cell; RNA transcription |
RNA polymerase II |
| Mitochondrion |
Energy production |
Succinate dehydrogenase; cytochrome c oxidase |
| Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
Lipid production; detoxification |
|
| Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
Protein production; in particular for export out of the cell |
Glucose-6-phosphatase |
| Golgi apparatus |
Protein modification and export |
|
| Peroxisome |
Lipid Destruction; containing oxidative enzymes |
|
| Lysosome |
Protein destruction |
Acid phosphatase |
| chloroplast |
Photosynthesis; trapping energy from sunlight |
Sialyl transferase |
| Vacuoles |
Storage; transportation; homeostasis balance |
Alkaline phosphodiesterase |
| Ribosomes |
Protein synthesis |
|
Cell Disruption and Homogenization
The first step of cell disruption is the removal of cell wall by enzymatic digestion and then homogenization of the cells. The homogenization process involves 5 steps: Dounce homogenization, filtration, grinding, sonication, and solubilization. In order to ensure the integrity of organelles, isotonic sucrose is usually added to the homogenization buffer to prevent osmotic rupture of organelle membranes during the homogenization process.
Plant Organelle Purification
Following homogenization, the next step is purifying organelles from homogenates. We provide several methods for isolating subcellular organelles, which include, but not limited to:
- Differential centrifugation. Differential centrifugation is one of the most widely-used techniques to separate cellular organelles. The sedimentation rate of a subcellular particle depends on its size, density, and shape. Usually, organelles that are relatively large or dense will sediment more rapidly than those are smaller and lighter under a given centrifugal force. This method is suitable for crude separations of organelles.
- Density-equilibrium centrifugation. This method is the second widely-used method for the separation of organelles. In this procedure, the density gradient is formed by layering increasing concentrations of sucrose solutions in a centrifuge tube. And the plant organelles initially layered on the density gradient will sediment until they arrive at the region of the gradient that is the same as their own.
- Affinity chromatography. This technique utilizes two-phase systems for phase separation. These systems occur when solutions of two different water-soluble polymers are mixed above critical concentrations, then the two immiscible liquid phases spontaneously separate.
- Free-flow electrophoresis (FFE). FFE is a continuous separation technique that delivers organelles with different electrophoretic mobilities to different collection points. FFE includes two types: zonal electrophoresis or isoelectric focusing mode.
- Affinity purification. Affinity purification of organelles relies on the availability of antibodies against proteins found on the surface of organelles of interest. The commonly used method of affinity purification is magnetic immunoabsorption, where organelles are detected by antibodies attached to magnetic beads, which can be separated under a specific magnetic field.
- Fluorescence-activated organelle sorting (FAOS). FAOS uses a flow cytometer to detect and sort organelles based on specific fluorescence and scattering characteristics. This technique requires labeling of organelle-specific proteins with fluorescently tagged antibodies or expression of organelle-specific fluorescent proteins.
- Microfluidic technology. This technology allows high-throughput, fast separations of plant organelles. By integrating the entire analysis workflow, sample preparation, enrichment, separation, and detection of organelles can be performed on a single platform.
Purity, enrichment, and integrity detection of organelles
Evaluation of the integrity, enrichment, as well as the presence of contaminating organelles for target organelles are important for the studying of their various biological processes. Our experts have developed a large variety of methods for analyzing the integrity and purity of plant organelles. The most commonly used methods are microscopic techniques and marker enzymes activity analysis.
- Microscopic techniques. Microscopic techniques are based on organelles’ morphological characteristics, which provide a quick and informative method for evaluating the purity and integrity of subcellular organelle fractions. These techniques include light microscopy, electron tomography, fluorescence microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and so on.
- Marker Enzymes. The verification of target organelle is typically based on the activity of specific enzymes - or marker enzymes, that are known to be localized exclusively in the target organelle. Marker enzymes can also provide information on the biochemical purity of the fractionated organelles. We offer activity analysis for multiple marker enzymes (Table1).
With cutting-edge equipment and experts in plant cell biology, we provide you with customized protocols for each specific plant organelle isolation and analysis. Working closely with Lifeasible, you will benefit from our fast, reliable, and cost-effective services for the separation of plant organelles. Welcome to contact us for technical consults and price quotes.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!